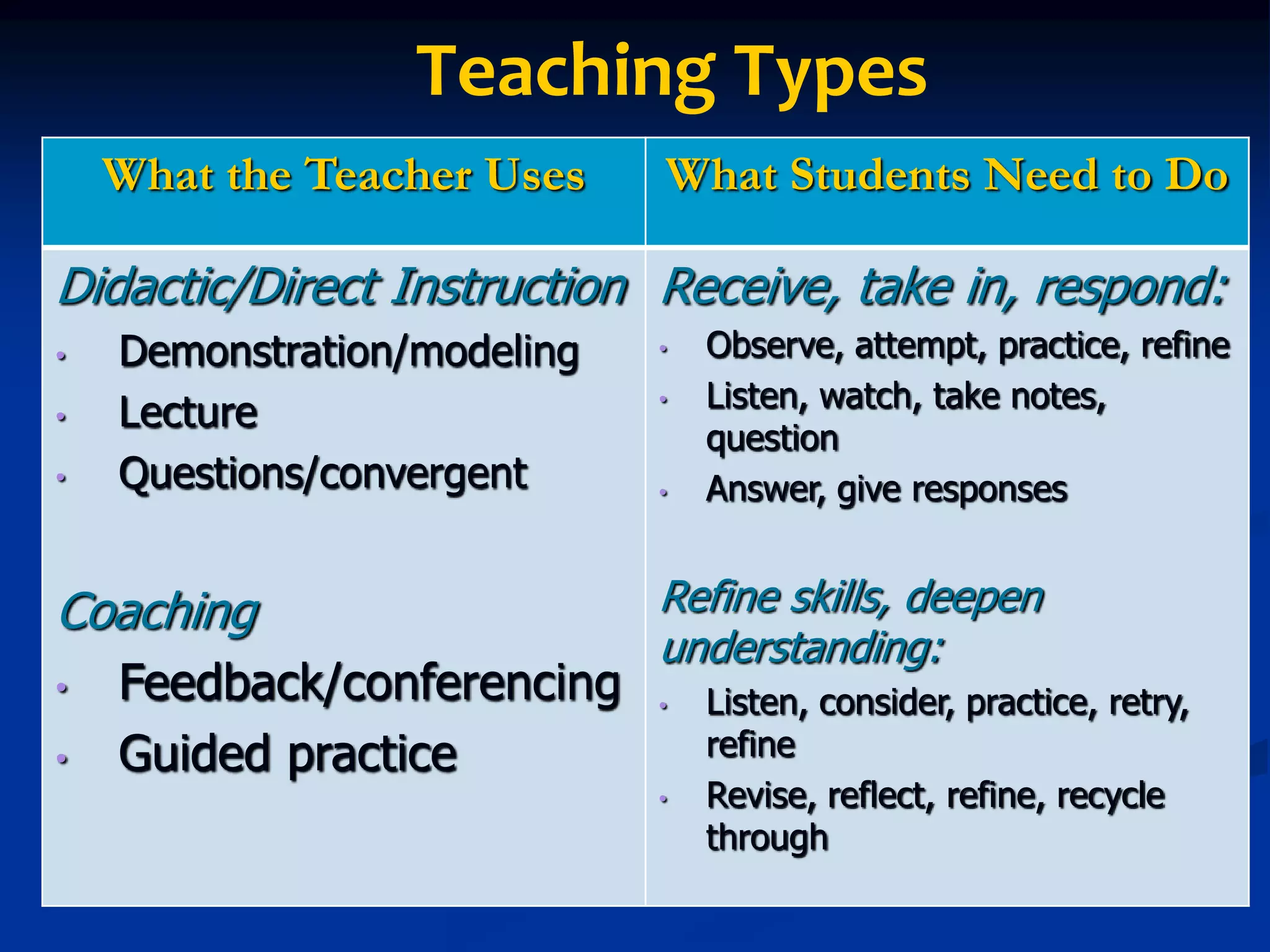
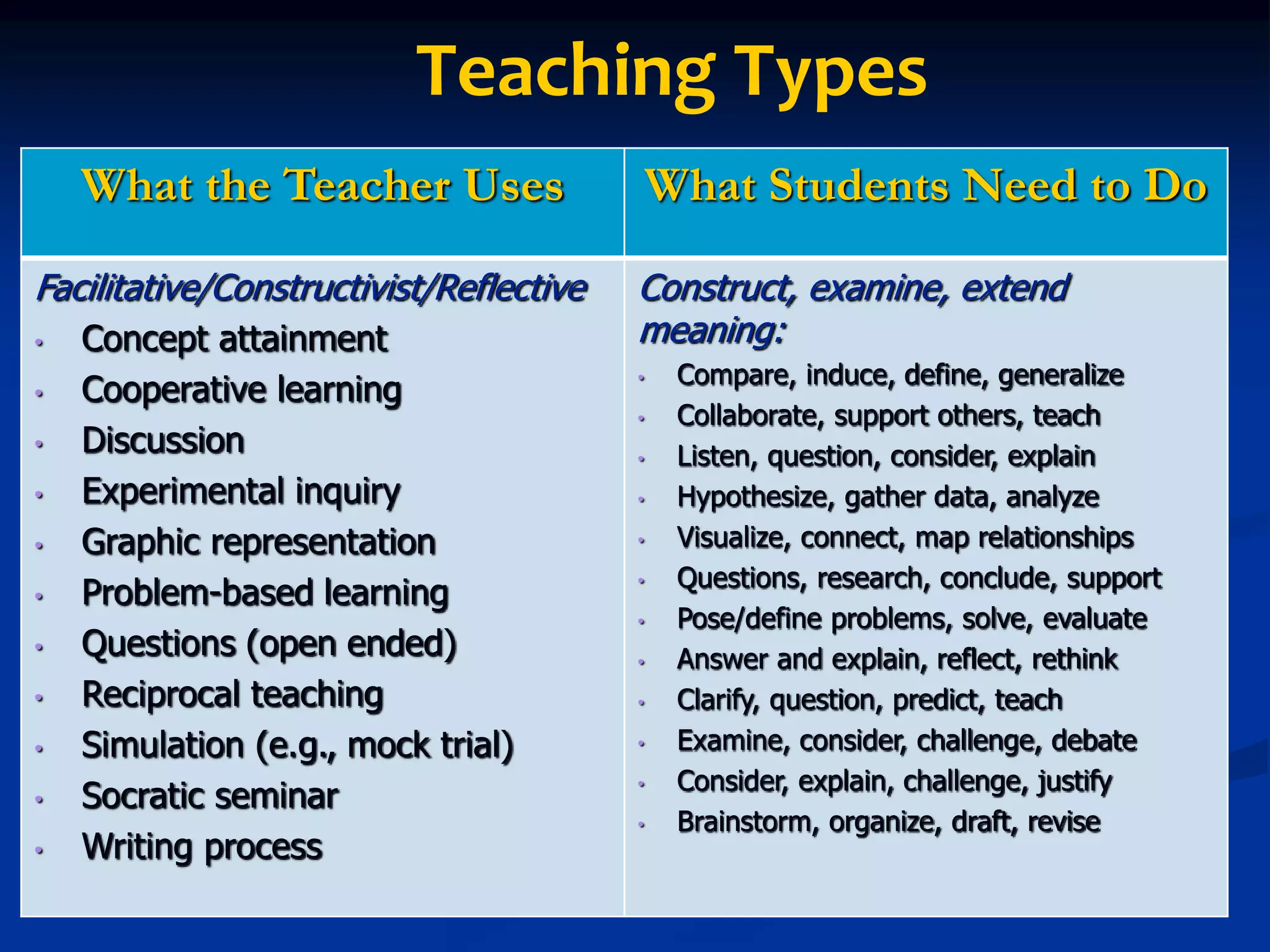
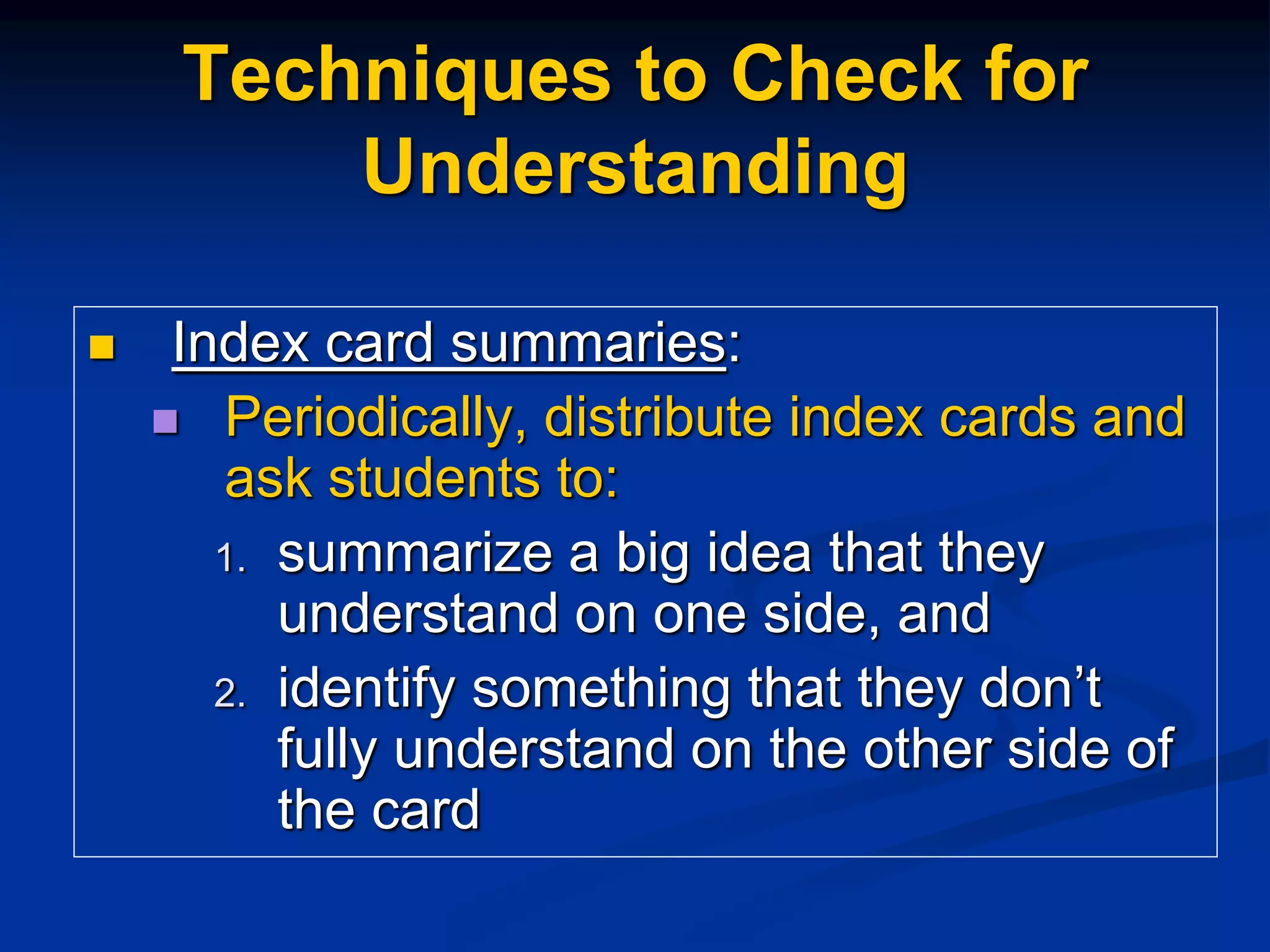
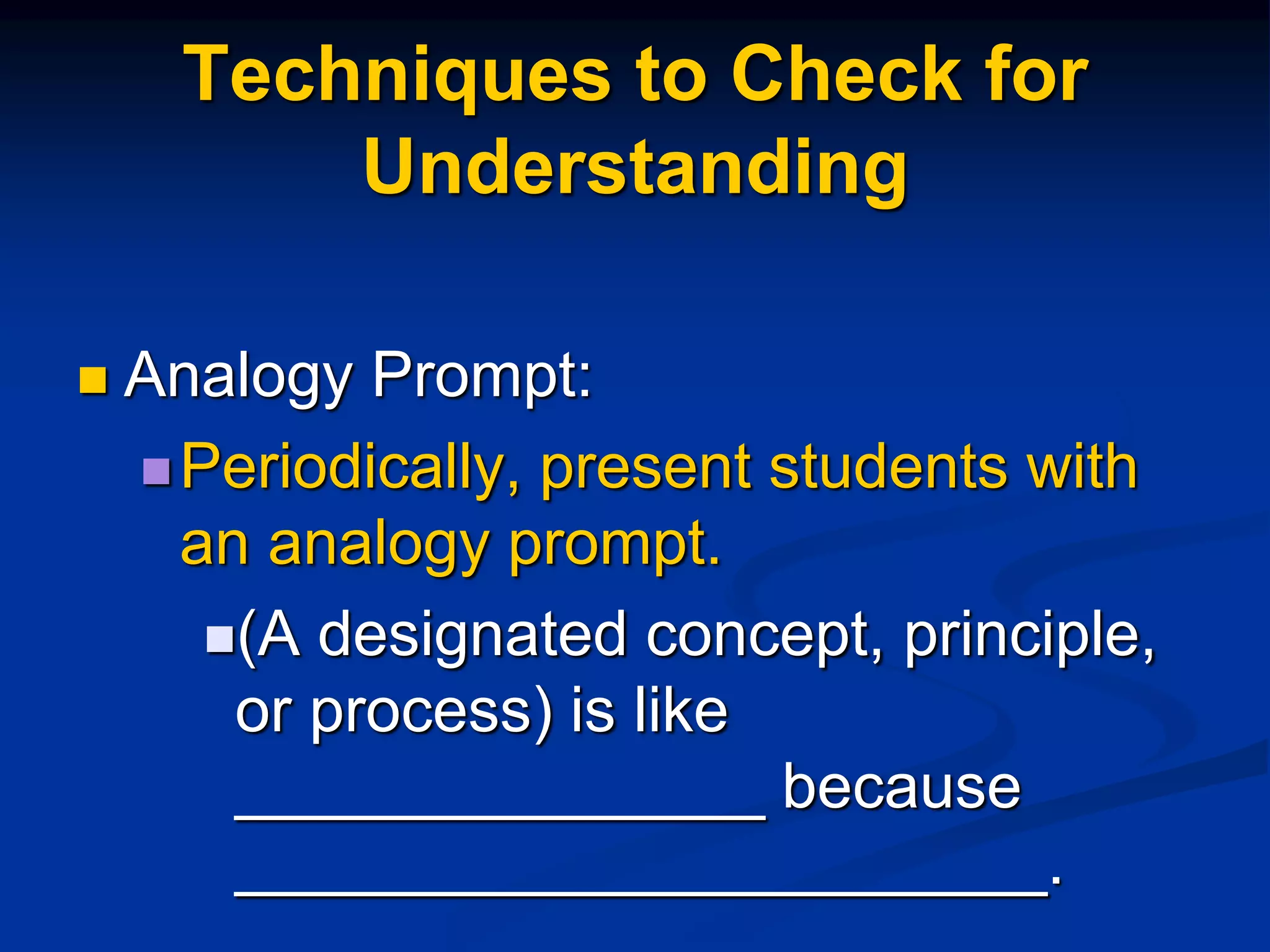
This document discusses techniques for assessing student understanding while teaching. It emphasizes the importance of using different teaching methods, including direct instruction, coaching, and constructivist approaches. The document recommends assessing student understanding informally and continuously throughout a lesson, rather than just with formal end-of-unit assessments. Some specific formative assessment techniques presented include having students write summaries on index cards, submit questions anonymously, create concept maps, and explain analogies.