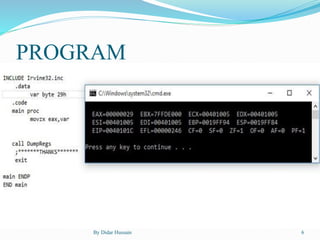
The document describes various assembly language instructions, including their syntax and usage, such as zx for zero extension, sx for sign extension, inc for increment, dec for decrement, xchg for exchanging register values, and neg for negation. It also covers the functions of instructions like lahf and sahf for loading and shifting status flags, ptr for pointer operations, as well as lengthof, sizeof, type, and loop. Additionally, it includes a brief tribute to Arfa Karim Randhawa, the youngest Microsoft Certified Professional.