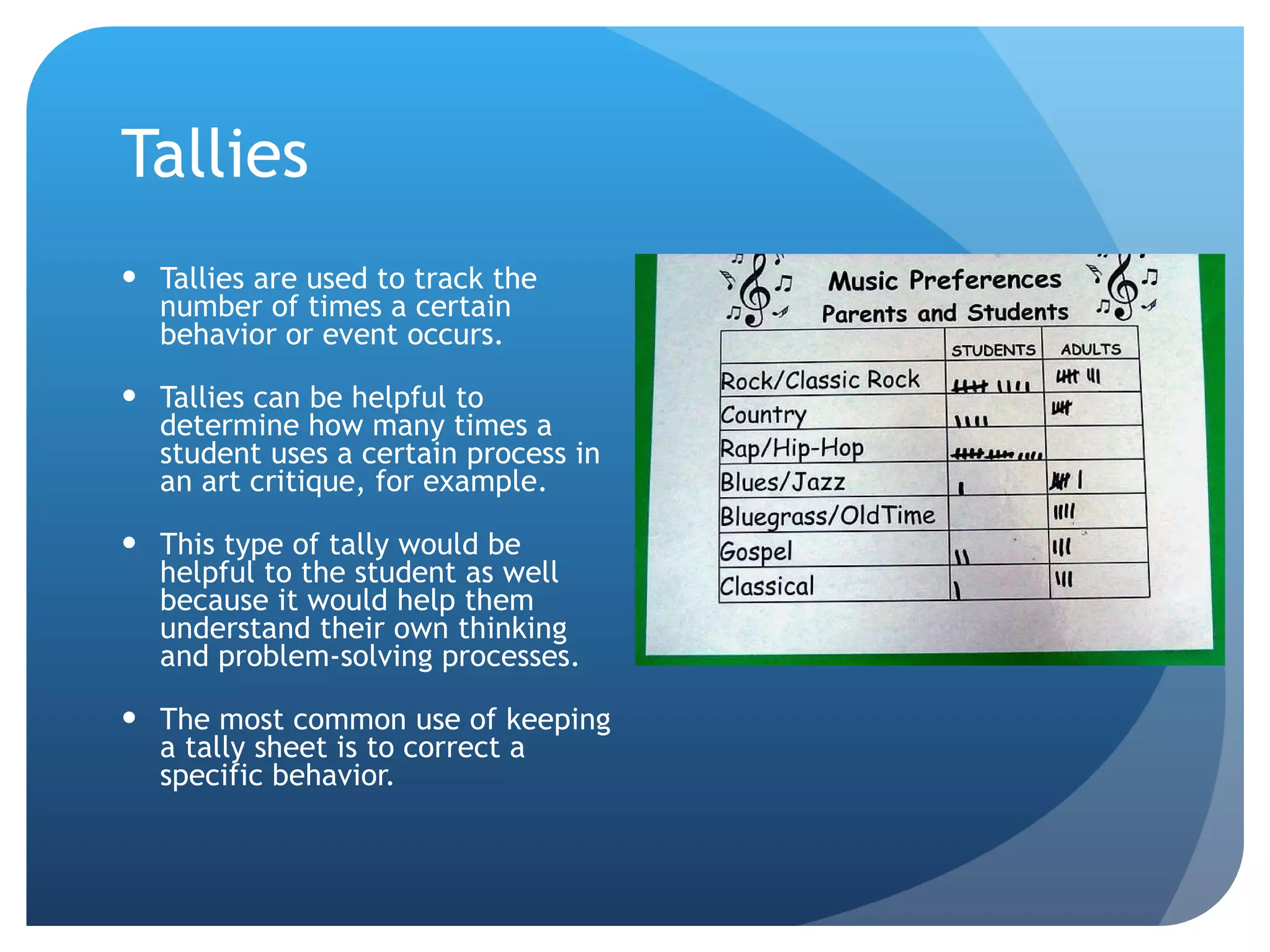
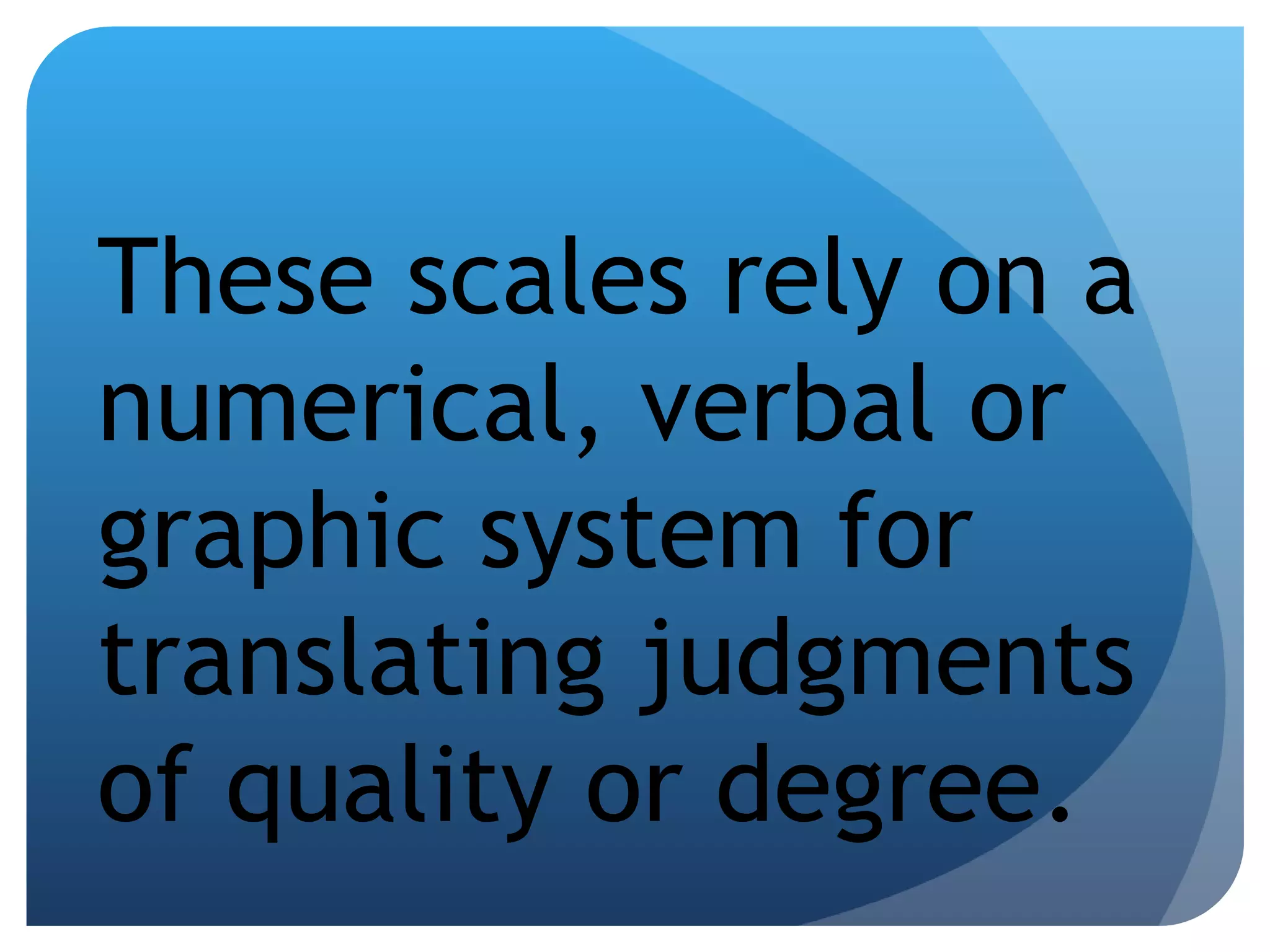
This document discusses various strategies for scoring and judging student artworks, including checklists, tallies, rating scales, critiques, interviews, observations, and student self-assessments. It defines objective and subjective scoring and notes that objective scoring will produce the same results across scorers while subjective scoring may produce different results depending on the individual scorer. It also outlines several types of errors that can occur with rating scales.