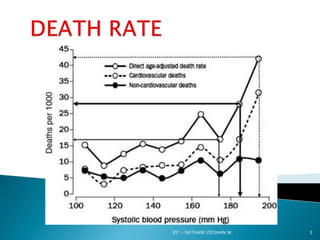
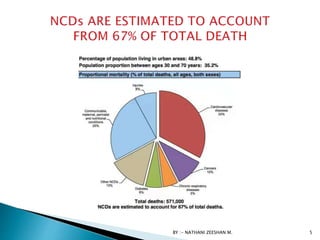
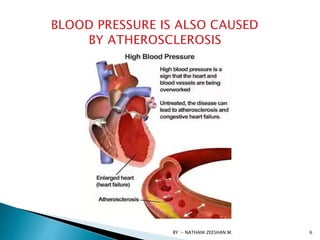
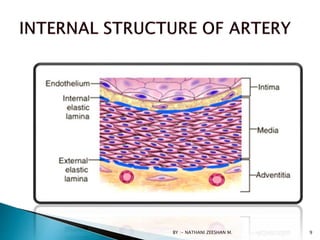
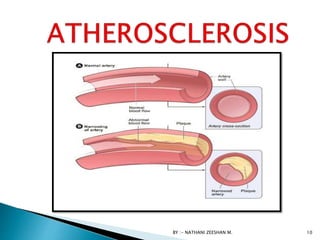
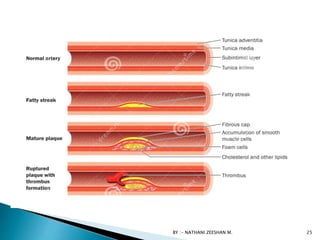
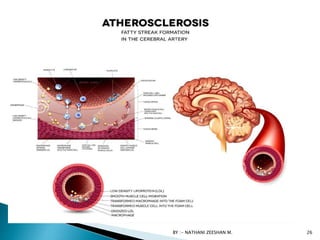
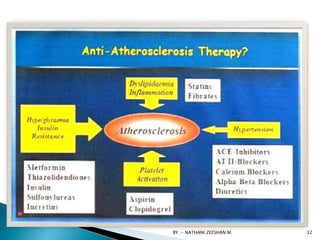
This document discusses atherosclerosis and plaque buildup in arteries. It begins with definitions of atherosclerosis and plaque, describing how plaque is made up of substances like fat, cholesterol, and calcium that build up in the arteries over time and restrict blood flow. The document then covers the pathophysiology and risk factors for atherosclerosis development, as well as signs, diagnosis, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of prevention through diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight control to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and associated heart conditions.