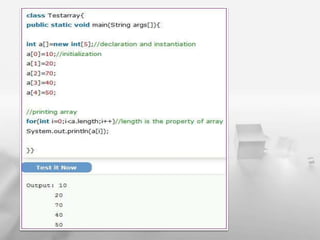
An array is a container that holds a fixed number of values of the same type. An array's length is determined when it is created and cannot be changed. The document then provides an example of creating an integer array called "scores" with 4 elements to store the scores of 4 cricket teams. It demonstrates accessing the elements of the array using indexes and printing the team scores.



![Ex:
class PrintTeamScores
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int[] scores = new int[4]; // LINE A - Creating the scores array.
scores[0] = 200; // assigning score for team 0 or India
scores[1] = 190; // assigning score for team 1 or Pakistan
scores[2] = 210; // assigning score for team 2 or Australia
scores[3] = 195; // assigning score for team 3 or Sri Lanka
System.out.println("India = " + scores[0]);
System.out.println("Pak = " + scores[1]);
System.out.println("Aus = " + scores[2]);
System.out.println("Sri Lanka = " + scores[3]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-4-320.jpg)
![One-Dimensional Array
A List of items can be given one variable name using only one
Subscript and such variable is called One-Dimensional Array.
The Subscript always begin with number 0
i.e., x[ 0 ].
We Create variable size as
int num [ ] = new int [ 12 ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-5-320.jpg)

![Array Declartion
Array in java Declared in Two Forms
Form 1: type arrayname[ ];
Ex:
Form 2: type[ ]arrayname;
Ex:
Int number[ ];
Int average[ ];
Int [ ] counter;
Int[ ] marks;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-7-320.jpg)
![Creation of Memory Allocation
Java allows us to create arrays using new operator only.
arrayname = new type[ size ];
Ex:
int number = new int [ 12 ];
float average = new float[ 5 ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-8-320.jpg)
![Initialization of Arrays.
Assigning the values into Arrays. This is
known as Initialization.
This is done using Array SubScripts.
arrayname[ SubScripts ] = value;
Ex:
number[ 0 ] = 46;
number[ 1 ] = 44;
number[ 2 ] = 37;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-9-320.jpg)
![ Array Initializer is a list of values seperated by Comas and
Surrounded by Curly braces.
No size is given.
Ex: int number[ ]= {10,20,30,40};
It is also possible to assign an array object to another.
Ex: int a[ ]={10,20,30};
int b[ ];
b=a;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-10-320.jpg)
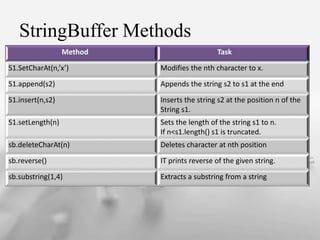
![Strings
Character array:
char charArray[ ]= new char[ 2 ];
charArray[ 0 ]=‘H’;
charArray[ 1 ]=‘I’;
Java Strings are more reliable and predictable
This is bascially due to C’s lack of bounds checking
Java String is not Character Array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-12-320.jpg)

![Immutable String
string objects are immutable. Immutable simply means unmodifiable or
unchangeable.
Once string object is created its data or state can't be changed but a new
string object is created.
class Testimmutablestring
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s="Sachin";
s.concat(" Tendulkar");//concat() method appends the string at the end
System.out.println(s);//will print Sachin because strings are immutable objects
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-14-320.jpg)
![ There are multiple ways to initialize a String Array.
Initialization can also be done at the same time as the declaration.
String[ ] StrArray = {"AAA", "BBB", "CCC", "DDD", "EEE"};
This will create a String Array of length 5. Element at index 0 will
have the value "AAA", element at index 1 will have the value
"BBB", and so on.
String[] StrArray = {"AAA", "BBB", "CCC", "DDD", "EEE"};
System.out.println(StrArray[0] );
System.out.println(StrArray[1] );
System.out.println( StrArray[2] );
System.out.println( StrArray[3] );
System.out.println( StrArray[4] );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-15-320.jpg)
![ We can also create and use arrays that contain strings.
String[] StrArray = new String[4];
The statement will create an StringArray of size 5 to hold 5
string constants.
private void StringArray()
{
StrArray [0] = “Jack”;;
StrArray [1] = “Mayn”;
StrArray[2] = “Aryan”;
StrArray[3] = “Arav”;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-160316104529/85/Arrays-in-java-16-320.jpg)