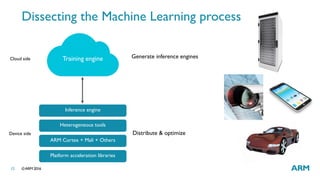
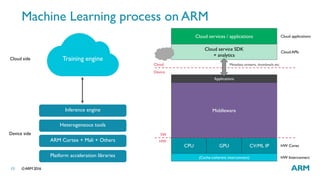
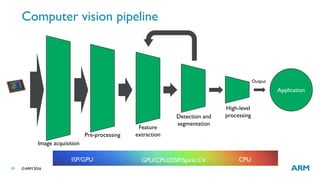
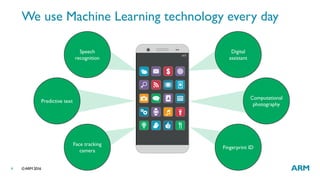
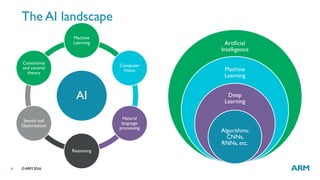
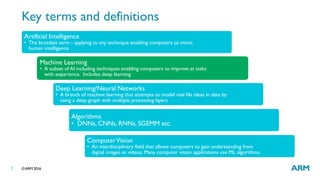
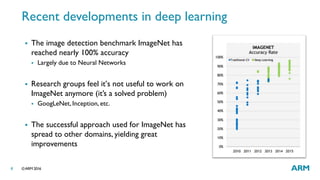
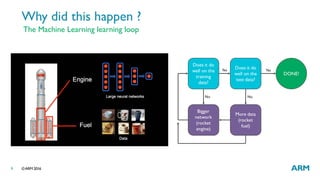
The document provides an overview of machine learning, highlighting its applications in areas such as speech recognition, image recognition, and computer vision. It explains key concepts such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and their interconnections, while discussing recent advancements and applications of these technologies. Additionally, it emphasizes the growing importance of machine learning in driving demand for advanced ARM processors and architectures.




![©ARM 201610
Basic neural network
[Inputs] [Output]
w2
w1
w3
wn
wn-1
y
)(
1
zHy
xwz
n
i
ii
=
= ∑=
x1
x2
x3
xn-1
xn
Squashing function
Sigmoid: y=1/(1+e^(-z))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningforarm-poweredclients-dec2016-170302172556/85/ARM-and-Machine-Learning-10-320.jpg)