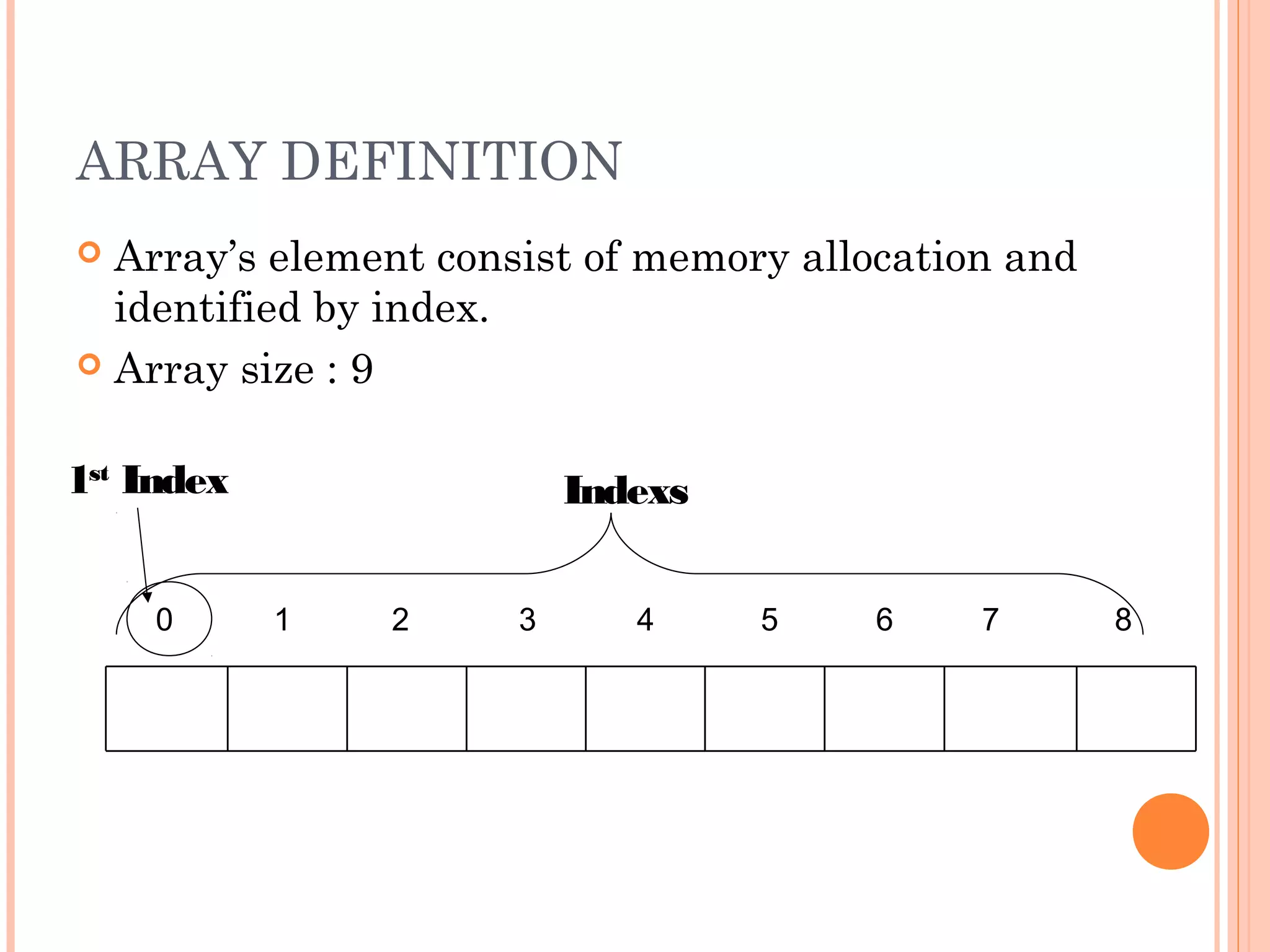
The document discusses arrays in C++. It explains one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays, how to declare, initialize, and access elements of arrays. Key points include arrays storing a collection of like-typed data, being indexed starting from 0, initializing during declaration, and accessing two-dimensional array elements requiring row and column indices. Examples are provided to demonstrate array concepts.




![DECLARING ONE DIMENSIONAL
ARRAY
Will have a single row and can have any number
of columns.
Will have only one subscript. Subscript refers to
the dimension of the array.
Array declaration of 10 alphabet
type array_name[size]
Eg : char huruf[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-7-2048.jpg)
![INITIALIZING ONE DIMENSIONAL
ARRAY
Initialization is the process of assigning values to
the array you have created.
To assign initial values to each one of array’s
elements we must enclose the values in curly
braces ({ }) and separate them with comma (,).
Eg : char huruf[5] = {‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-8-2048.jpg)
![INITIALIZING ONE DIMENSIONAL
ARRAY
Eg: int nombor[3] = {3, 24, 31};
first index 0 1 2
nombor 3 24 31
nombor[0];//3
nombor[1];//24
nombor[2];//31
nombor[0+1];//nombor[1];//24
nombor[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-9-2048.jpg)
![ACCESSING ELEMENT OF ONE
DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Element is accessed by its index
Array index refers to the location of the values in an
array.
The first element will always have the array index as
0.
Syntax :
<Variable name>[Array index] = Value;
For example:
marks[0]=95;
marks[1]=85;
marks[2]=75;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-10-2048.jpg)
![ACCESSING ELEMENT OF ONE
DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Eg:
int my_array[5] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
to store the value 75 in the third element
of my_array, we could write the following
statement:
my_array[2] = 75;
to pass the value in 4th element of my_array and
store the value into temporary variable,
temp_value:
int temp_value = my_array[3]; // also
equals to 44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-11-2048.jpg)
![ACCESSING ELEMENT OF ONE
DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
if the name of an array is name, then name[0] is
the name of the element that is in position 0,
name[1] is the name of the element that is in
position 1, etc.
in general, the nth element is in position n-1. So
if the array has n elements, their names are
name[0], name[1], name[2], …, name[n-
1].
it is important to be able to clearly distinguish
between the two uses that brackets [ ] have
related to arrays:
int name[5]; // declaration of a new array
name[2] = 75; // access to an element of the
array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-12-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{ marks[0] : 95
int marks[]={95,85,75,80,65}; marks[1] : 85
cout<<"marks[0] : "<<marks[0]; marks[2] : 75
marks[3] : 80
cout<<"nmarks[1] : "<<marks[1];
marks[4] : 65
cout<<"nmarks[2] : "<<marks[2];
cout<<"nmarks[3] : "<<marks[3];
cout<<"nmarks[4] : "<<marks[4];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-14-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int y[4]={8,7,6,4};
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
cout<<y[i]<<"n";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-16-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
char stud_name[]={‘M',‘A',‘F','I','A'};
for(int i=0;i<=4;i++)
{
cout<<stud_name[i];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-18-2048.jpg)
![ENTERING DATA INTO AN ARRAY
When more number of values are to be stored
in an array, a for loop can be used.
The sample code shows how to use a for loop
in an array.
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<“Enter the marks: ";
cin>>marks[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-19-2048.jpg)
![READING DATA FROM AN ARRAY
You can use a for loop with a single cout
statement to print the values from an array.
for (int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<"Marks : "+marks[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-20-2048.jpg)

![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int marks[5];
//Accepting the marks
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout<<"Enter mark :";
cin>>marks[i];
}
cout<<"nThe marks you have enter is"<<endl;
//Displaying the array
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout<<"Marks:"<<marks[i]<<endl;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-22-2048.jpg)


![ Declare an array alpha of 15 elements of type
int.
int alpha [15];
Access the value of tenth element of array alpha.
alpha [9];
Set the value of fifth element of array alpha to
35.
alpha [4] = 35;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-25-2048.jpg)
![ Set the value of ninth element of array alpha to
the sum of fifth and sixth element of array
alpha.
alpha [8] = alpha [4] + alpha [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-26-2048.jpg)
![ What is the output
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
double num []= {2.0, 4.0, 6.5, 8.7};
cout<<num[1+2];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-27-2048.jpg)

![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int num[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
cout << num[i]<< "n";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-29-2048.jpg)

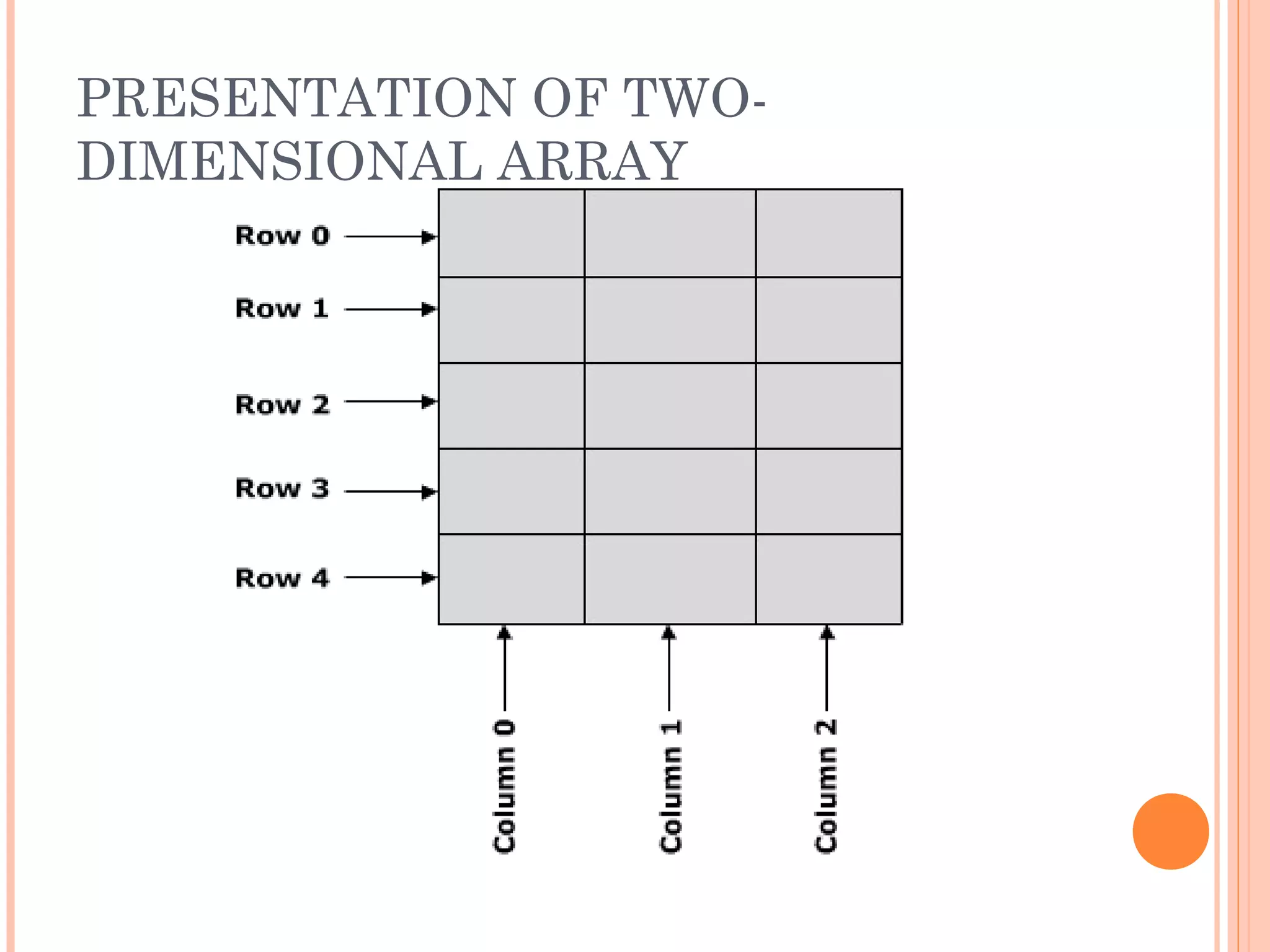
![Example
int marks_table [5][3];
Syntax
<Data type> <Variable name> [Row][Column];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-33-2048.jpg)
![TWO-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Table jimmy represents a bidimensional array of
3 by 5 elements of type int.
The way to declare this array in C++ would be:
int jimmy [3][5];
column
row](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-34-2048.jpg)
![INITIALIZING TWO-DIMENSIONAL
ARRAY
Eg:
int array1[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
Output:
123
456
int array2[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Output:
123
450
int array3[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { { 1, 2 }, { 4 } };
Output:
120
400](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-35-2048.jpg)
![ACCESSING ELEMENT IN TWO-
DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
Element is accessed by the index of its row and
column.
Eg:
Toaccess the element in the 2nd row and at the 4th
column of this two-dimentional array, we can used
the following code:
jimmy[1][3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-36-2048.jpg)
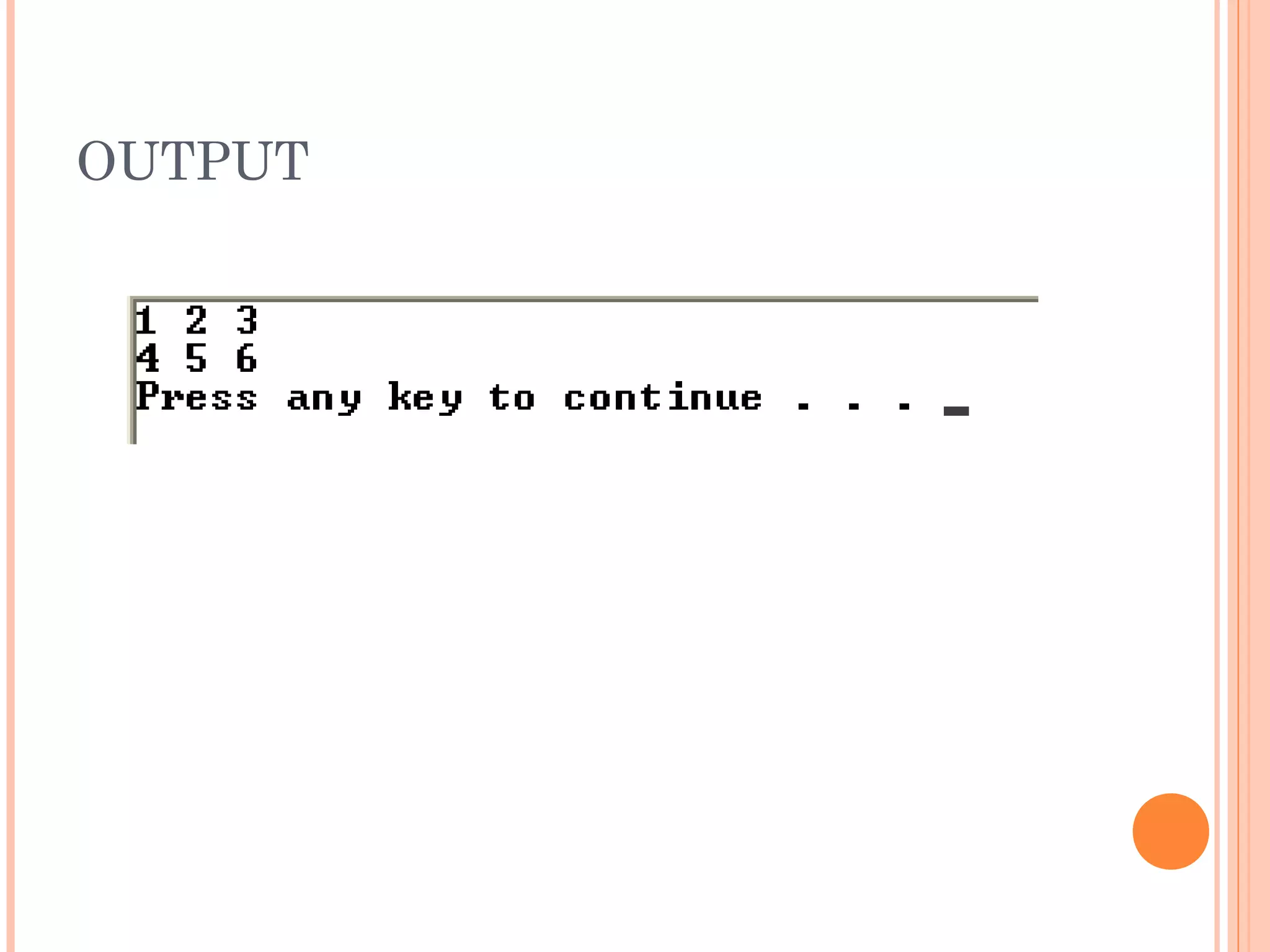
![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int array2[ 2 ][ 3 ] = {{ 1, 2, 3} ,{4, 5,6 }};
for(int index1=0;index1<2;index1++)
{
for(int index2=0;index2<3;index2++)
cout<<array2[index1][index2] << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-37-2048.jpg)
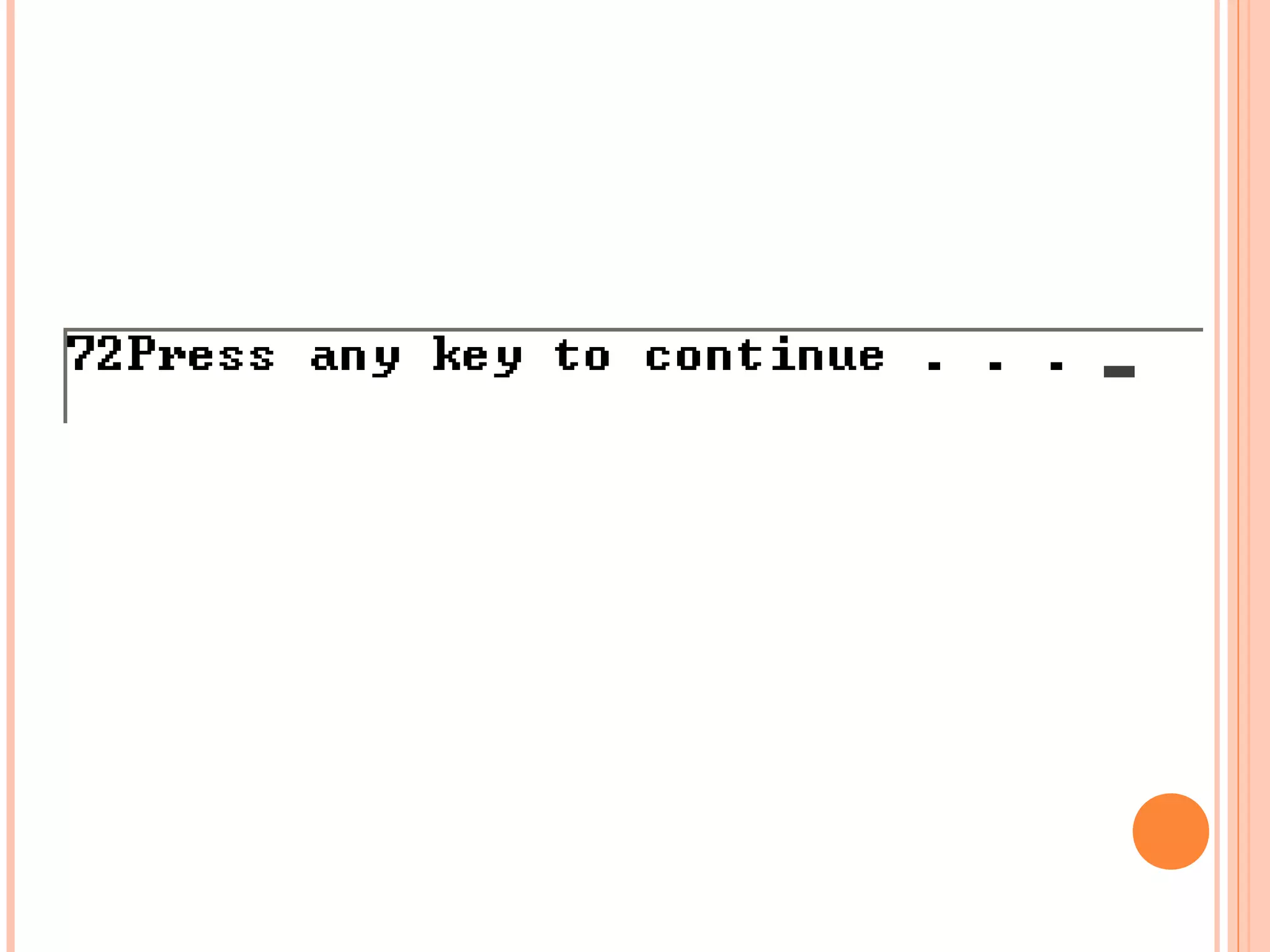
![WHAT IS OUTPUT?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
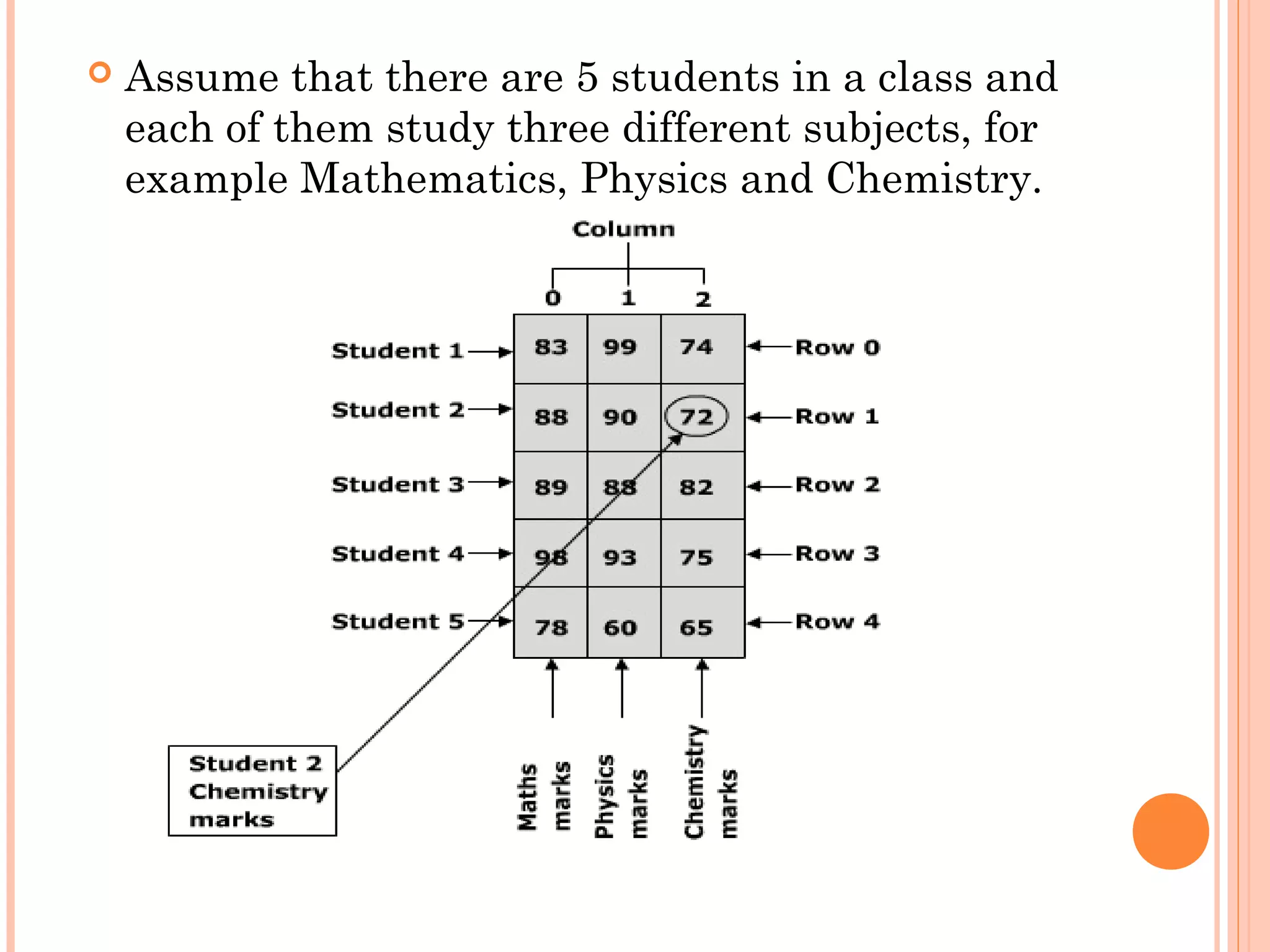
int marks_table[5][3] = {{83,99,74},
{88,90,72},{89,88,82},
{98,93,75},{78,60,65}};
cout<<marks_table[1][2];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-39-2048.jpg)
![#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
string Data [2][3];
//For first fow
Data[0][0] = "Lisa"; //lastname
Data[0][1] = "Sulaiman"; //firstname
Data[0][2] = "Kedah"; //location
//Second row
Data[1][0] = "Ali"; //lastname
Data[1][1] = "Muhammad"; //firstname
Data[1][2] = "Johor"; //location
cout<<"LastnametFirstnametLocationn";
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cout<<Data[i][j]<<"tt";
}
cout<<"n";//move to new line
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-41-2048.jpg)
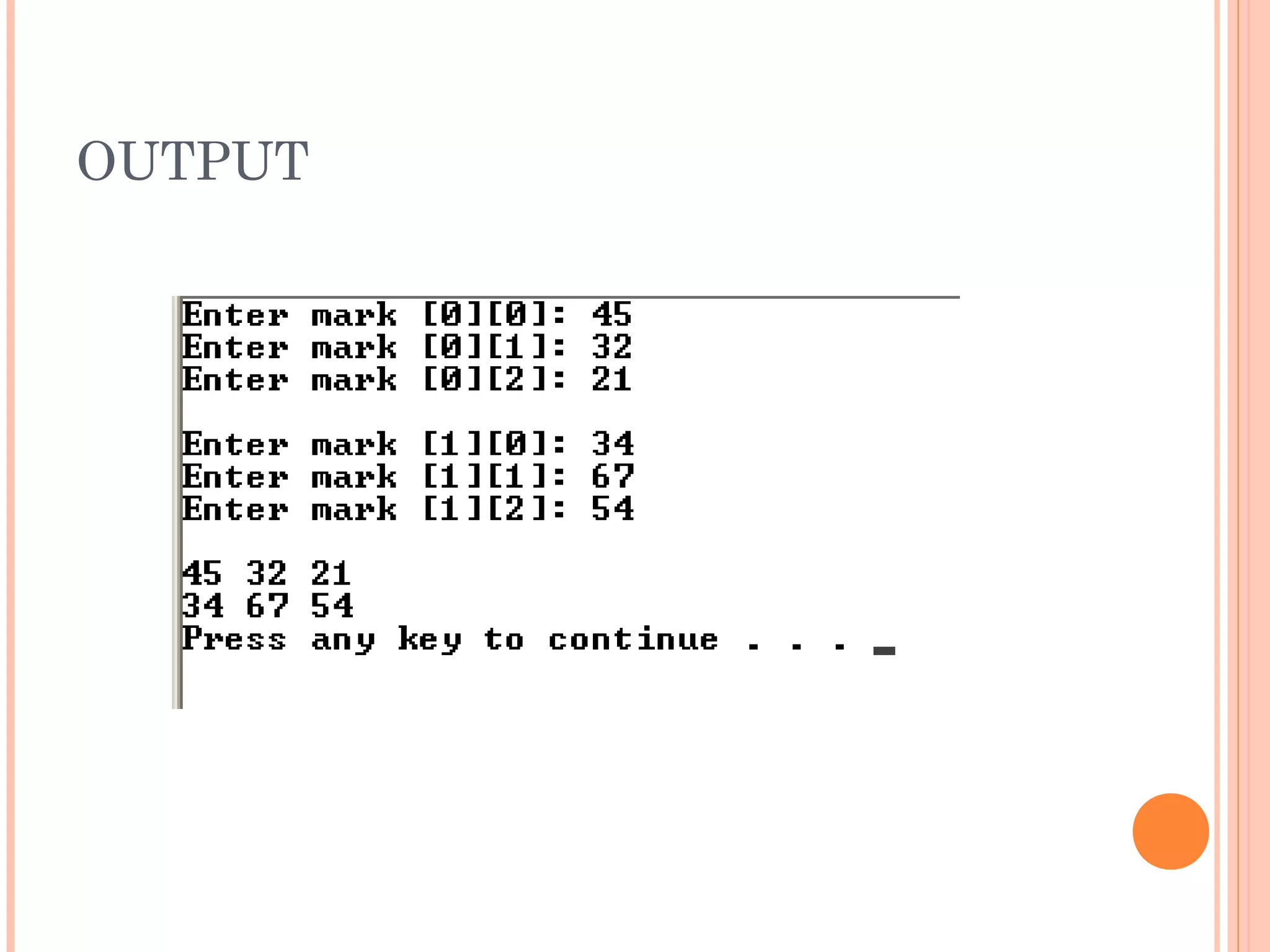
![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int array2[ 23 ][ 4 ];
//Accepting the marks
for (int row=0; row<2; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<3; col++){
cout<<"Enter mark ["<<(row)<<"][" <<col <<"]: ";
cin>>array2[row][col];
}
cout<<endl;
}
//display
for(int row=0; row<2; row++){
for(int col=0; col<3; col++)
cout<<array2[row][col] << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-42-2048.jpg)
![IN CLASS EXERCISE 4.2
Declare an array beta of 10 rows and 20 columns
of type int.
Examine the following:
double values[ ] [ ] = {
{1.2, 9.0, 3.2},
{9.2, 0.5, 1.5},
{7.3, 7.9, 4.8} } ;
What is the value of values[2][1]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-44-2048.jpg)
![ Which of the following statements constructs
an array with 5 rows of 7 columns?
long stuff[5][7];
long[5][7];
long stuff[7][5];
long [7][5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-45-2048.jpg)
![ Declare an array beta of 10 rows and 20 columns
of type int.
int beta [10][20]
o Value of values[2][1]? 7.9
o long stuff[5][7];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fp201unit4-121113061922-phpapp02/75/Fp201-unit4-46-2048.jpg)
