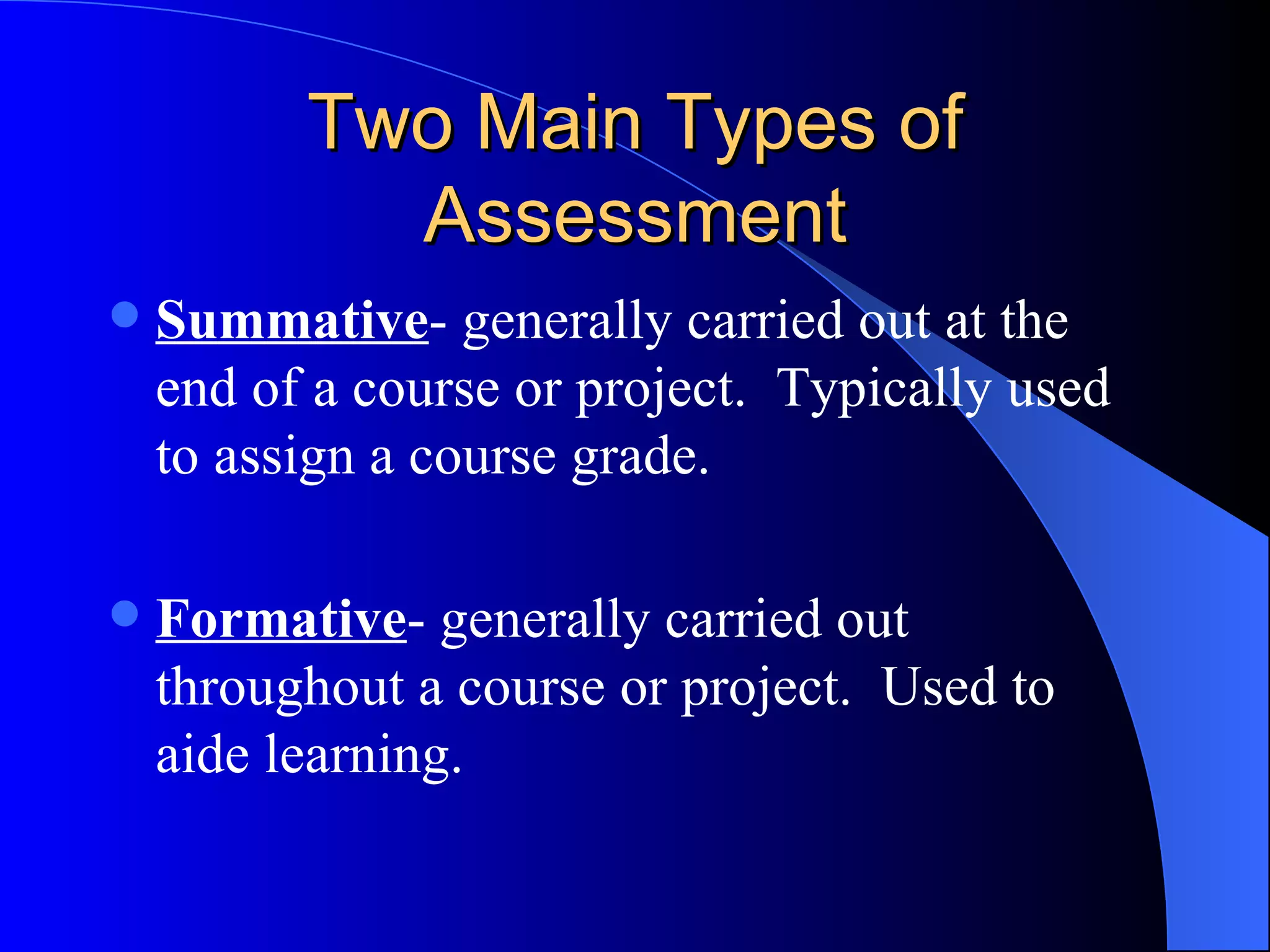
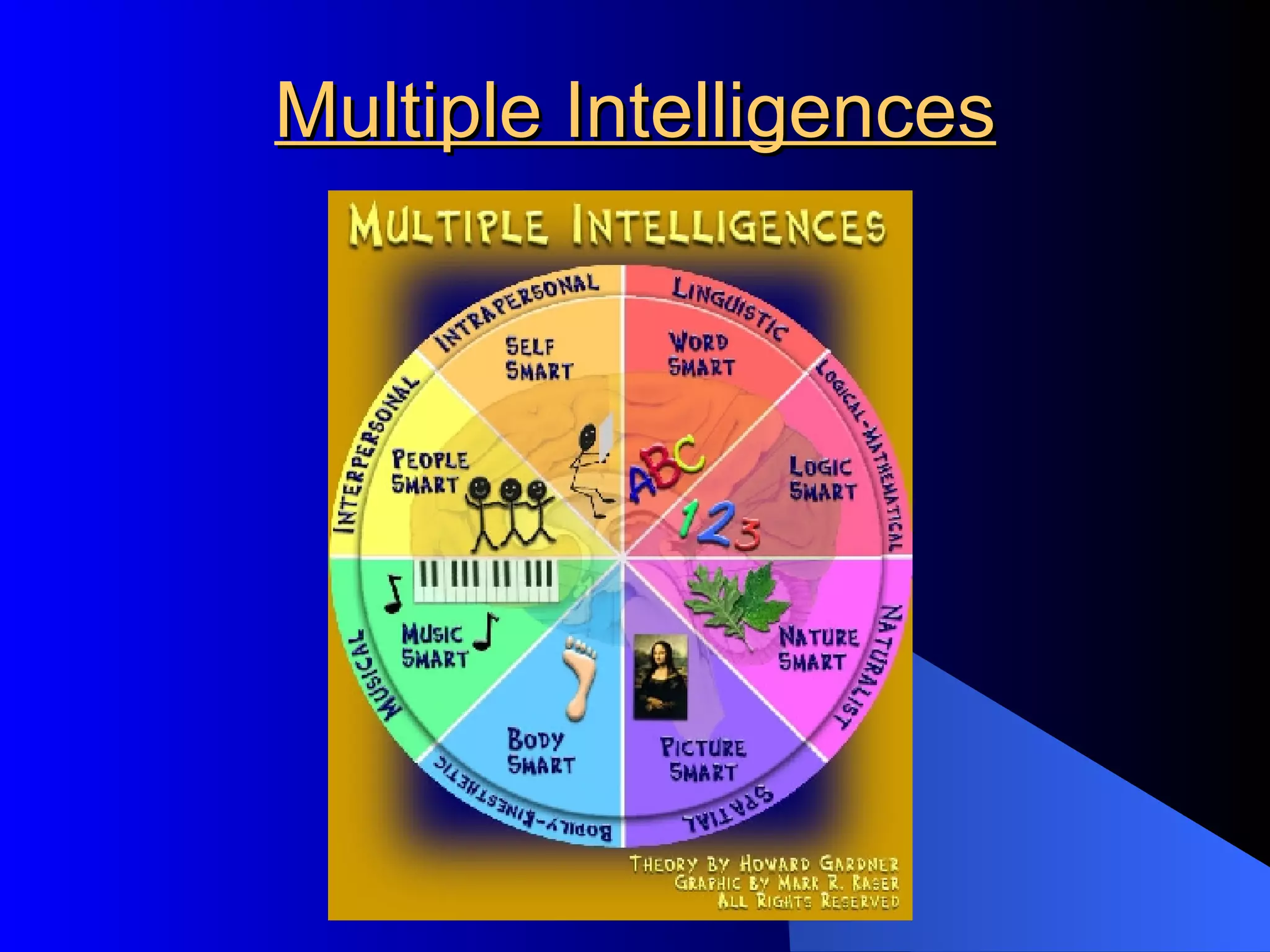
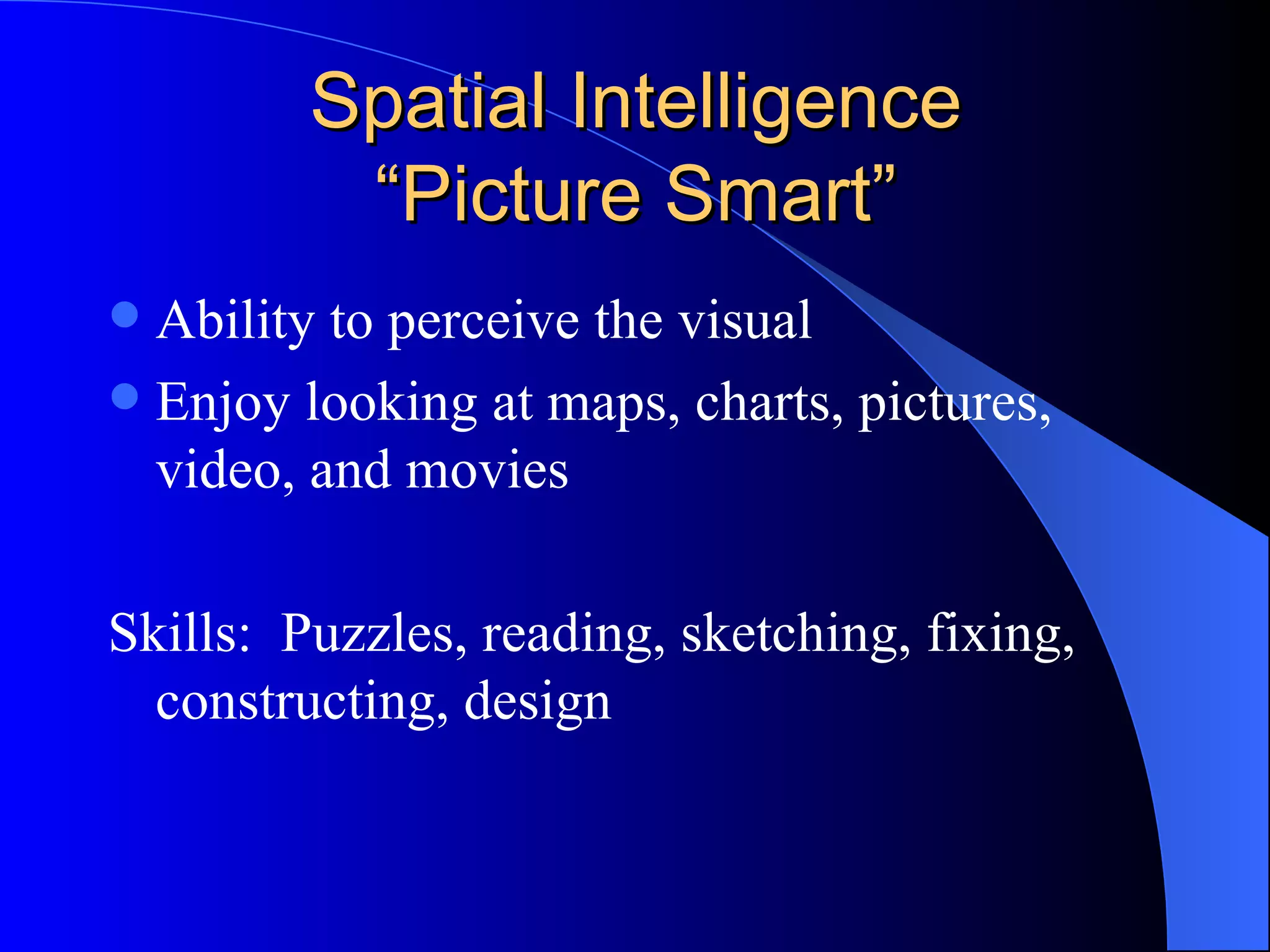
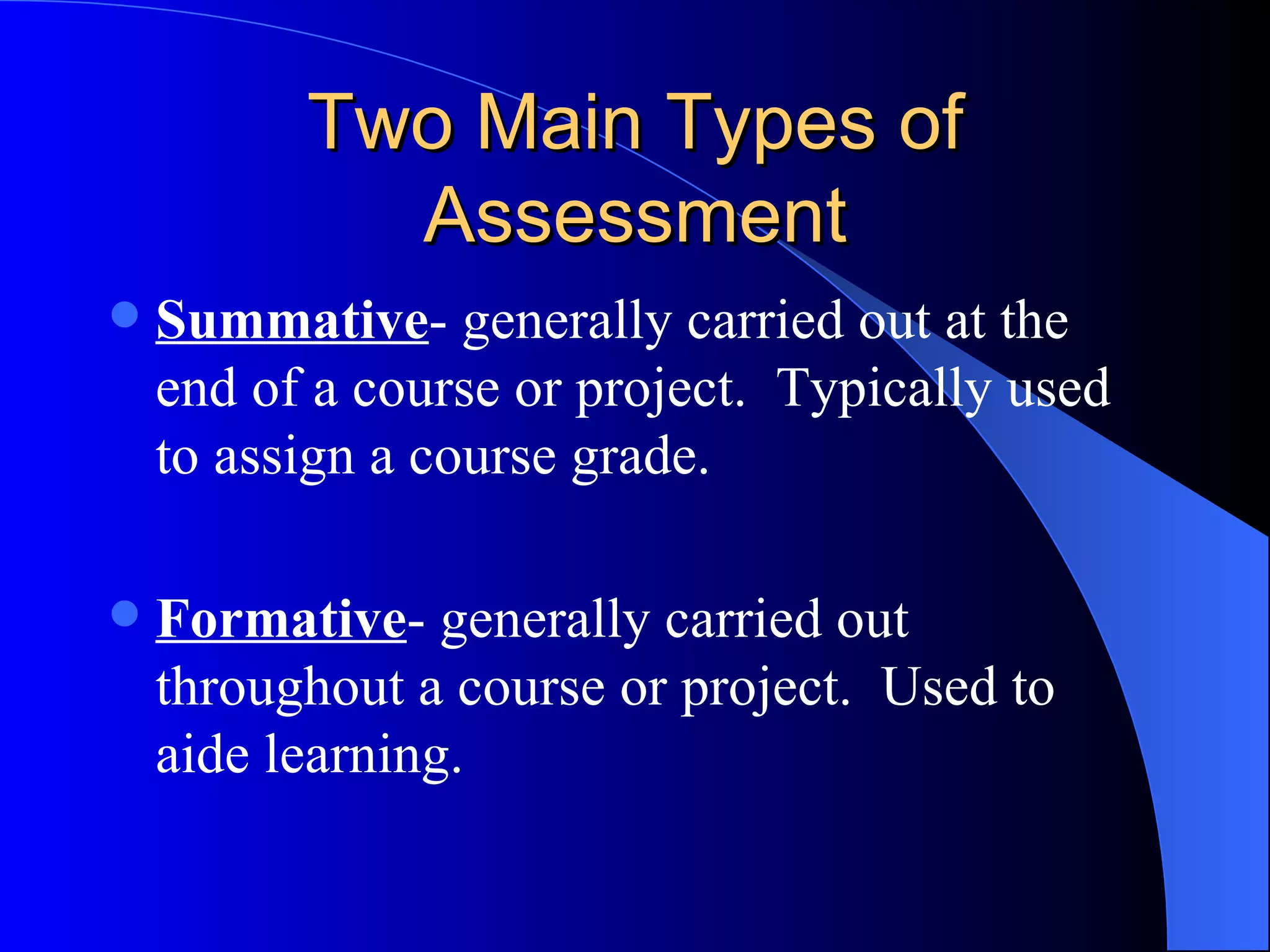
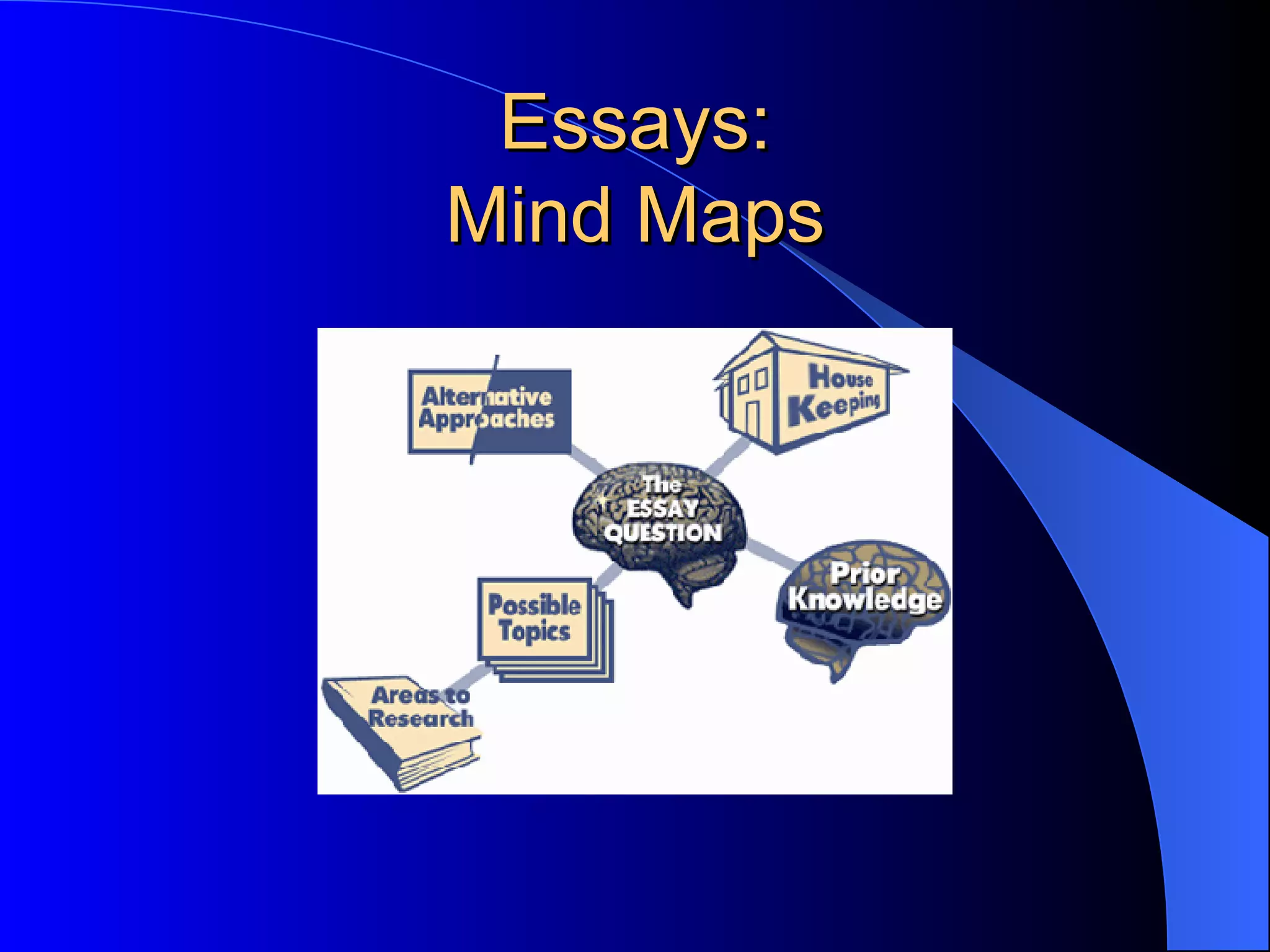
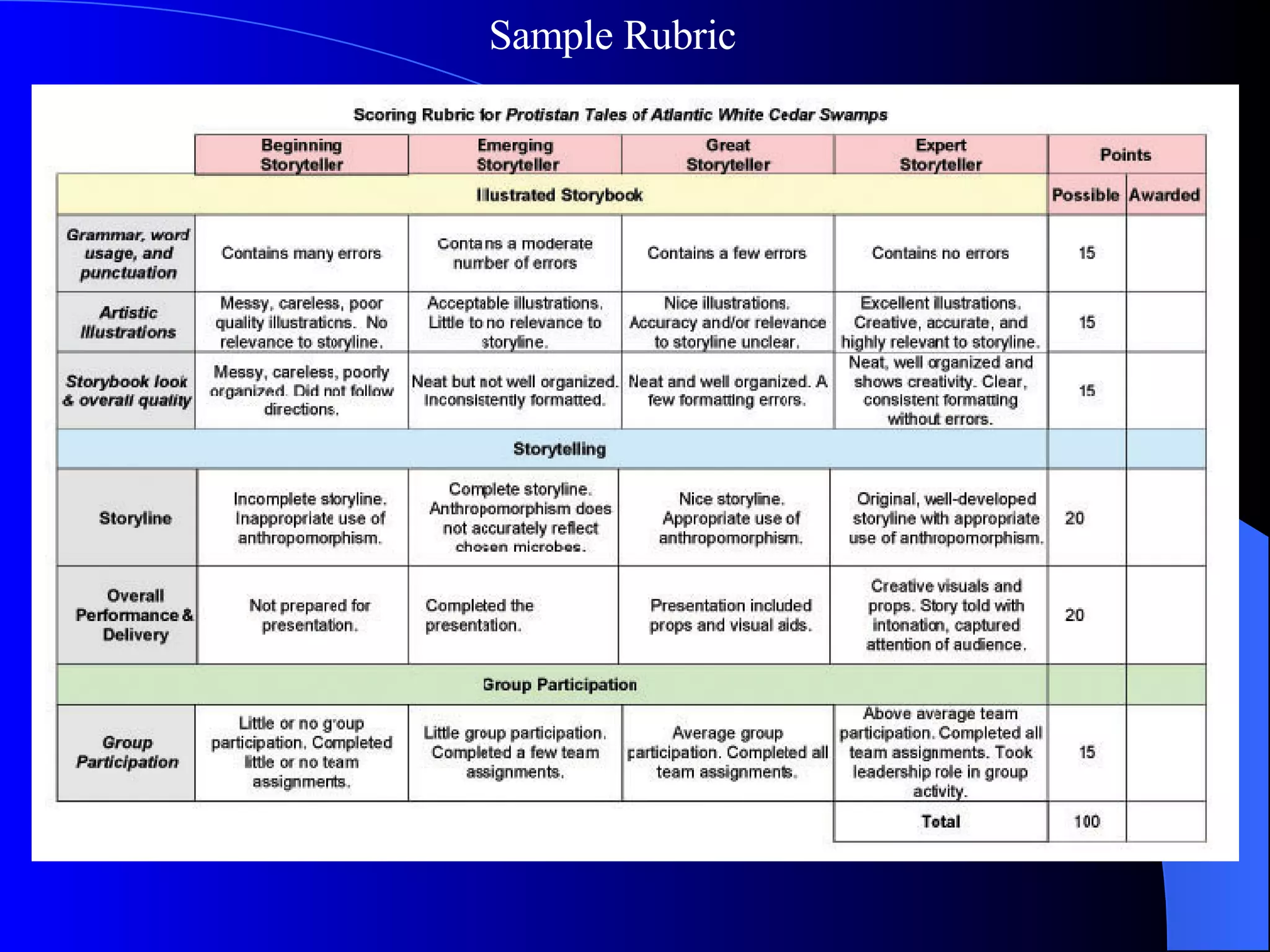
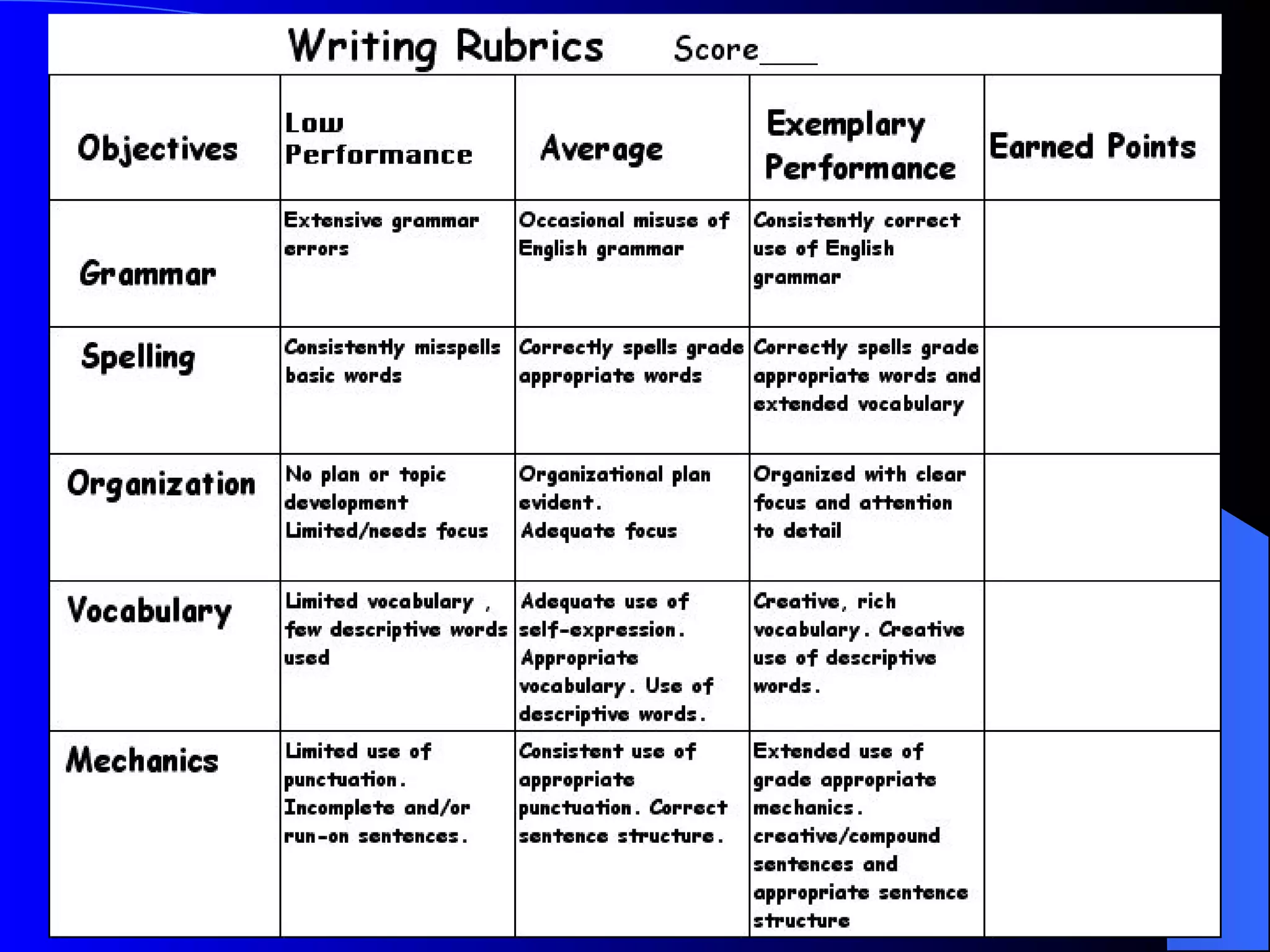
The document discusses various methods of assessment in education. It describes formative assessment, which is used throughout a course to aid learning, and summative assessment, which is used at the end to assign grades. It also discusses traditional assessments like multiple choice and standardized tests, as well as alternative and authentic assessments, which more closely resemble real-world tasks like essays, projects, interviews, and observations. Authentic assessments are presented as being more effective at evaluating students' skills and understanding.