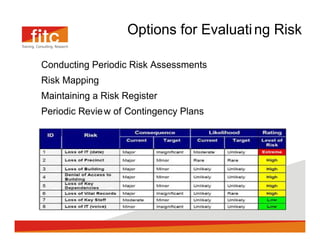
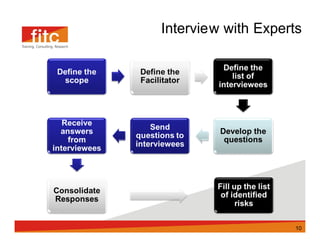
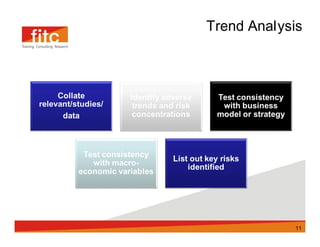
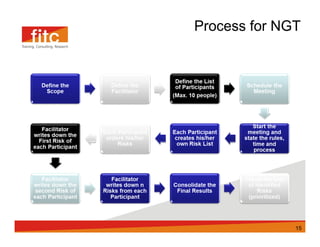
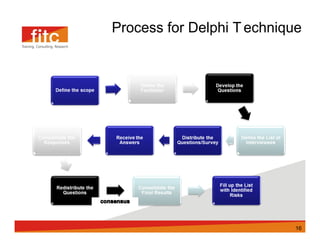
The document discusses risk assessment and mitigation strategies for a bank. It outlines the process of assessing risk, which includes identifying prevalent risks, assessing their impact and frequency, developing controls, and reassessing exposures. It also evaluates options for mitigating risk, such as periodic assessments, maintaining a risk register, and reviewing contingency plans. Key considerations for selecting mitigation actions include ensuring effectiveness, cost efficiency, alignment with business operations, and consistency with regulatory requirements.