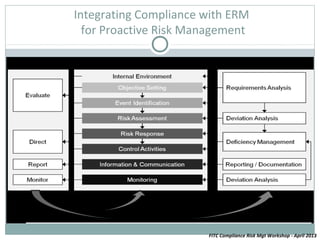
The document discusses leveraging compliance risk management to create value by outlining a risk-based approach to compliance, the functions of a compliance department, and how to develop an effective compliance program through measures like guidance, education, and warnings. It also examines the roles of management and the board, internal and external drivers of compliance risk, and integrating compliance with enterprise risk management.