This document provides information on arrays in Java, including:
- Arrays are used to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. There are single-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays.
- Arrays are initialized using the new keyword, and elements can be accessed by their index. The length property returns the size of the array.
- Loops like for can be used to iterate through arrays. Multi-dimensional arrays contain one or more arrays. Jagged arrays can have rows of different lengths.
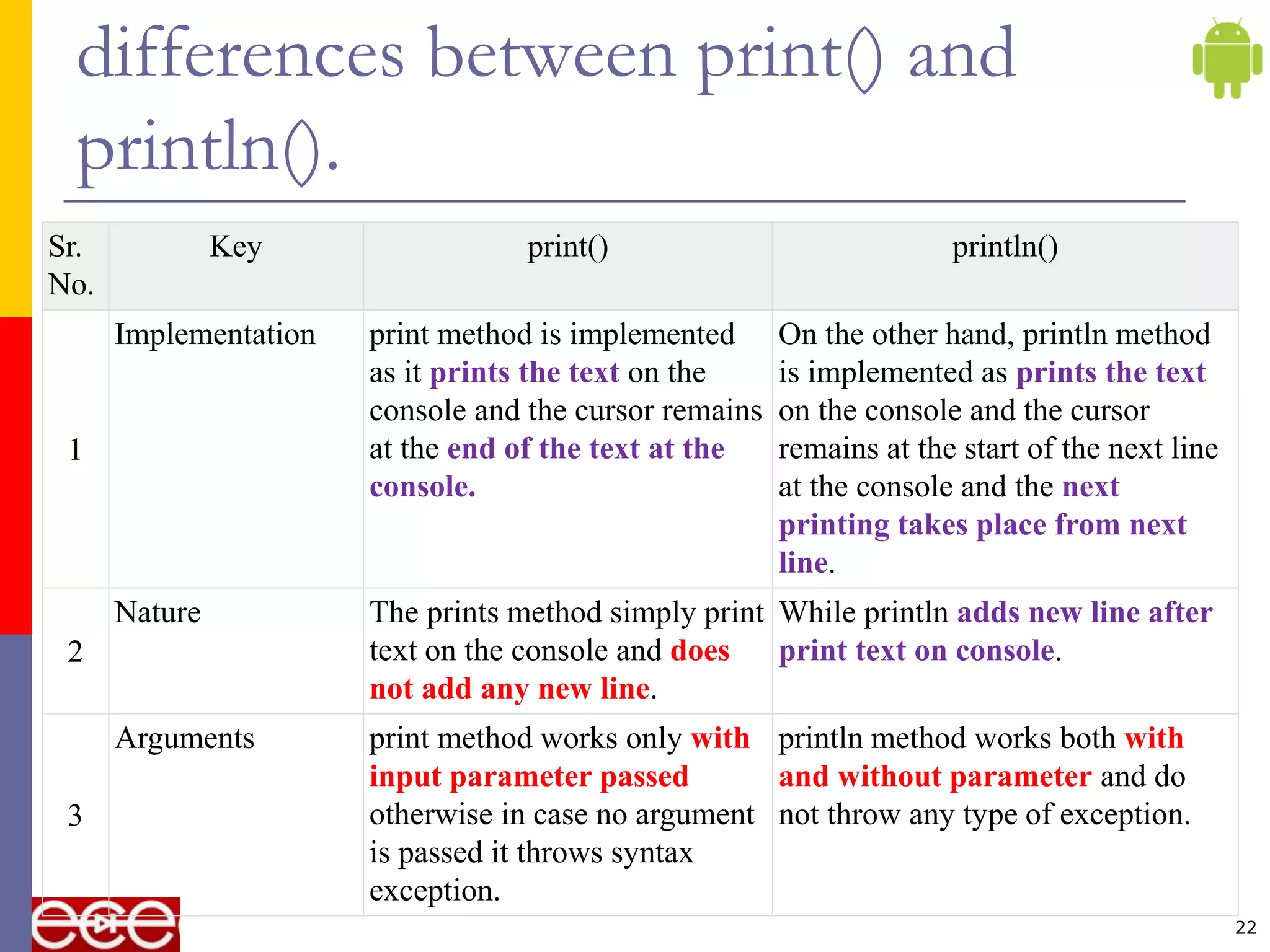
- The print() and println() methods differ in that println() adds a new line while print() does not.

![Array
used to store multiple values in a single
variable, instead of declaring separate
variables for each value.
To declare an array, define the variable type
with square brackets []
an array is a collection of similar types of
data.
For example, if we want to store the names
of 100 people then we can create an array
of the string type that can store 100 names.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-2-2048.jpg)

![Define an Array Variable in Java
Syntax:
datatype[] identifier; //preferred way
or
datatype identifier[];
Example:
char refVar[];
char[] refVar;
int[] refVar;
short[] refVar;
long[] refVar; 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-4-2048.jpg)
![Initialize an array
By using new operator array can be initialized
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
int[] age = new int[5]; //5 is the size of array.
int age[5]={22,25,30,32,35};
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-5-2048.jpg)
![ String[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford",
"Mazda"};
int[] myNum = {10, 20, 30, 40};
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-6-2048.jpg)
![Access the Elements of an Array
access an array element by referring to
the index number.
String[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford",
"Mazda"};
System.out.println(cars[0]);
// Outputs Volvo
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-7-2048.jpg)
![Array Length
String[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford",
"Mazda"};
System.out.println(cars.length);
// Outputs 4
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-8-2048.jpg)
![Loop Through an Array
the array elements with the for loop, and
use the length property to specify how
many times the loop should run.
String[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford",
"Mazda"};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
System.out.println(cars[i]);
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-9-2048.jpg)
![//Java Program to illustrate the use of declaration, instantiation
//and initialization of Java array in a single line
class Testarray1{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization
//printing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}}
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-10-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays
containing one or more arrays.
add each array within its own set of curly
braces:
dataType[][] arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or)
dataType []arrayRefVar[];
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-11-2048.jpg)
![int[][] arr=new int[3][3];
//3 row and 3 column
arr[0][0]=1;
arr[0][1]=2;
arr[0][2]=3;
arr[1][0]=4;
arr[1][1]=5;
arr[1][2]=6;
arr[2][0]=7;
arr[2][1]=8;
arr[2][2]=9;
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-12-2048.jpg)
![class Testarray3{
public static void main(String args[]){
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}};
//printing 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}} 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-13-2048.jpg)
![int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7} };
int x = myNumbers[1][2];
System.out.println(x); // Outputs 7
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-14-2048.jpg)
![class Testarray5{
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating two matrices
int a[][]={{1,3,4},{3,4,5}};
int b[][]={{1,3,4},{3,4,5}};
//creating another matrix to store the sum of two matrices
int c[][]=new int[2][3];
//adding and printing addition of 2 matrices
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
System.out.print(c[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();//new line
}
}}
15
addition of two matrices in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-15-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner;
class ExString
{
public static void main(String ar[])
{
int[] a=new int[2];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the elements");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Print the elements");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-16-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner;
class ExString
{
public static void main(String ar[])
{
int[][] a=new int[2][2];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the elements");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
a[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Print the elements");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-17-2048.jpg)
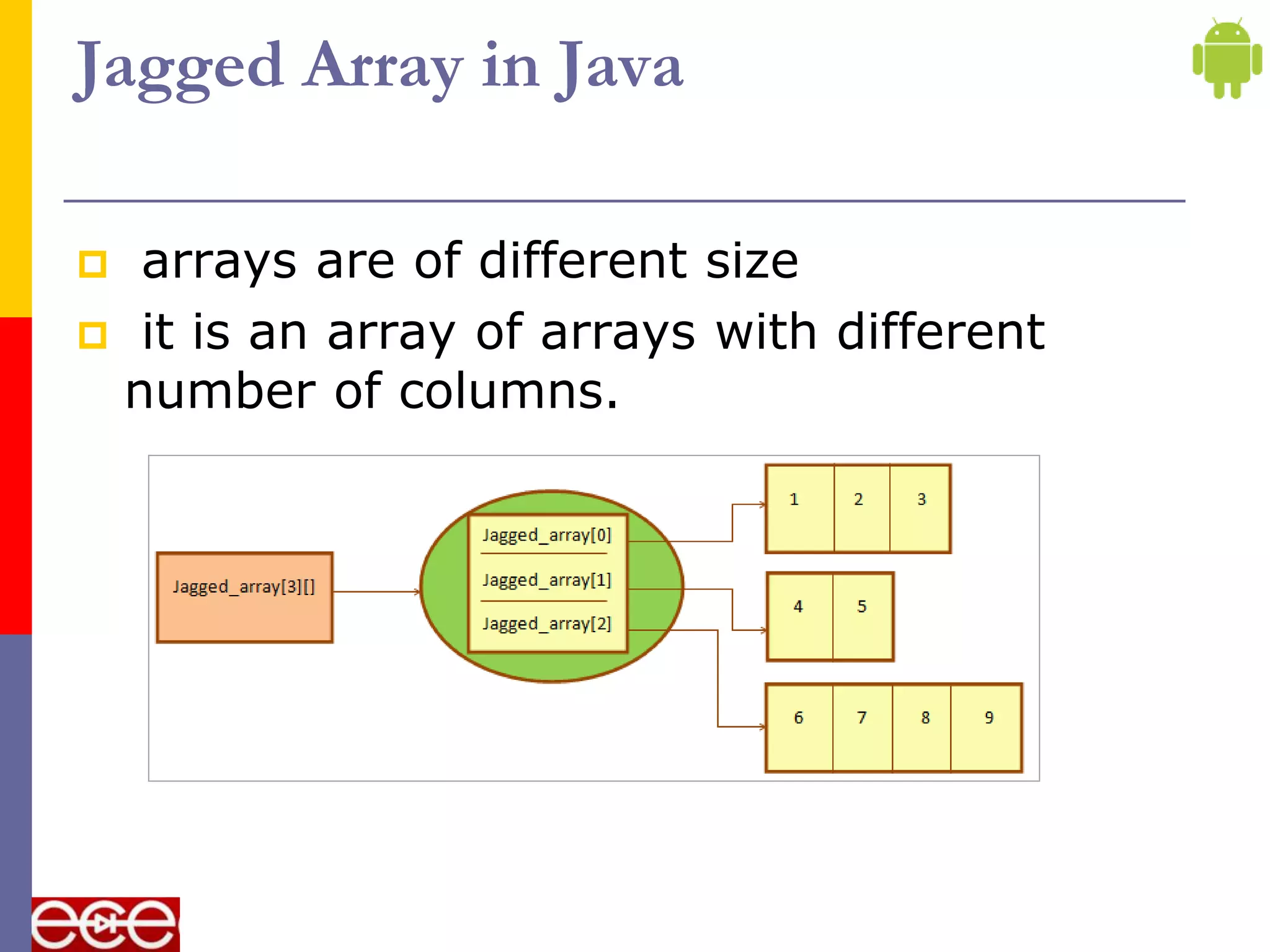
![Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declare a 2-D array with 3 rows
int myarray[][] = new int[3][];
// define and initialize jagged array
myarray[0] = new int[]{1,2,3};
myarray[1] = new int[]{4,5};
myarray[2] = new int[]{6,7,8,9,10};
// display the jagged array
System.out.println("Two dimensional Jagged Array:");
for (int i=0; i<myarray.length; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<myarray[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(myarray[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-19-2048.jpg)
![declaring a 2D array with different
columns
int arr[][] = new int[3][];
arr[0] = new int[3];
arr[1] = new int[4];
arr[2] = new int[2];
int myarray[][] = new int[][]{
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
new int[] { 4, 5, 6, 7 };
new int[] { 8, 9 };
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-20-2048.jpg)
![//initializing a jagged array
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++)
arr[i][j] = count++;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-21-2048.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
class JavaTester {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("Hello");
System.out.print("World");
}
}
23
Output
HelloWorld](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-23-2048.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
class JavaTester {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("World");
}
}
24
Output
Hello
World](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-210616083401/75/Array-24-2048.jpg)