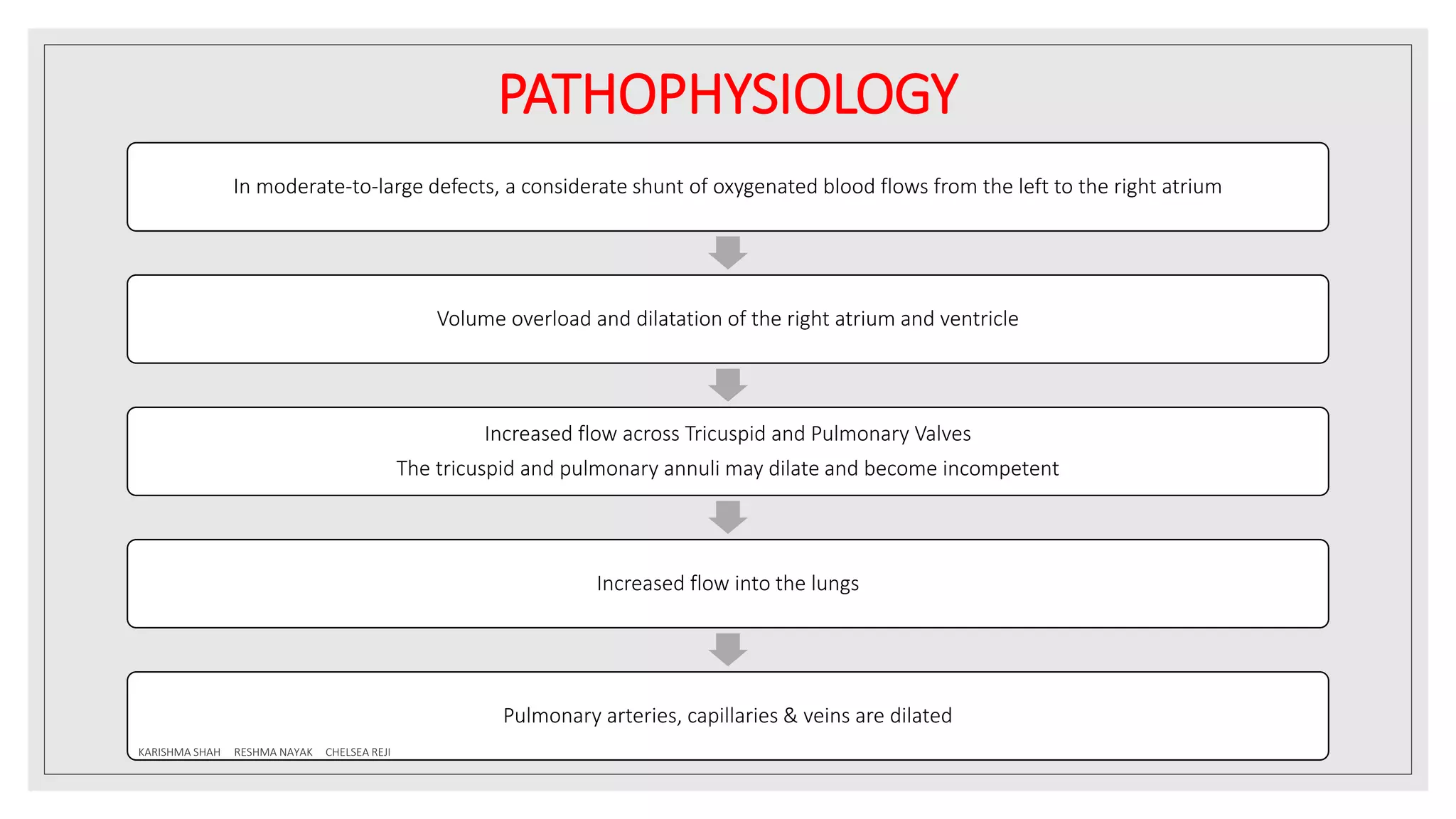
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect characterized by a hole in the interatrial septum that allows oxygen-rich blood to mix with oxygen-poor blood. The document discusses the definition, prevalence, genetic factors, embryology, classification, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and management of ASD. It highlights that ASD is more common in females and can lead to complications such as heart failure and pulmonary hypertension if left untreated.