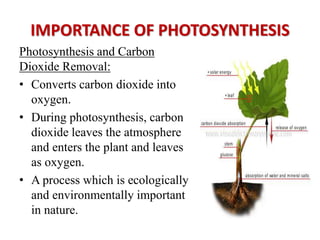
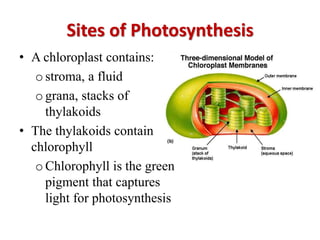
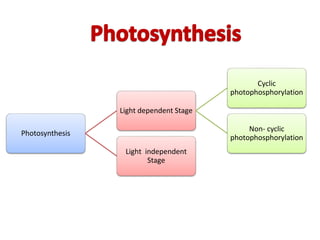
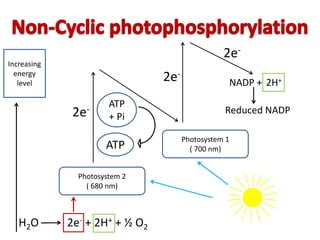
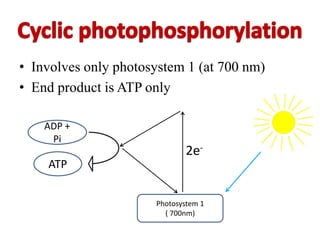
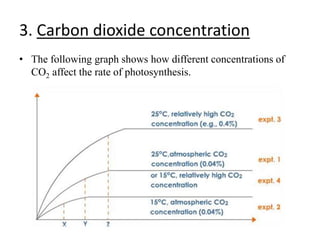
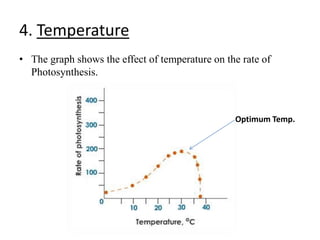
The document provides a comprehensive overview of photosynthesis, detailing its definition, importance, processes, and the factors affecting it. It explains how plants, algae, and some prokaryotes convert light energy into chemical energy, illustrating the significance of photosynthesis in ecosystems and carbon dioxide removal. Additionally, it discusses artificial photosynthesis as a potential method for combating global warming and the essential dependence of life on this process.