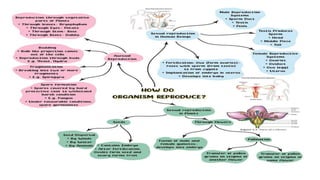
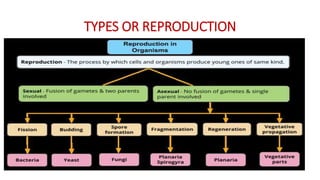
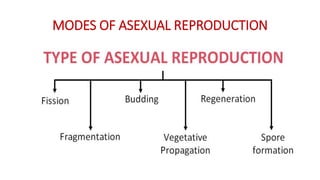
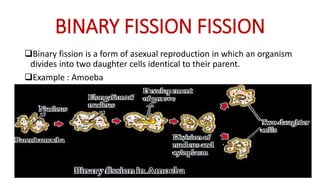
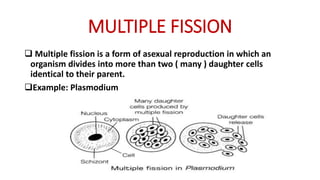
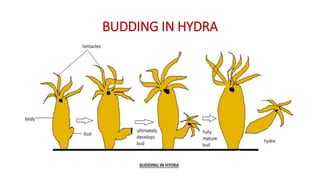
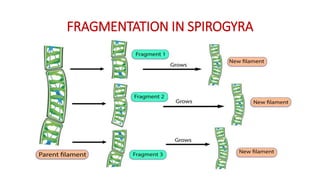
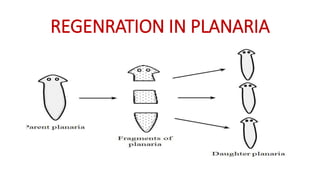
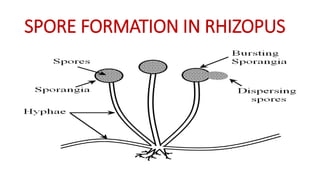
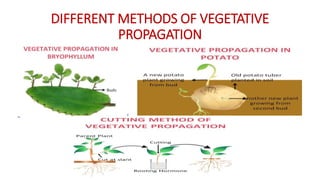
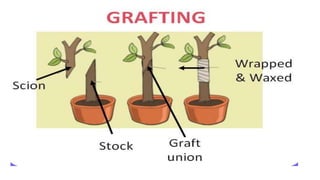
This document discusses different types of reproduction in organisms. It describes asexual reproduction as a mode where offspring are produced from a single parent, resulting in genetically identical clones. Various forms of asexual reproduction are discussed, including binary fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, spore formation, and vegetative propagation. The document also provides examples to illustrate different modes of asexual reproduction like binary fission in amoeba, budding in hydra, and spore formation in rhizopus fungus.