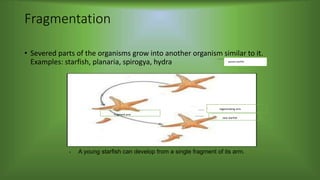
This document defines asexual reproduction and describes its various types. It explains that asexual reproduction involves a single parent producing offspring that are genetically identical. Various types of asexual reproduction are described, including fission, fragmentation, budding, parthenogenesis, spore production, and vegetative propagation. Examples of each type are provided. The objectives are to define asexual reproduction, describe its different types, and classify organisms by their reproductive methods.