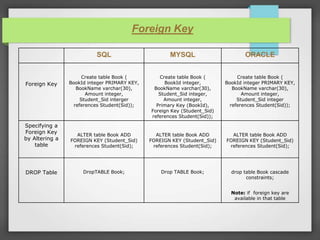
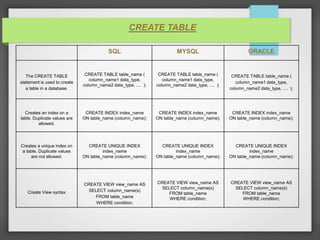
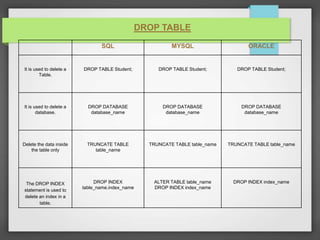
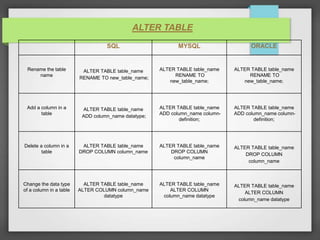
The document compares and contrasts SQL, MySQL, and Oracle databases. It discusses the definitions of SQL, MySQL, and Oracle and how they are different types of database management systems. It also provides examples of how to create tables, define primary keys, add foreign keys, create indexes, drop tables, and alter tables using SQL, MySQL, and Oracle syntax.