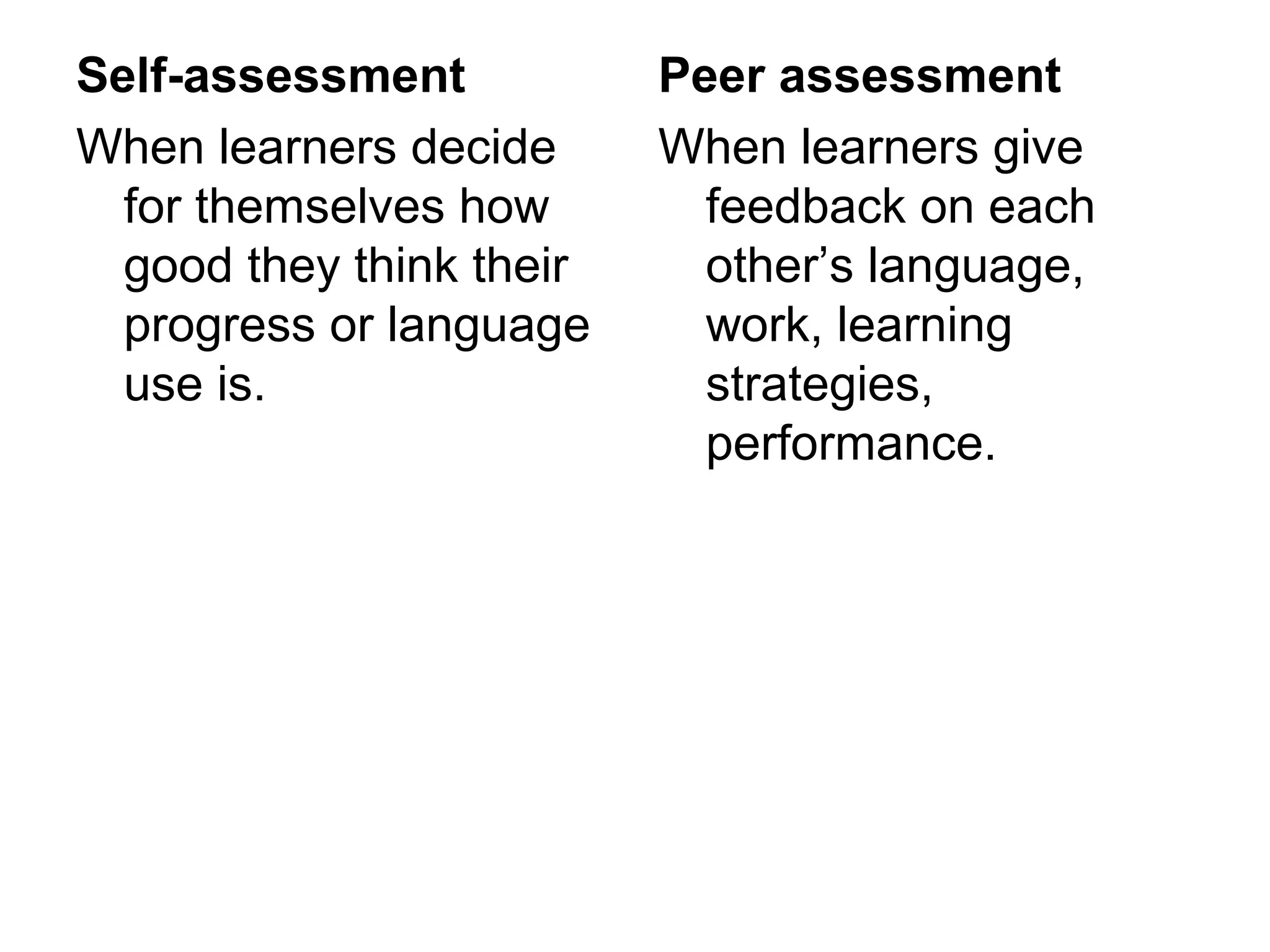
This document discusses different types of assessment used to evaluate learner performance. Formal assessment includes tests and exams with numerical grades, while informal assessment observes learner skills through comments without grades. Self-assessment and peer assessment also allow learners to evaluate themselves and each other. Examples of assessment tasks that can be used formally or informally include gap fills, multiple choice questions, interviews, compositions and dictation. Tasks vary in what they measure, from communication skills to language accuracy, and in how easy they are to score objectively versus subjectively. Informal methods include observation, note-taking and self/peer evaluation sheets.