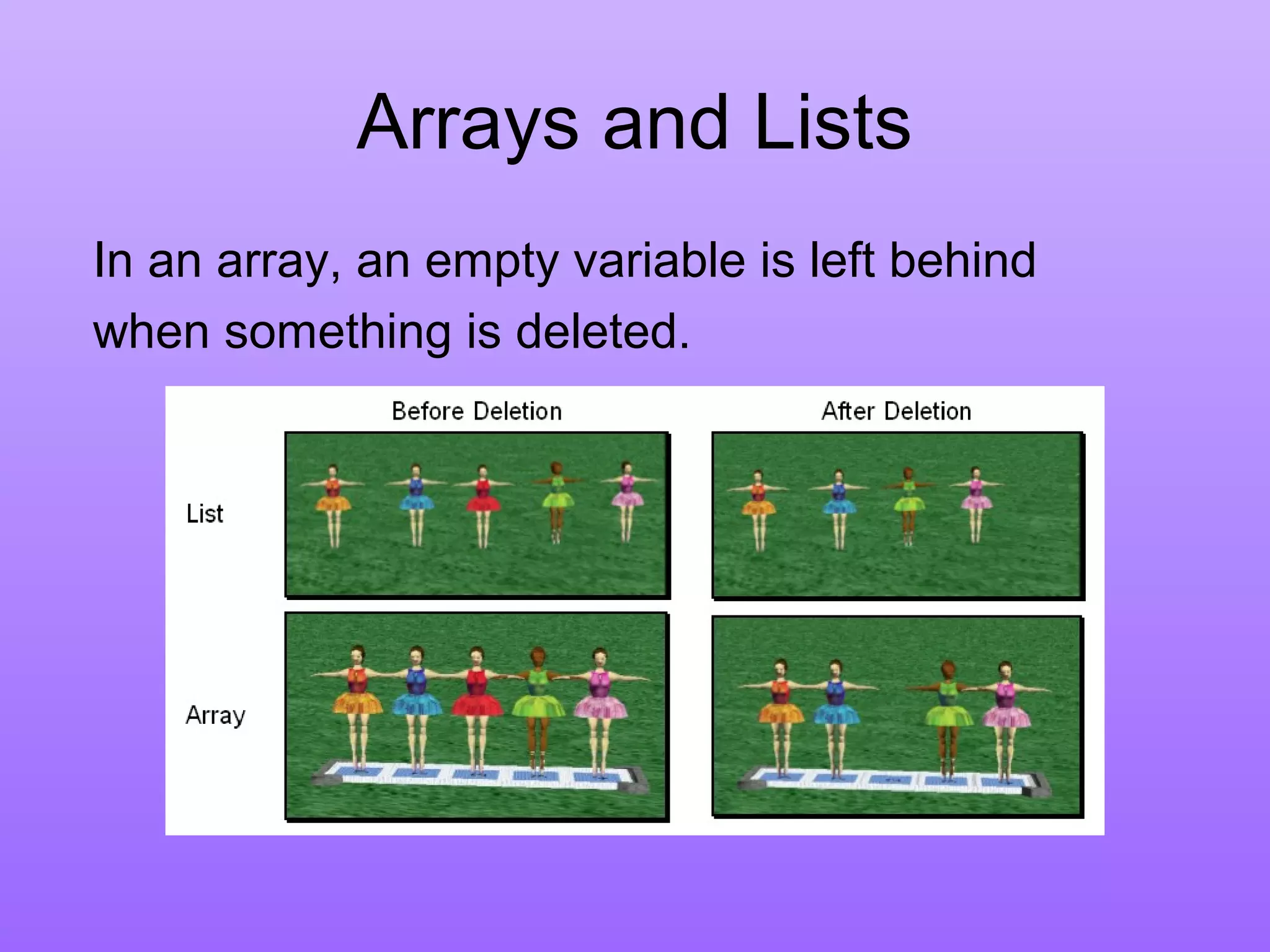
Arrays are indexed sets of variables that store items in boxes like slots. Lists are sets of items where a missing item causes other items to shift, while in arrays a missing item leaves an empty slot. Arrays can be created using built-in functions and the Array Visualization object, which has properties and methods for manipulating array elements. Arrays represent collections of the same type of data, have a fixed size once created, and can be initialized using loops or shorthand notation.

![Arrays
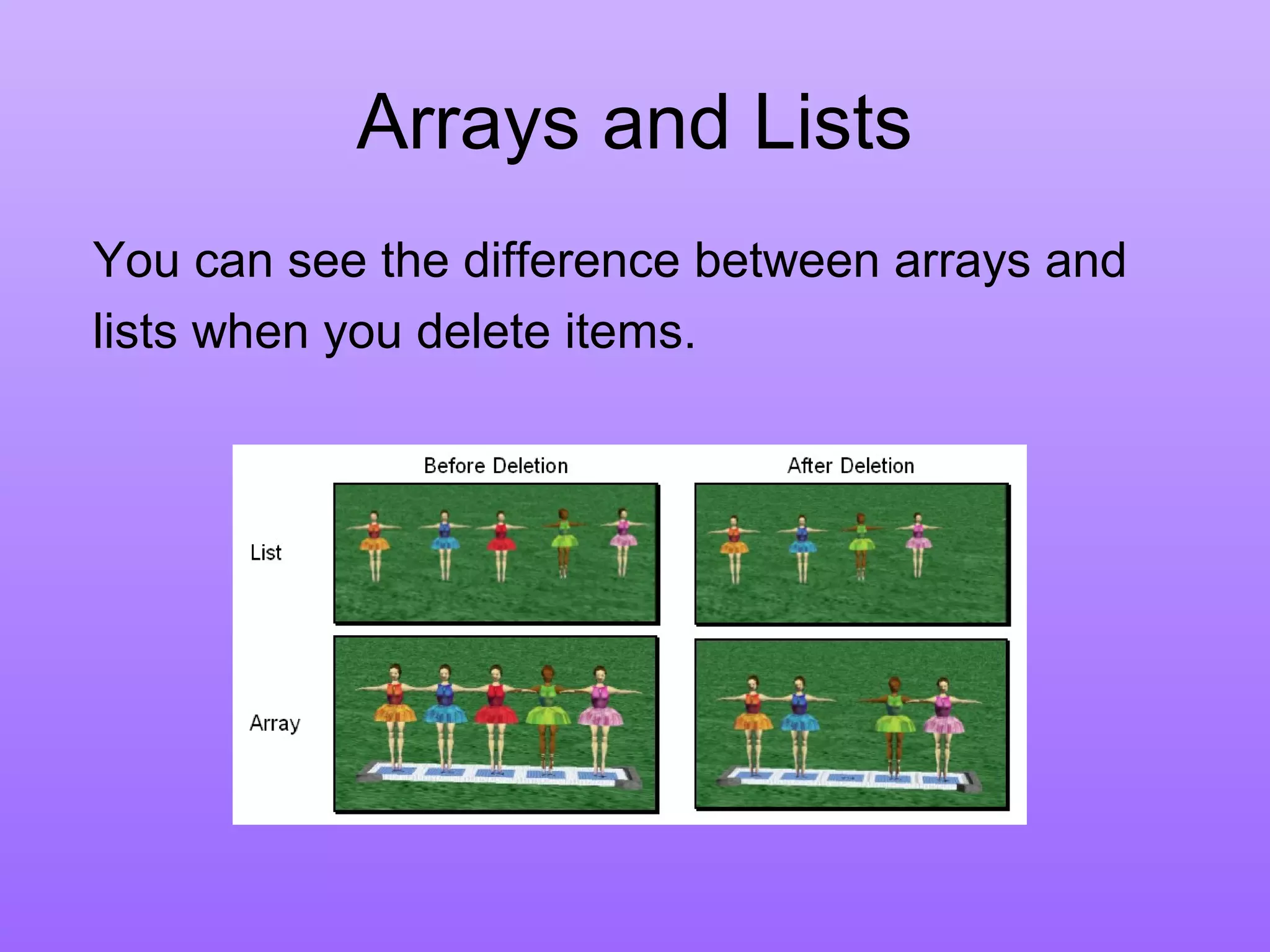
An array is an indexed set of variables, such as
dancer[1], dancer[2], dancer[3],… It is like a set of
boxes that hold things.
A list is a set of items.
An array is a set of
variables that each
store an item.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-2-2048.jpg)



![Introducing Arrays
Array is a data structure that represents a collection
of the same types of data.
myList[0]
myList[1]
myList[2]
myList[3]
myList[4]
myList[5]
myList[6]
myList[7]
myList[8]
myList[9]
double[] myList = new double[10];
myList reference
An Array of 10
Elements
of type double](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-8-2048.jpg)
![Declaring Array Variables
• datatype[] arrayname;
Example:
double[] myList;
• datatype arrayname[];
Example:
double myList[];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-9-2048.jpg)
![Creating Arrays
arrayName = new datatype[arraySize];
Example:
myList = new double[10];
myList[0] references the first element in the
array.
myList[9] references the last element in the
array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-10-2048.jpg)
![Declaring and Creating
in One Step
• datatype[] arrayname = new
datatype[arraySize];
double[] myList = new double[10];
• datatype arrayname[] = new
datatype[arraySize];
double myList[] = new double[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-11-2048.jpg)

![Initializing Arrays
• Using a loop:
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
myList[i] = i;
• Declaring, creating, initializing in one step:
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
This shorthand syntax must be in one
statement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-13-2048.jpg)
![Declaring, creating, initializing
Using the Shorthand Notation
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
This shorthand notation is equivalent to the
following statements:
double[] myList = new double[4];
myList[0] = 1.9;
myList[1] = 2.9;
myList[2] = 3.4;
myList[3] = 3.5;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array1-150626051946-lva1-app6892/75/Array1-14-2048.jpg)