This document discusses tests used to evaluate facial nerve function including:
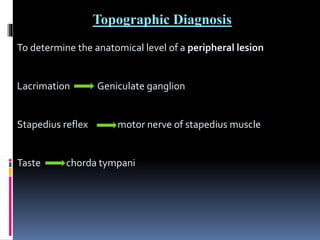
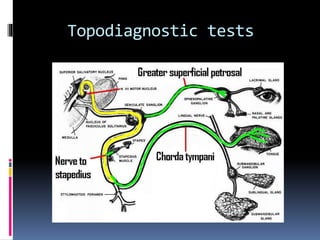
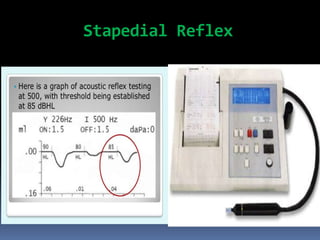
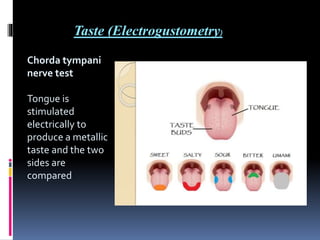
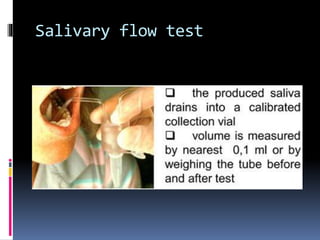
1. Topographic or topodiagnostic tests evaluate specific branches of the facial nerve including the Schirmer test for lacrimation (geniculate ganglion), stapedial reflex test (stapedius branch), taste testing (chorda tympani nerve), and measuring salivary flow rates and pH (chorda tympani nerve).
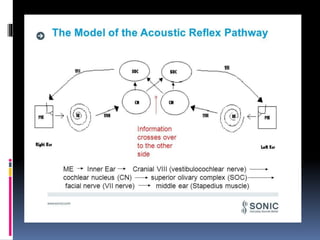
2. Electrophysiological tests include nerve excitability testing, electromyography, maximal stimulation testing, and electroneuronography.
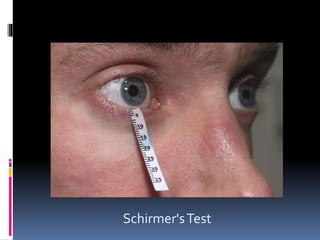
3. The Schirmer test evaluates lacrimation mediated by the geniculate ganglion and petrosal nerve. A difference in wetted