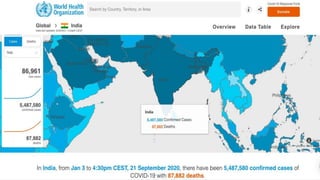
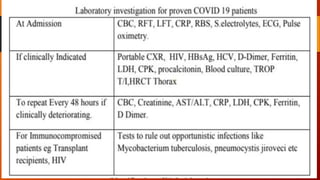
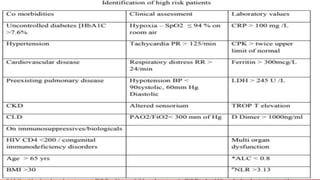
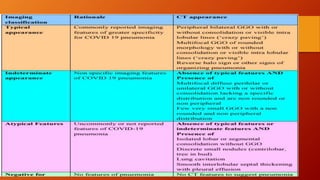
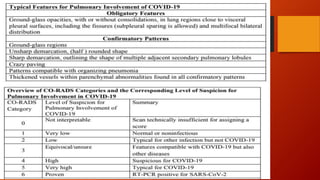
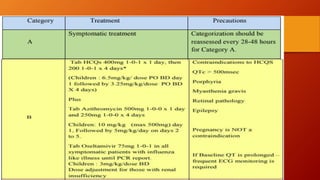
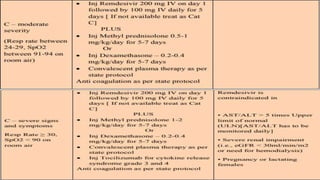
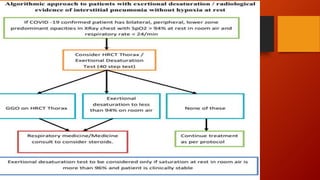
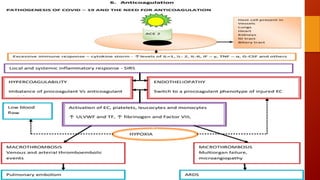
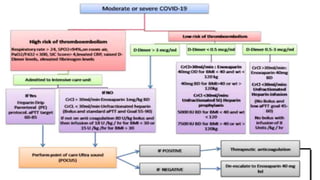
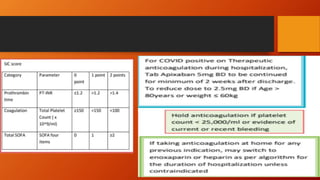
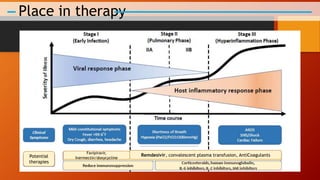
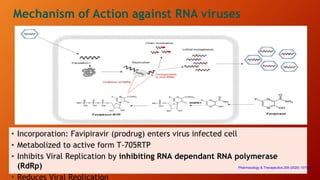
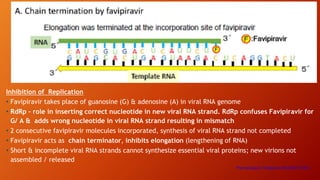
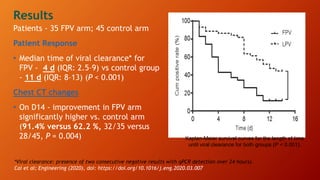
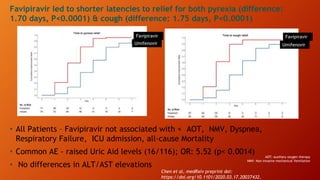
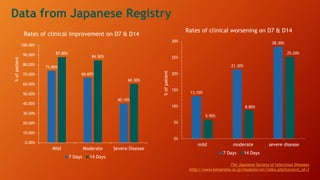
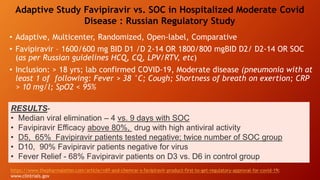
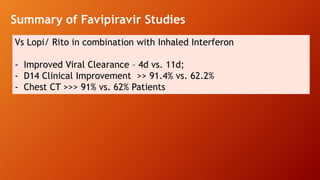
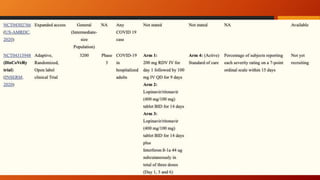
Favipiravir is an antiviral drug being studied for the treatment of COVID-19. The document summarizes several studies on favipiravir including: a randomized controlled trial from China finding favipiravir led to faster viral clearance and improved chest imaging outcomes compared to lopinavir/ritonavir; observational data from Japan showing clinical improvement in most patients, especially those with mild/moderate disease; and a Russian study demonstrating improved viral clearance and fever relief with favipiravir versus standard of care. The document also reviews favipiravir's mechanism of action, potential adverse effects, and prescribing guidelines.






























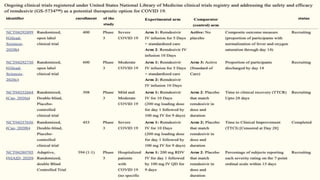

![Secondary outcome: (dexamethasone vs usual
care)
• Mechanically ventilated: 28-day mortality – significantly reduced in dexamethasone group
• Patients receiving O2: 28-day mortality – significantly reduced in dexamethasone group
• 21.5% vs 25% [Rate Ratio 0.80; 95% CI 0.70-0.92, p = 0.002]
• Patients not receiving respiratory support: no significant difference
• 17% vs 13.2% [Rate Ratio 1.22; 95% CI 0.93-1.61 p=0.14]
Dexamethasone was associated with a reduction in 28-day mortality among those symptoms for
>7 days but not among those with symptoms for <7 days (test for trend p<0.001)
• Length of hospital stay – significantly reduced in dexamethasone group
Composite secondary outcome of invasive mechanical ventilation and death –
significantly reduced in dexamethasone group
• Rate Ratio 0.91; 95% CI 0.82-1.00, p=0.049
• Use of ventilation – significantly reduced in dexamethasone group
• Rate Ratio 0.76; 95% CI 0.61-0.96, p=0.021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/covid19therapeutics-210126143240/85/Covid-19-therapeutics-56-320.jpg)