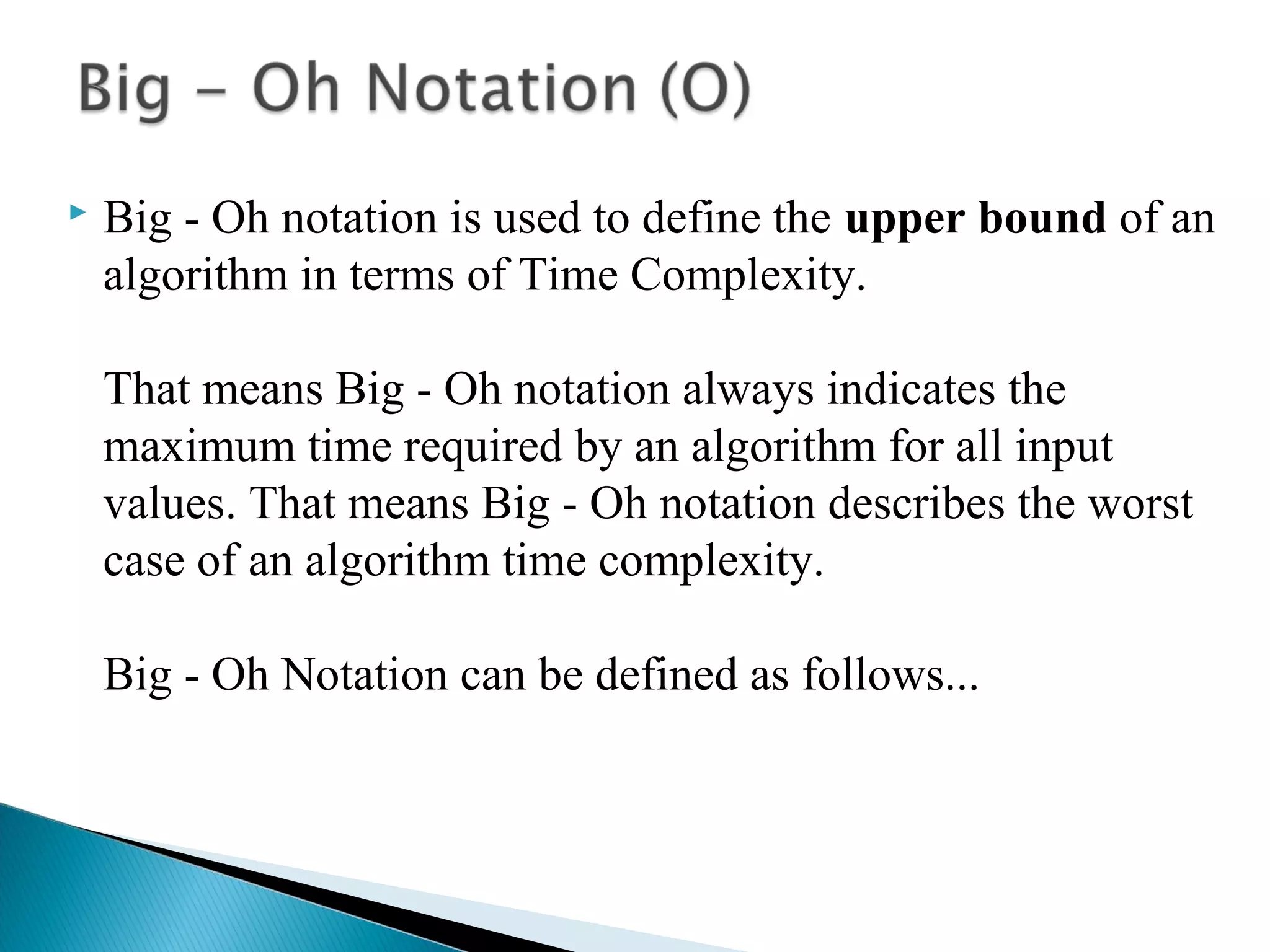
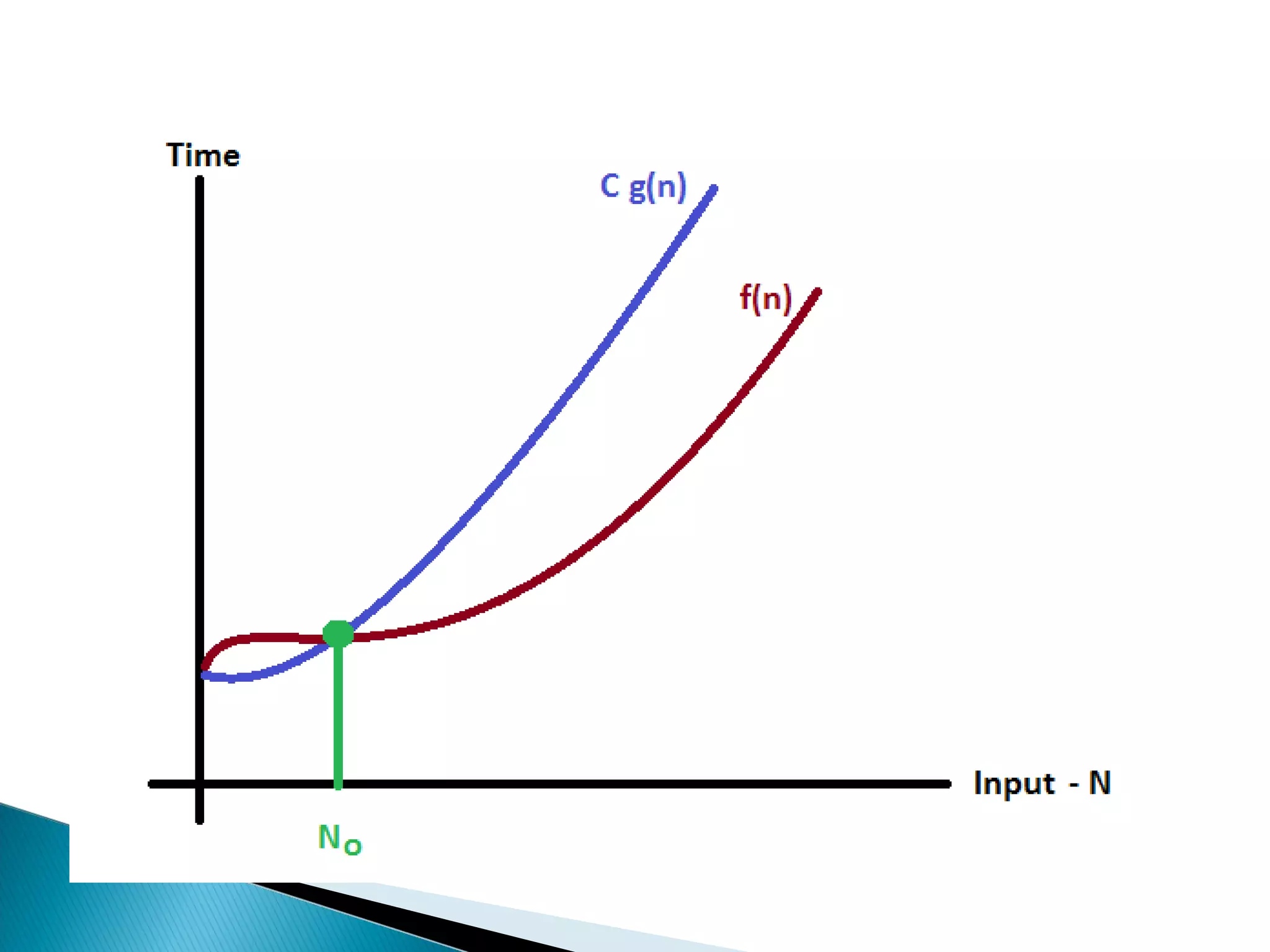
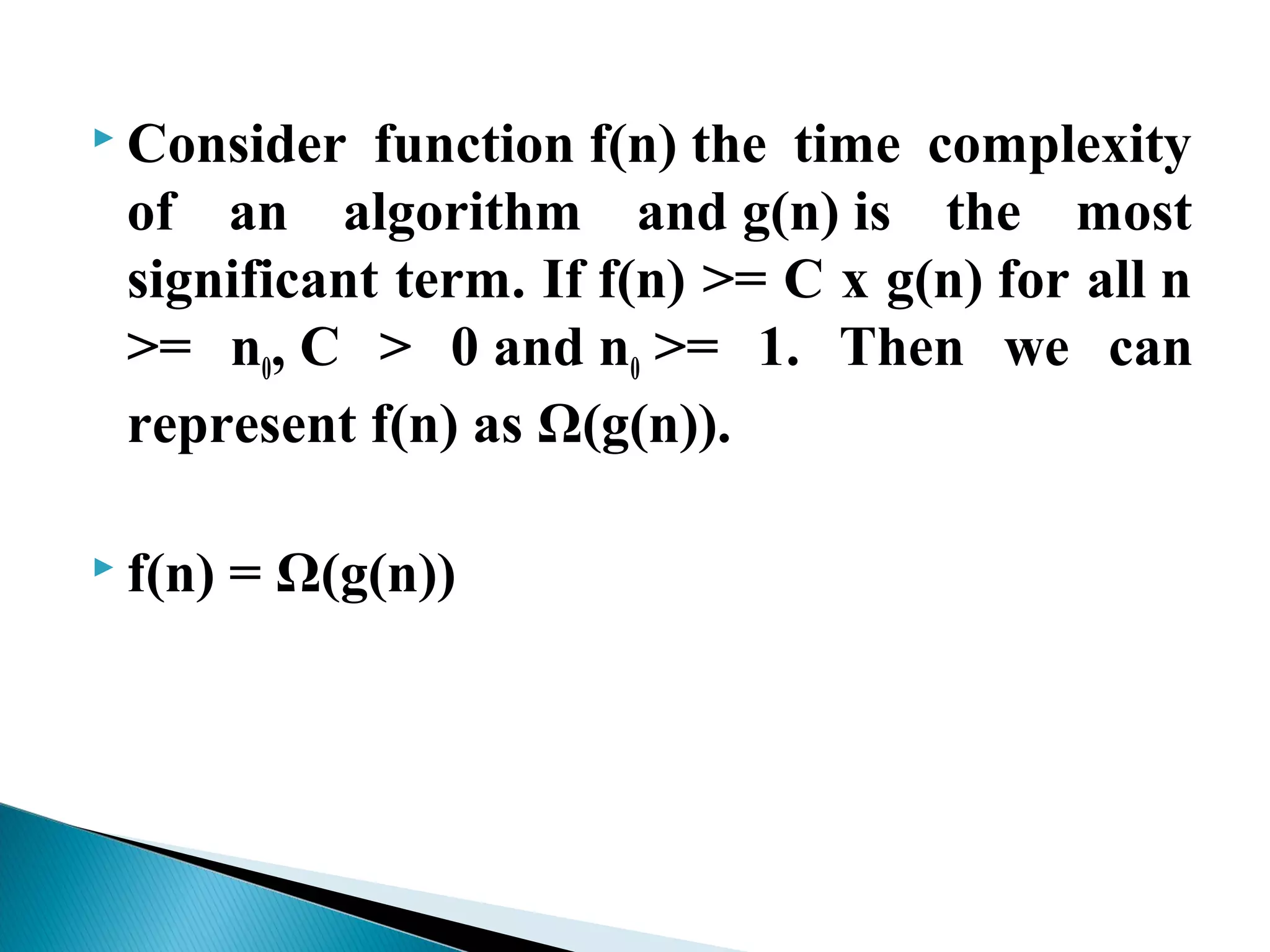
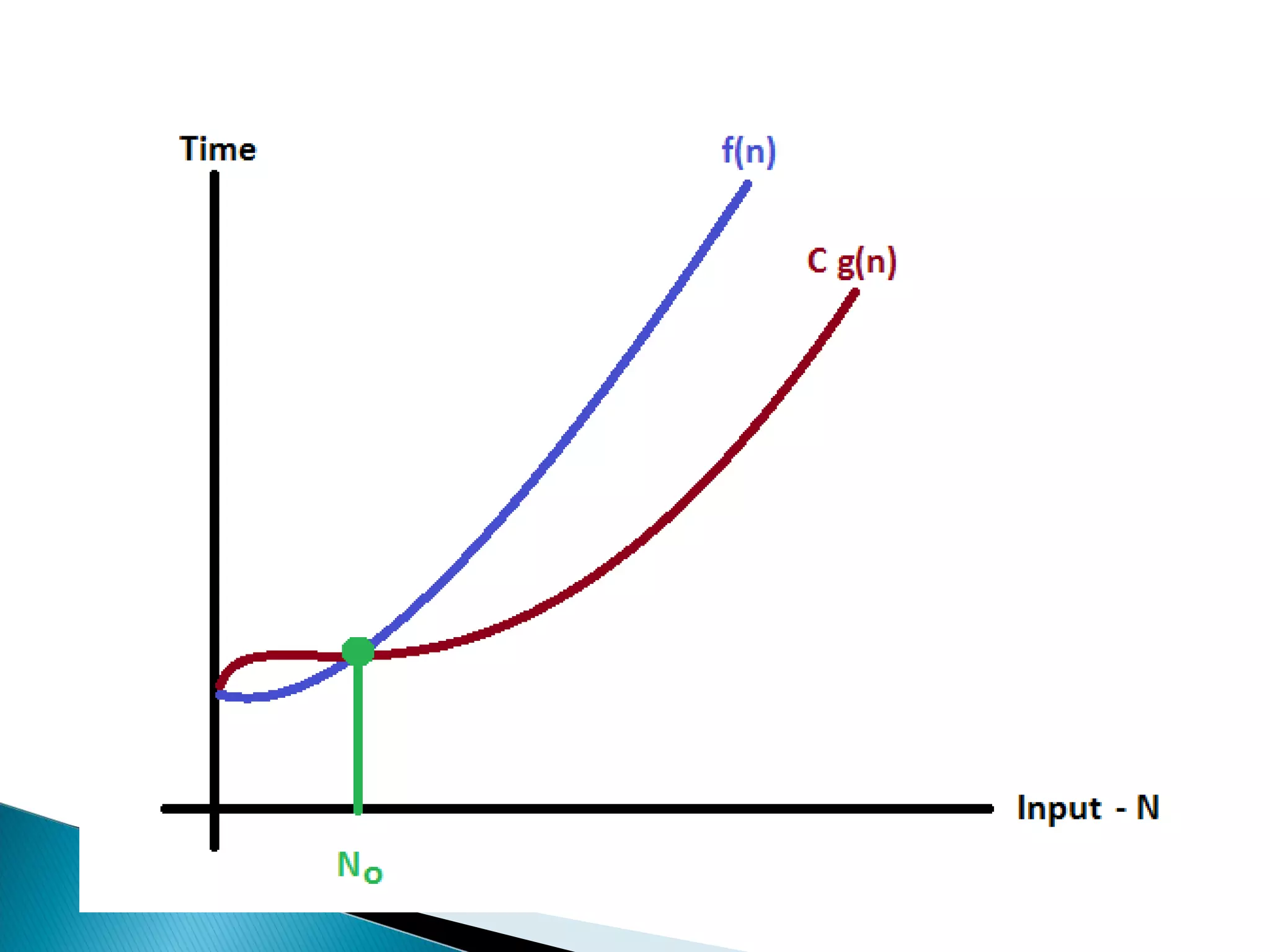
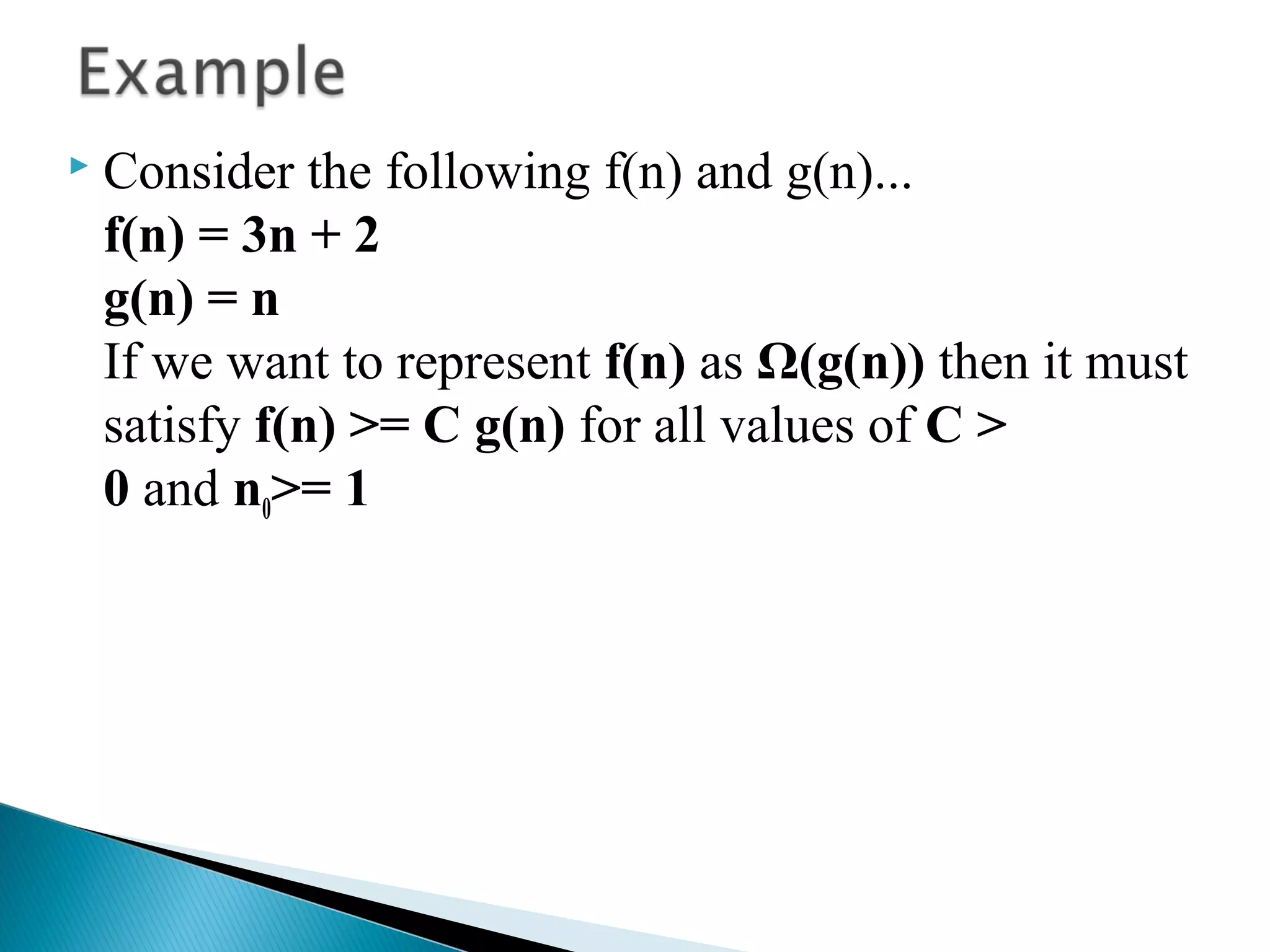
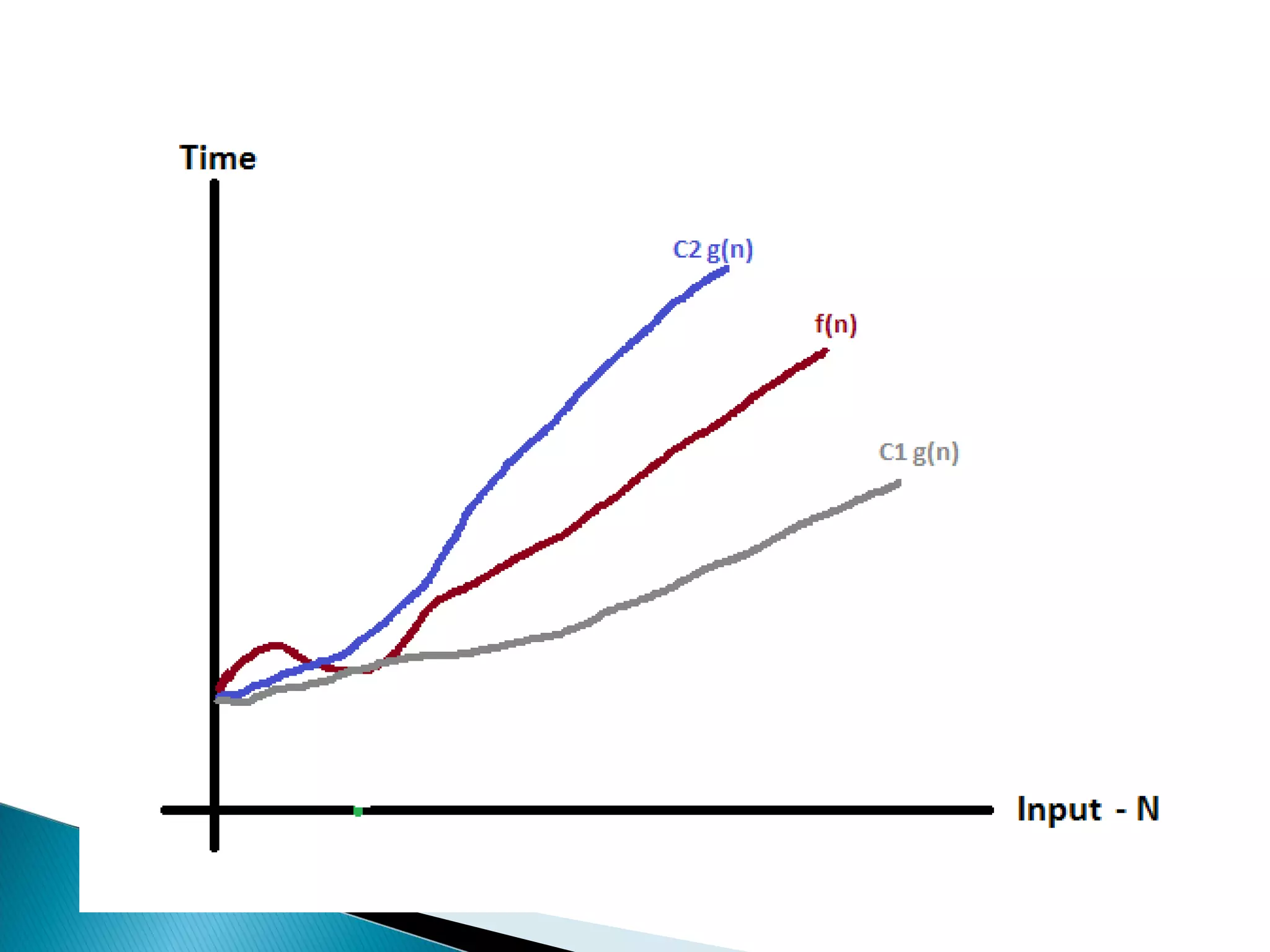
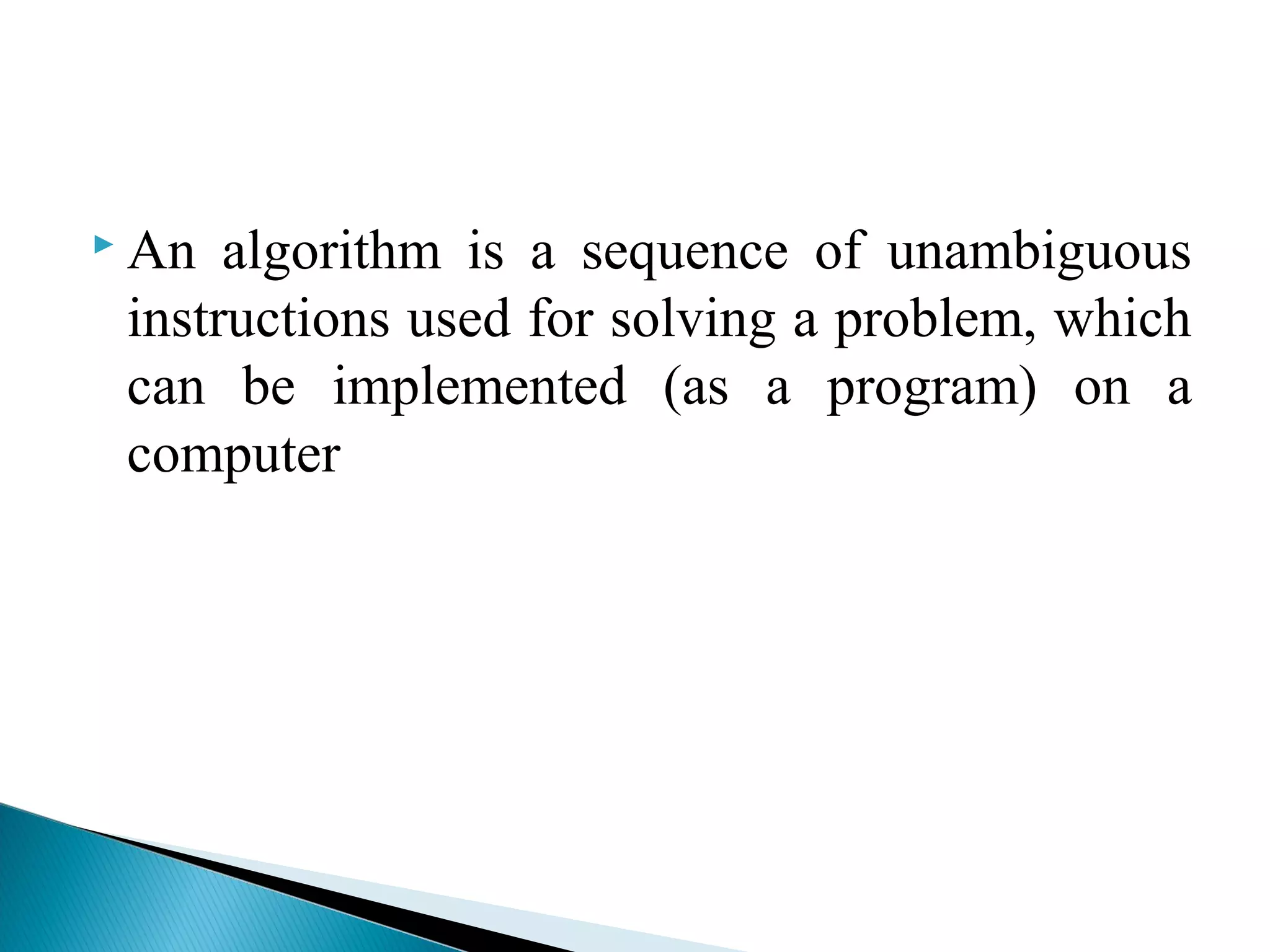
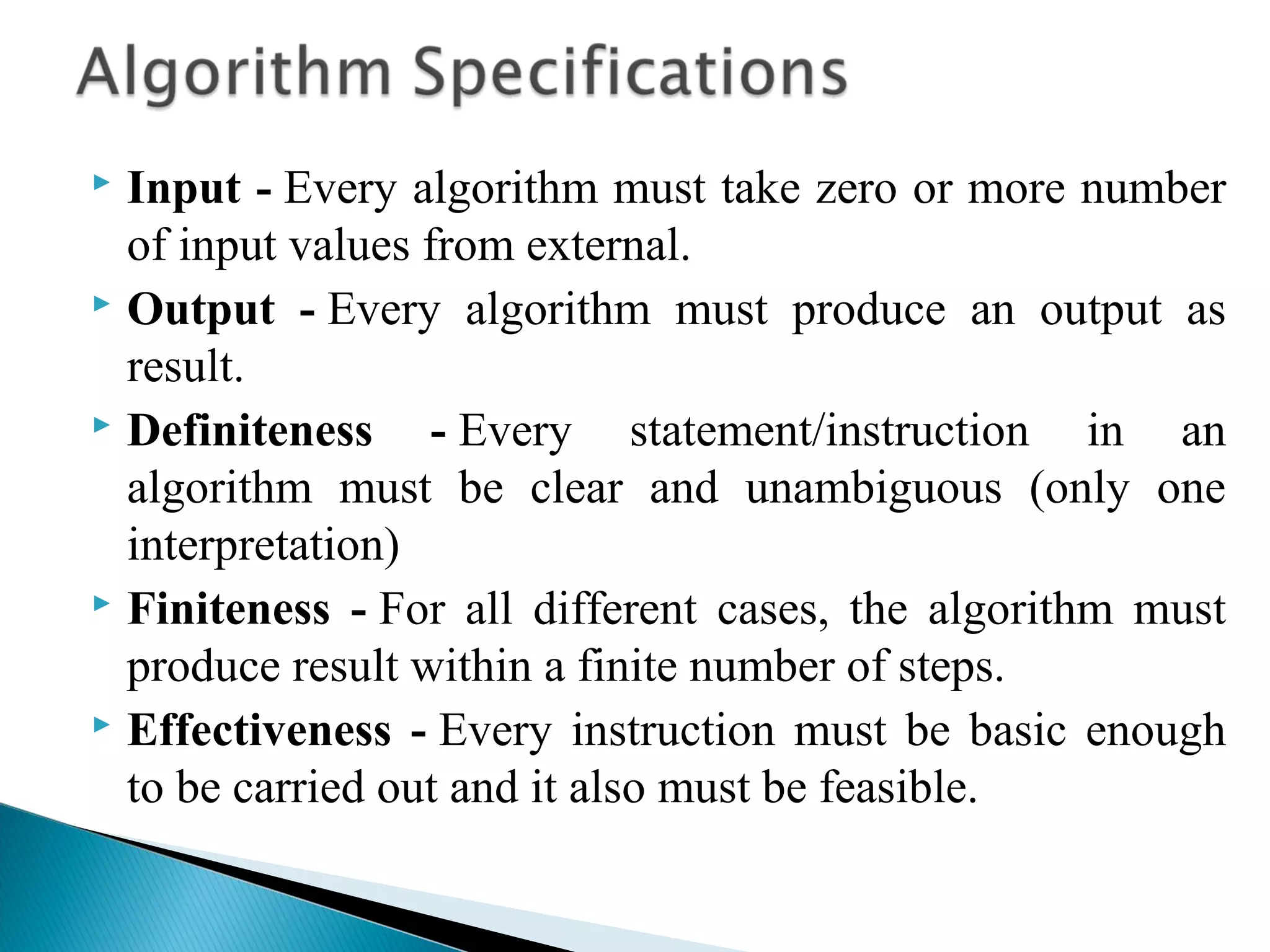
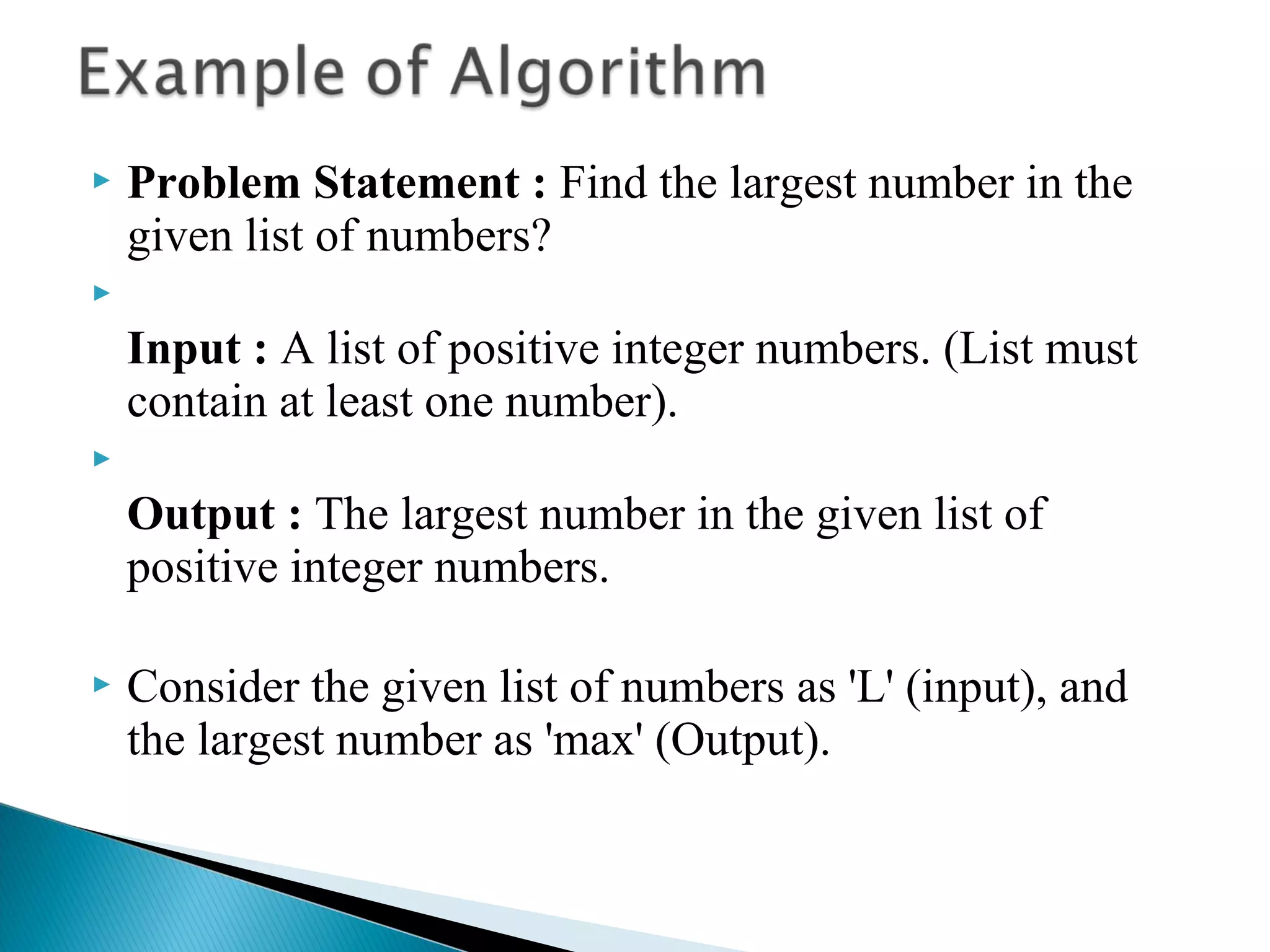
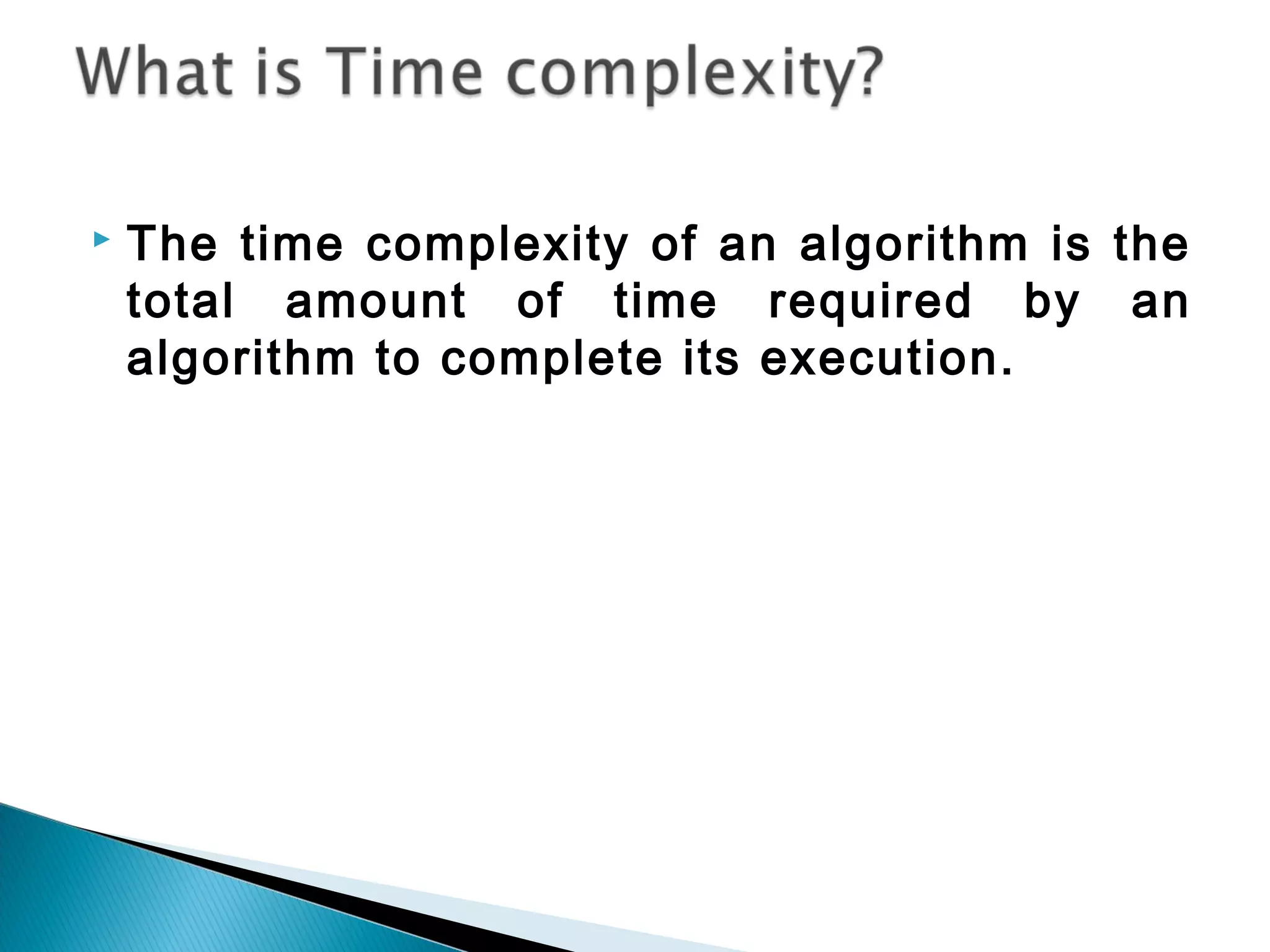
An algorithm is a set of clear instructions for solving a problem that can be executed by a computer, requiring inputs and producing outputs. Performance analysis is essential to determine the most efficient algorithm based on space and time complexity, which measures memory usage and execution duration respectively. Asymptotic notation is used to classify algorithms' performance, including big-oh, big-omega, and big-theta to describe their upper, lower, and average bounds in terms of time complexity.


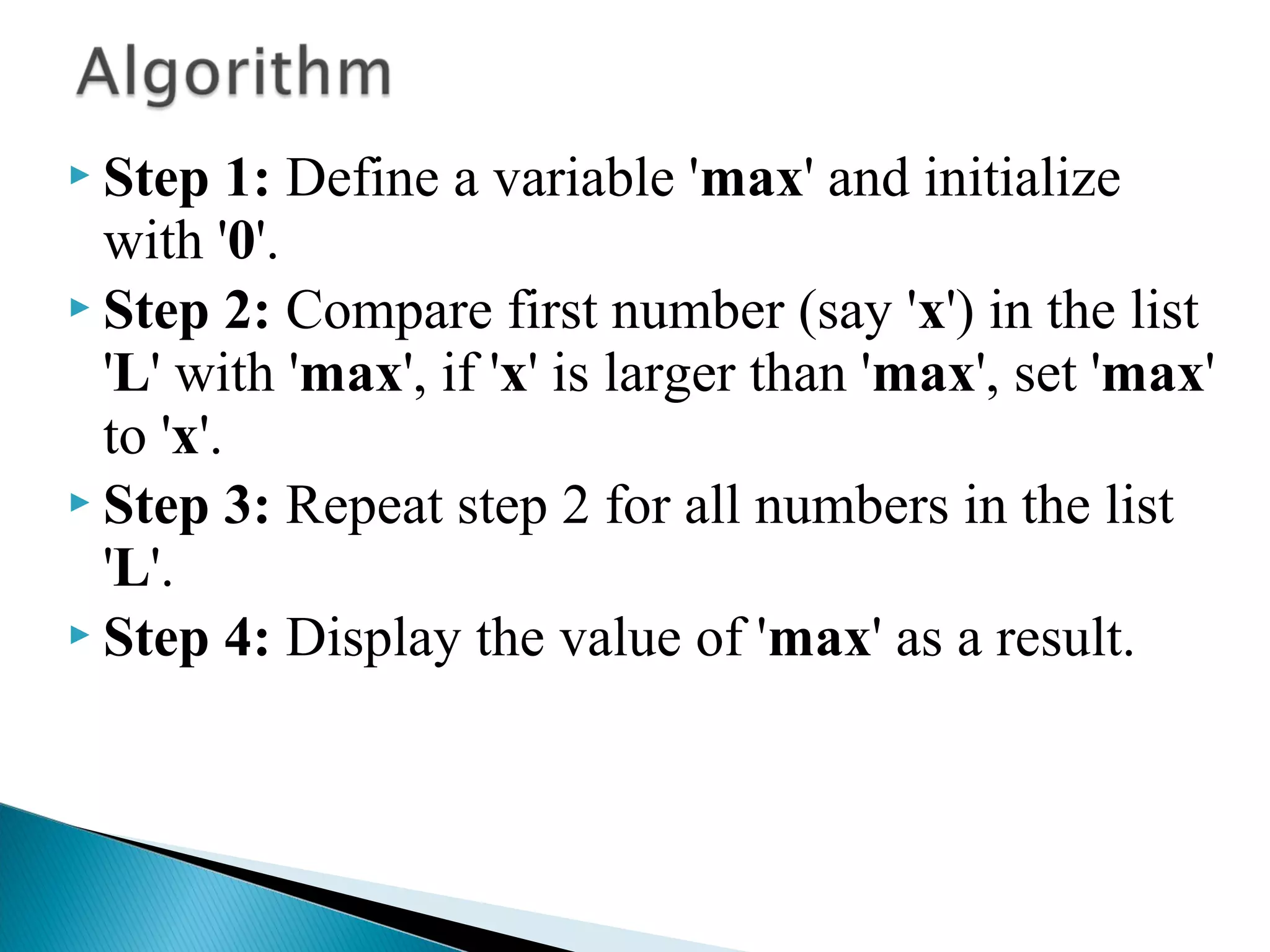
![ int findMax(L)
{
int max = 0,i;
for(i=0; i < listSize; i++)
{
if(L[i] > max) max = L[i];
}
return max;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisanalgorithm-170713071044/75/Asymptotic-Notation-7-2048.jpg)
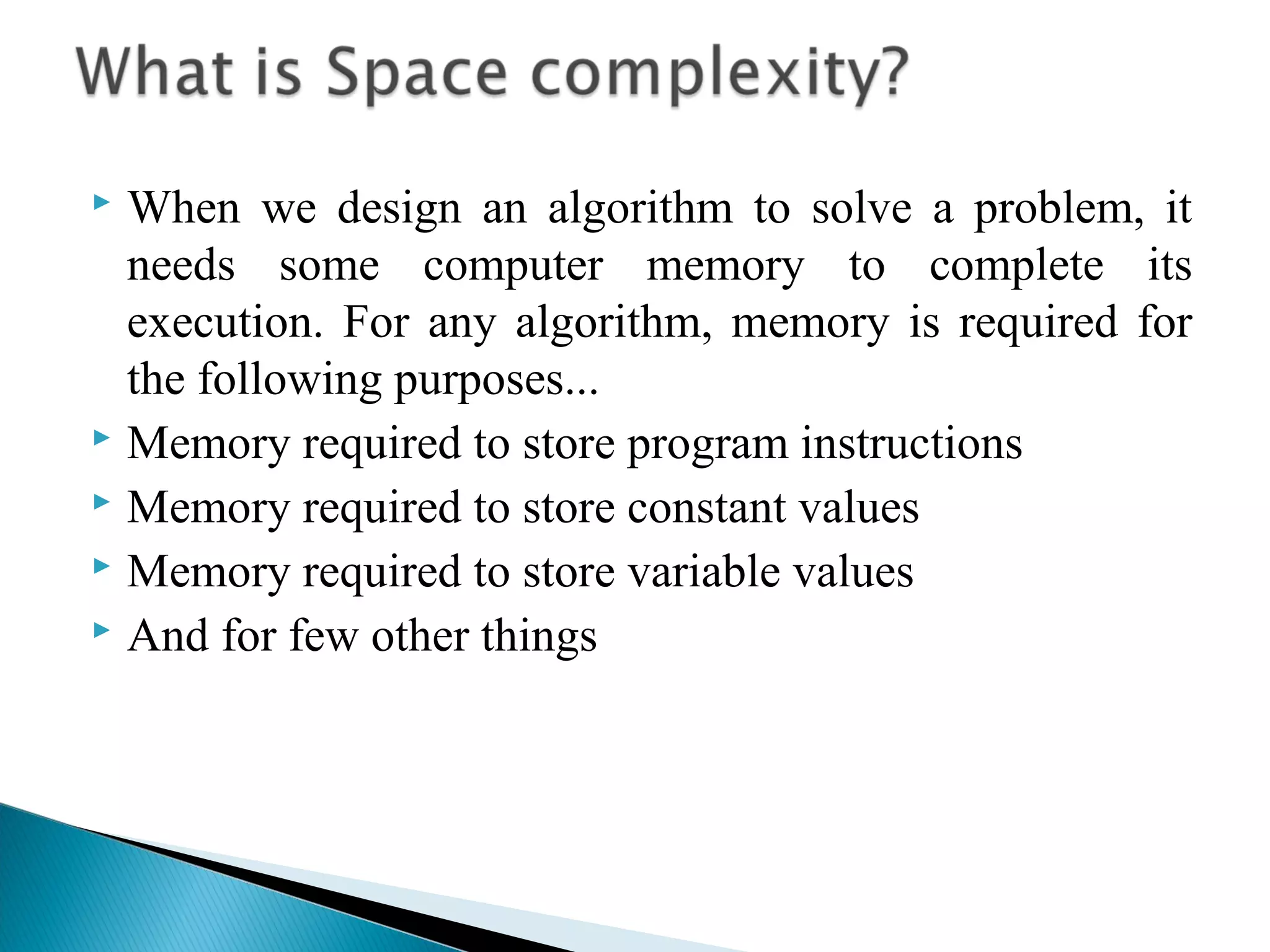
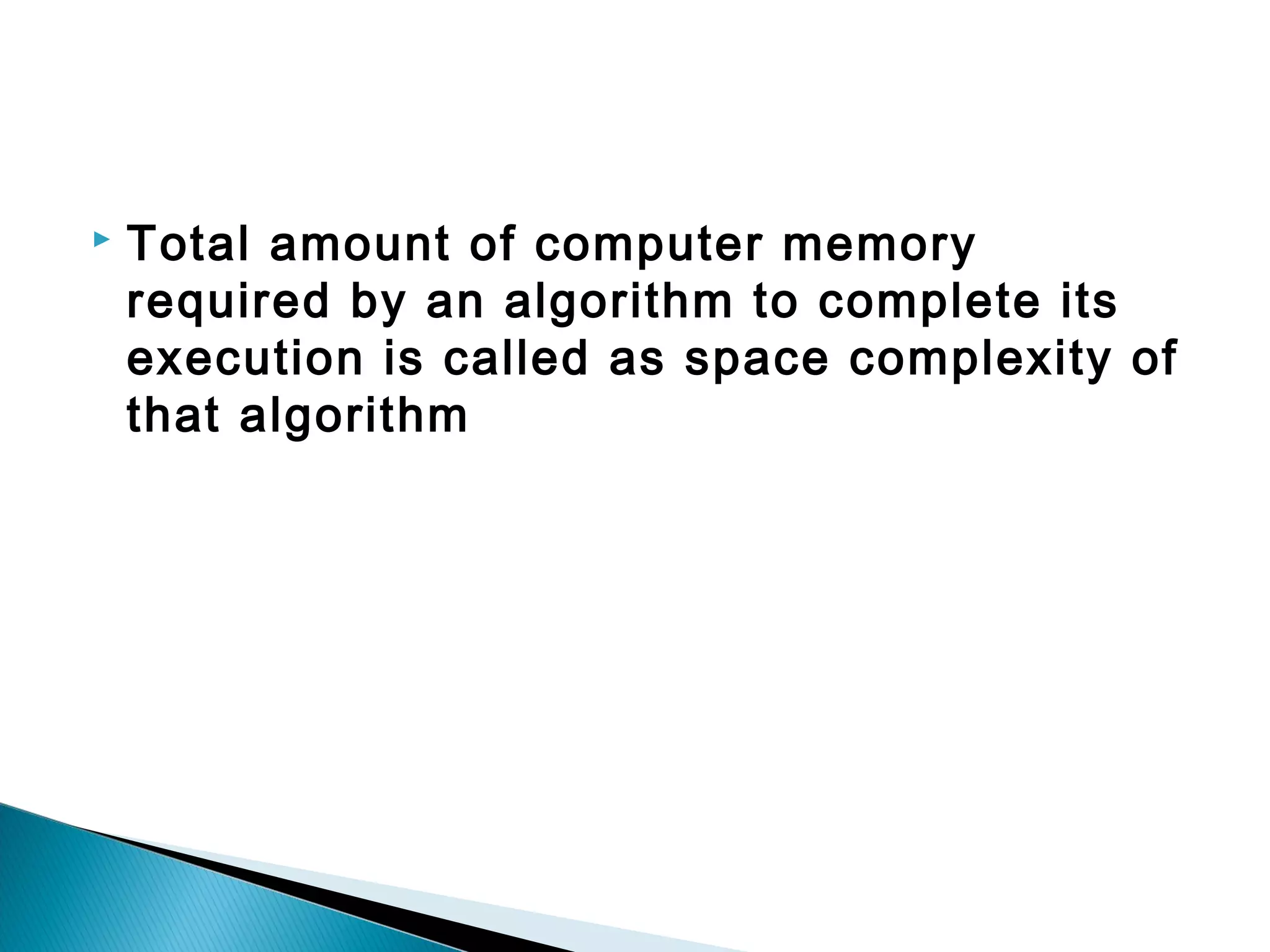

![ If the amount of space required by an
algorithm is increased with the increase of
input value, then that space complexity is
said to be Linear Space Complexity.
int sum(int A[], int n)
{
int sum = 0, i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum = sum + A[i];
return sum;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisanalgorithm-170713071044/75/Asymptotic-Notation-14-2048.jpg)



![ int sum(int A[], int n)
{
int sum = 0, i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum = sum + A[i];
return sum;
}
If the amount of time required by an algorithm is
increased with the increase of input value then that
time complexity is said to be Linear Time
Complexity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisanalgorithm-170713071044/75/Asymptotic-Notation-21-2048.jpg)