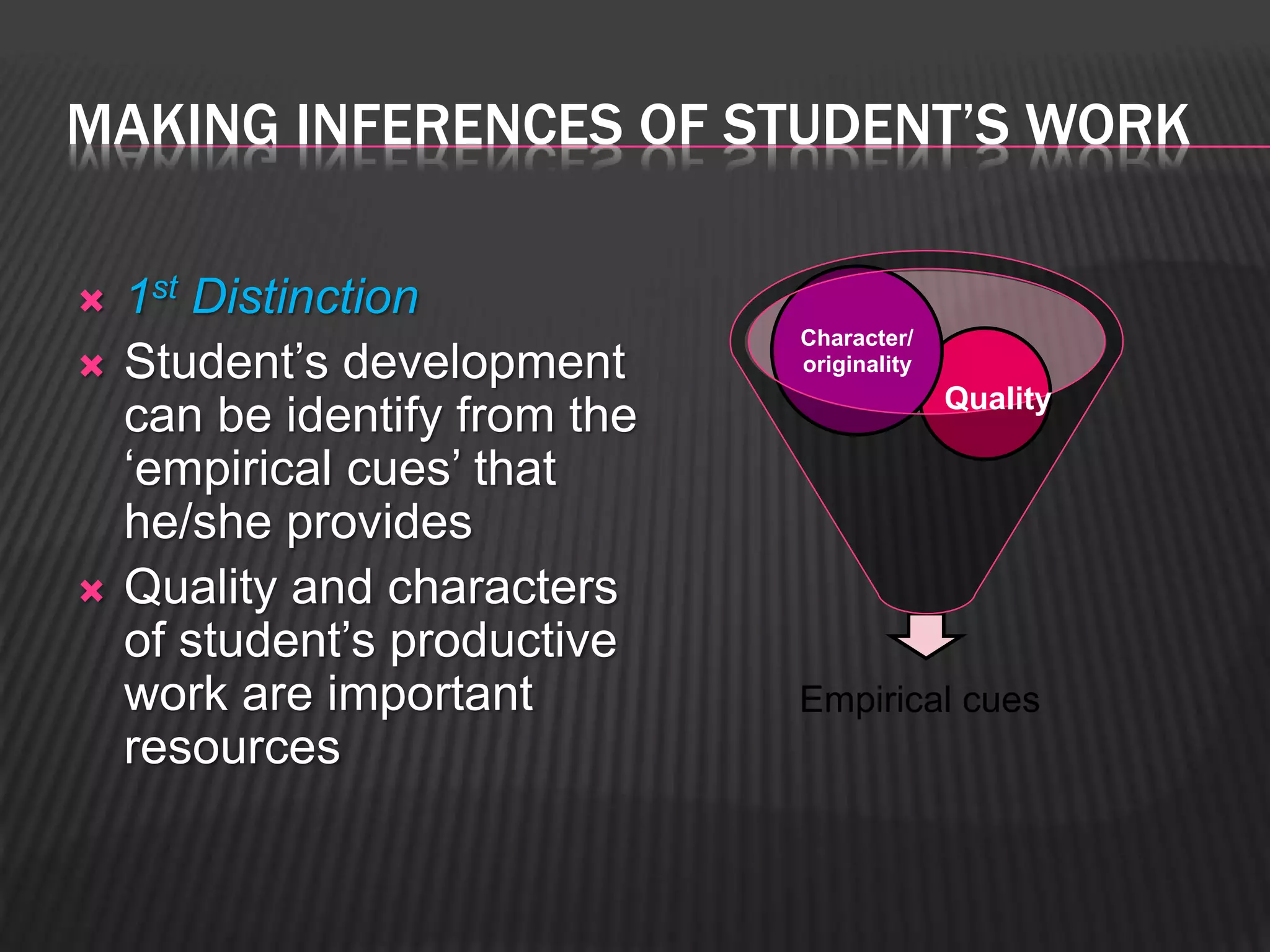
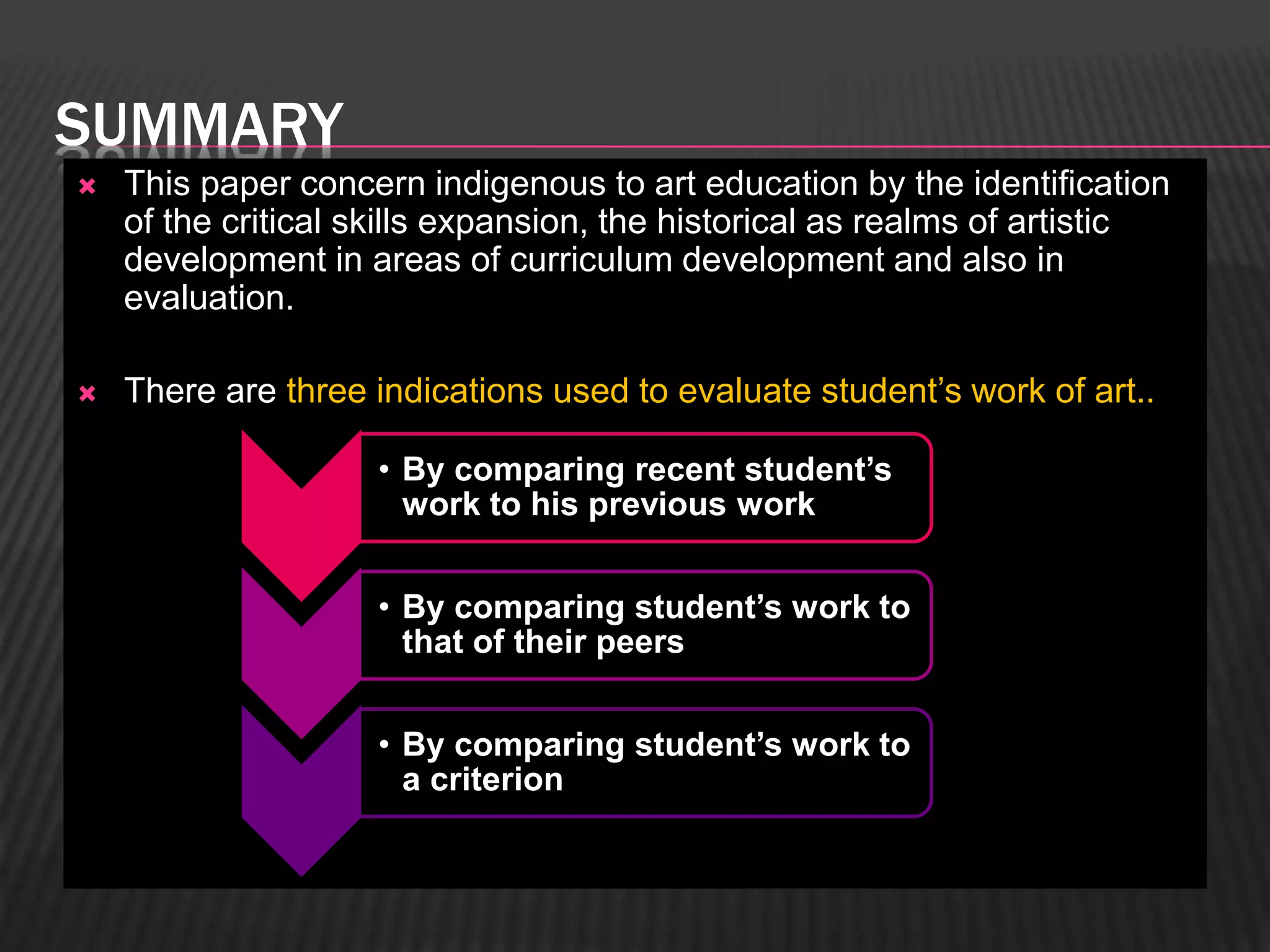
This paper discusses evaluation in art education. It distinguishes evaluation from measurement, testing, and grading. Evaluation involves judging the value of something based on educational objectives. The paper examines three ways to evaluate students' artworks: by comparing to prior work, peers' work, and criteria. It emphasizes evaluating both artistic production and creative process. The goal of evaluation is to improve curriculum and instruction by collecting data on student achievement.