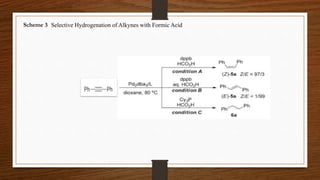
This document discusses the selective hydrogenation of alkynes using a combination of carboxylic acids and group 10 transition metal complexes. Specifically:
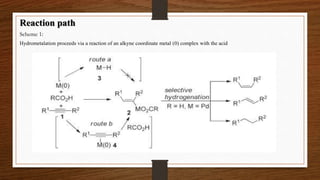
- The combination of carboxylic acids and group 10 transition metals like Pd(0) efficiently catalyzes transformations of alkynes, but the reaction mechanisms were unclear.
- The objective is to achieve facile and stereoselective hydrometalation of alkynes, generating isolated alkenyl metal complexes.
- Hydrometalation proceeds via the reaction of an alkyne-coordinated metal complex with the acid. This provides direct evidence for the involvement of carboxylic acid and zerovalent metals in the reaction mechanism.
- Based on this