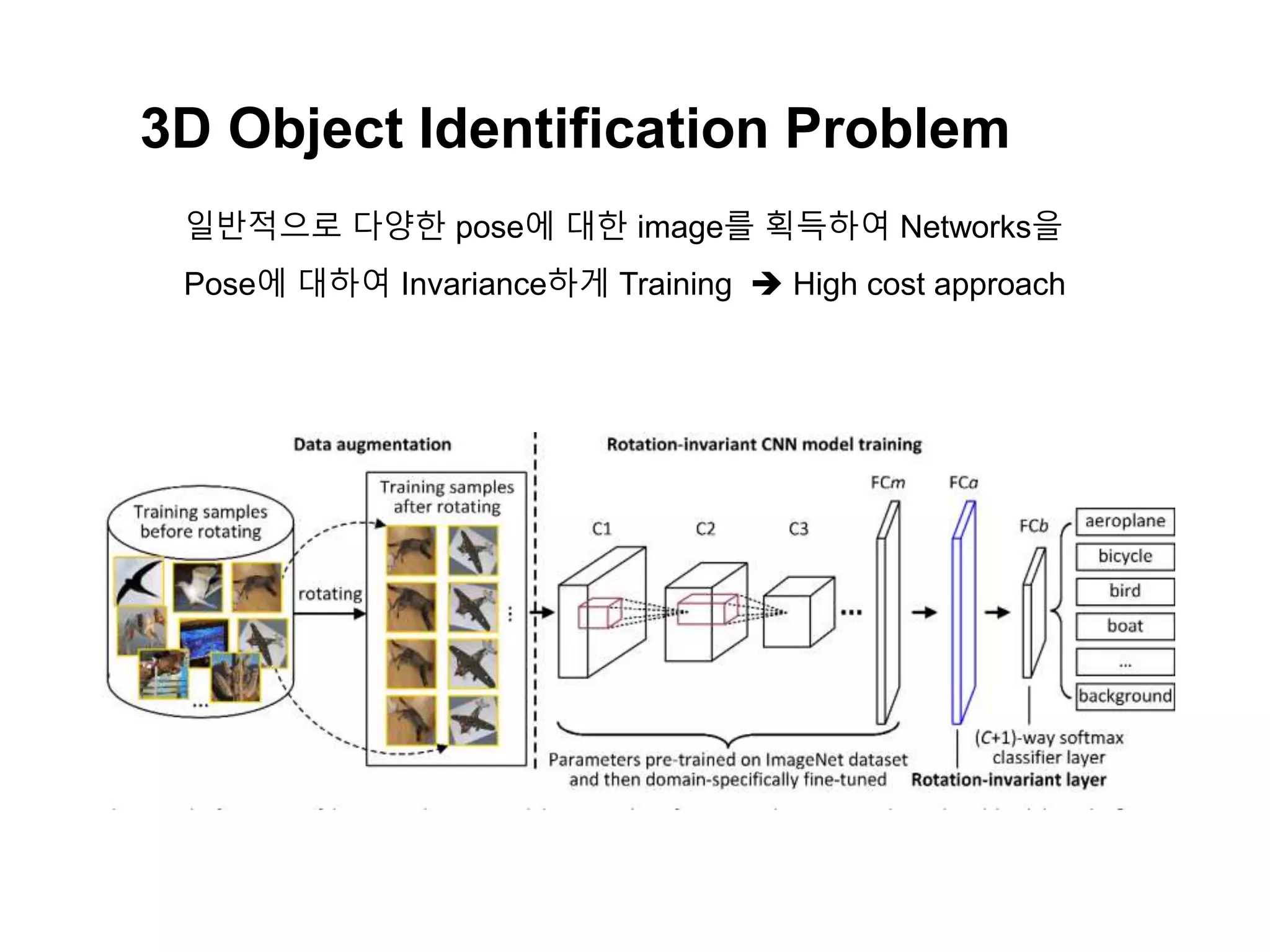
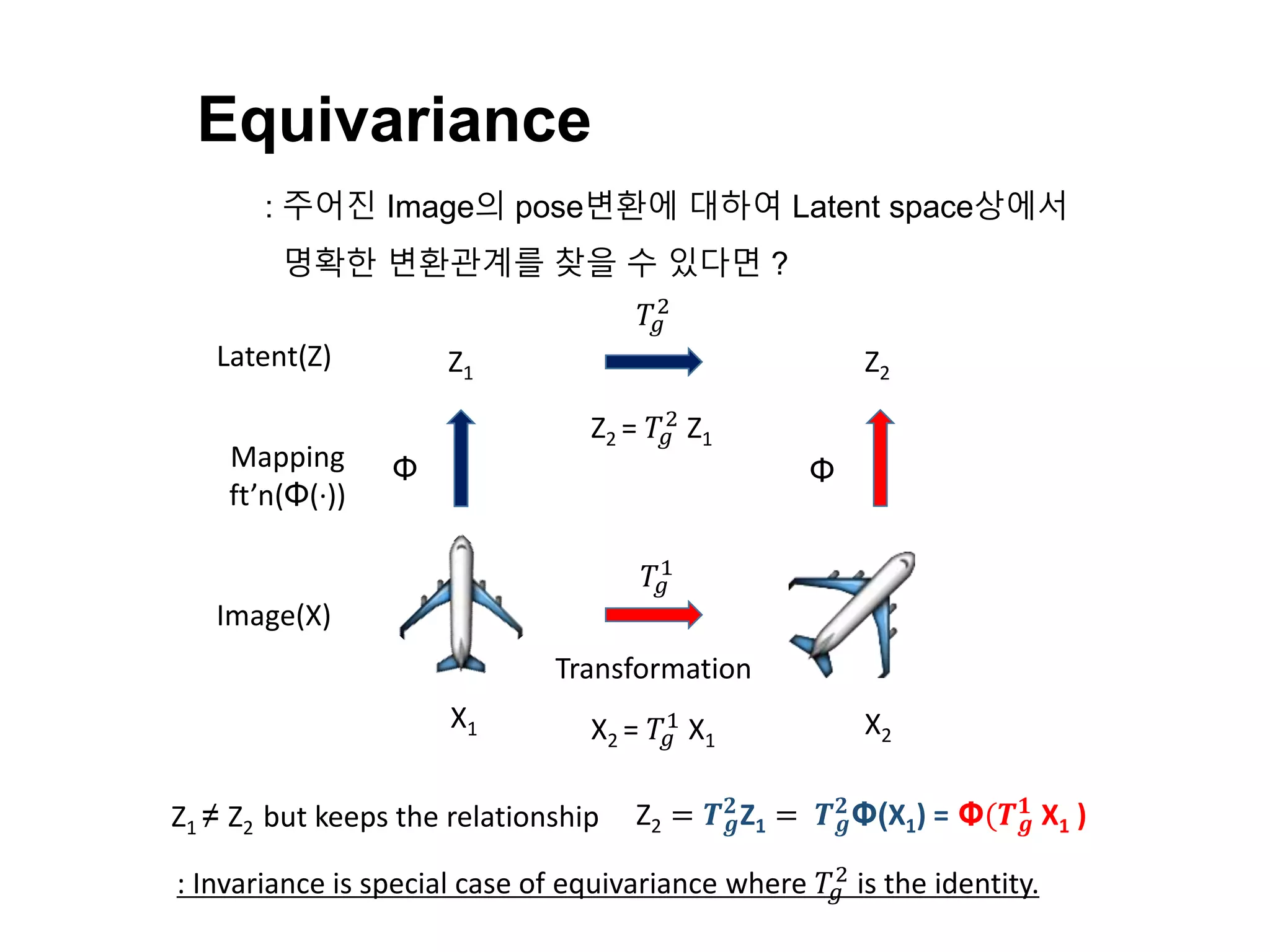
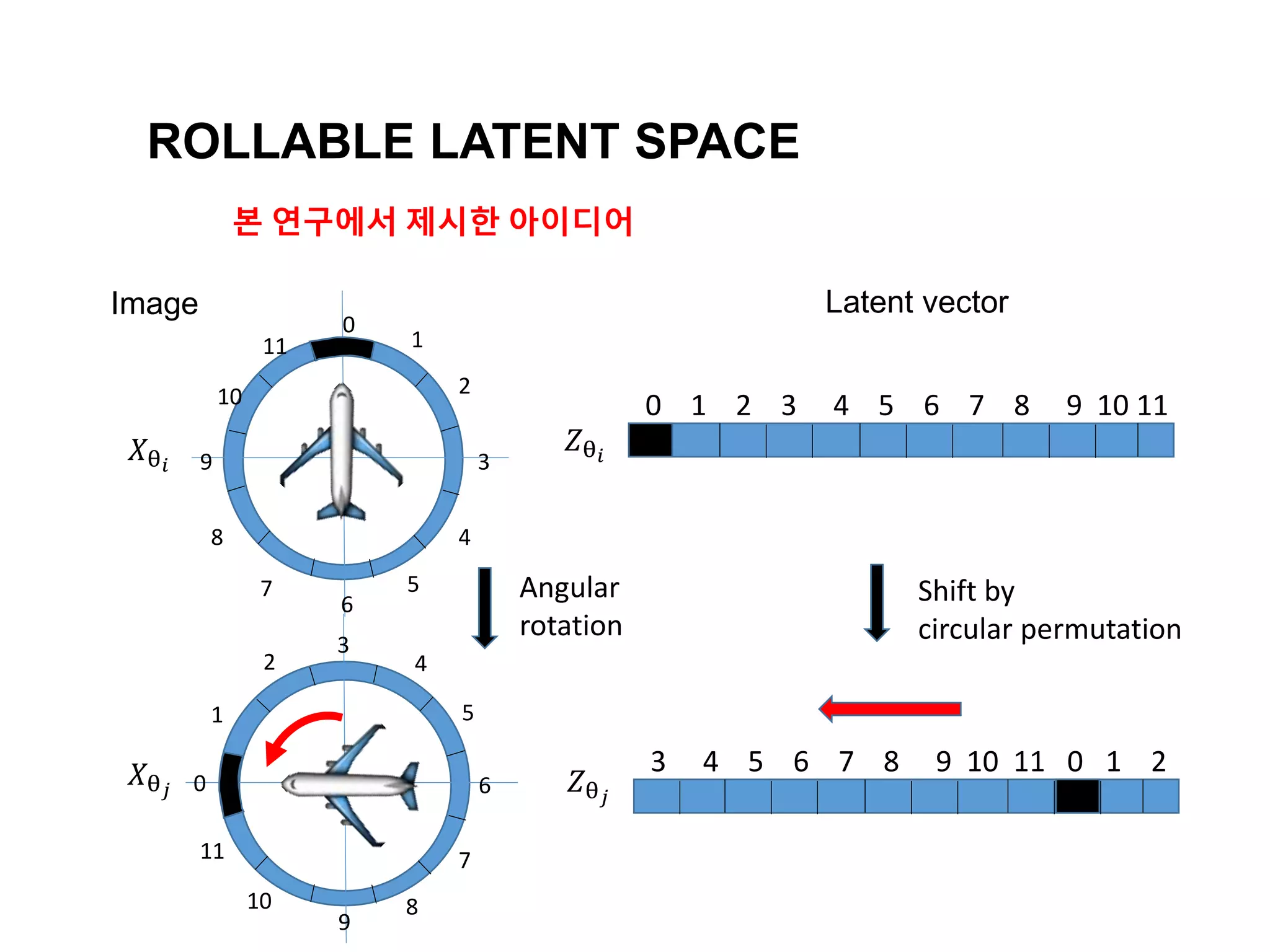
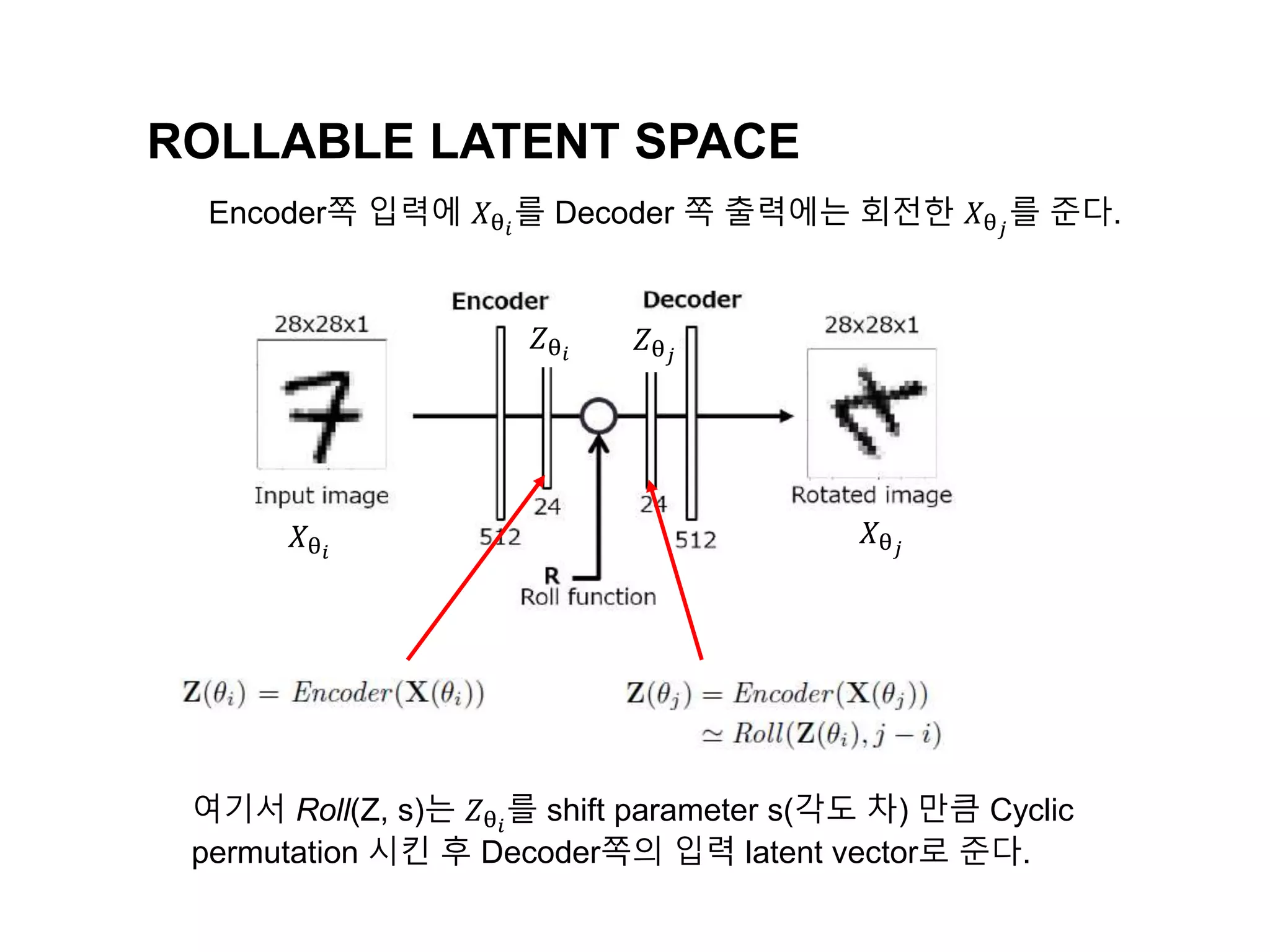
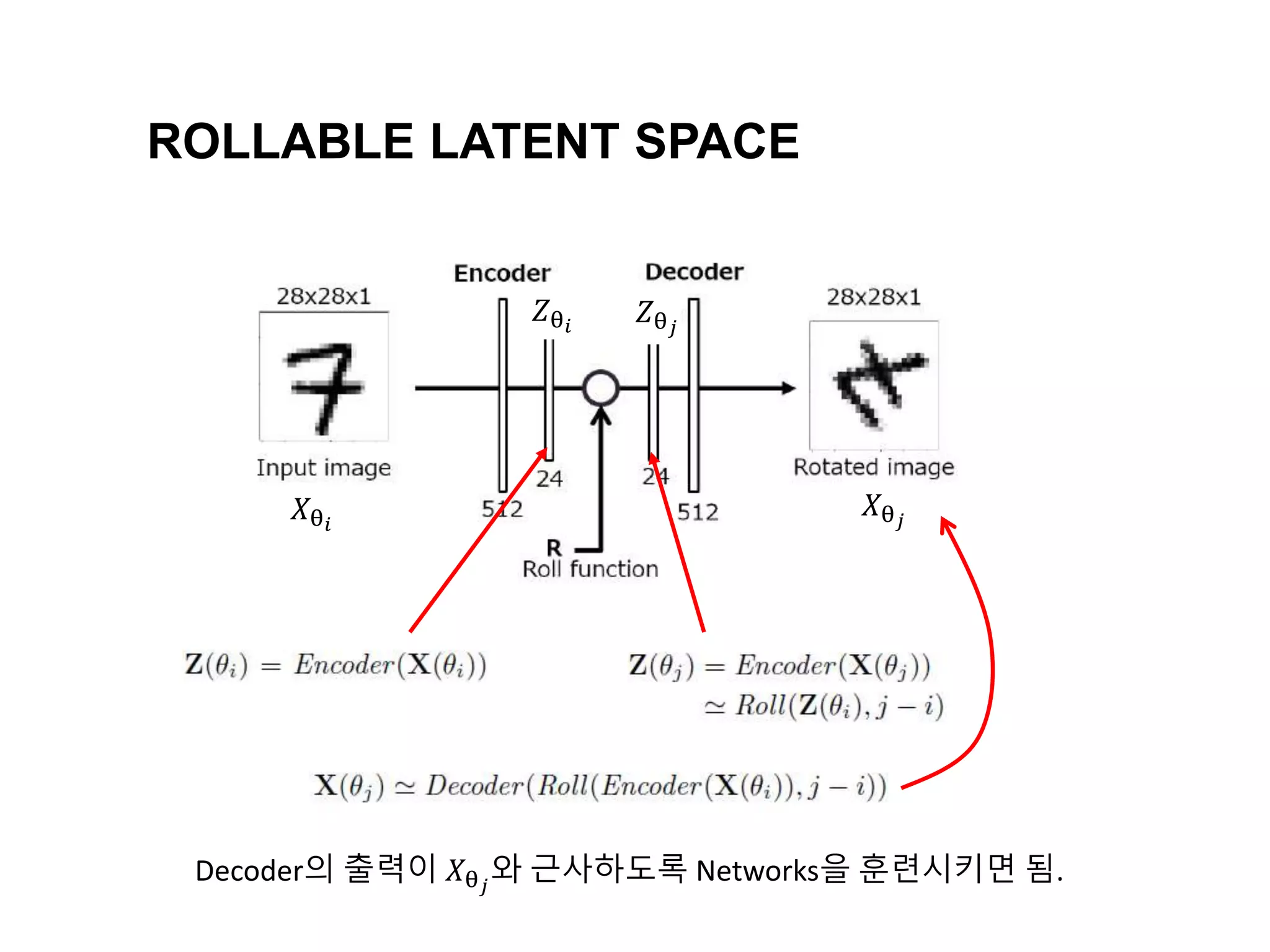
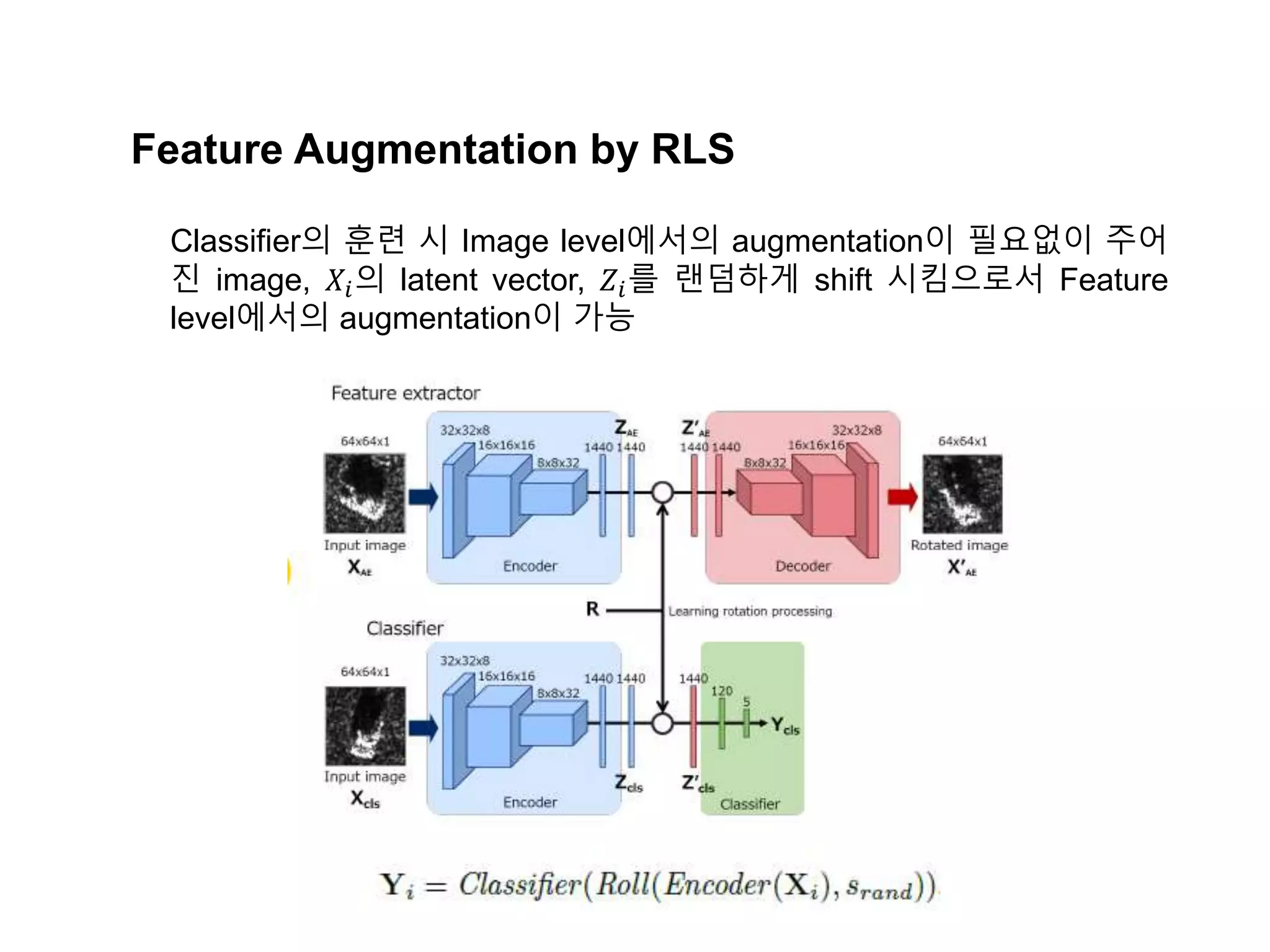
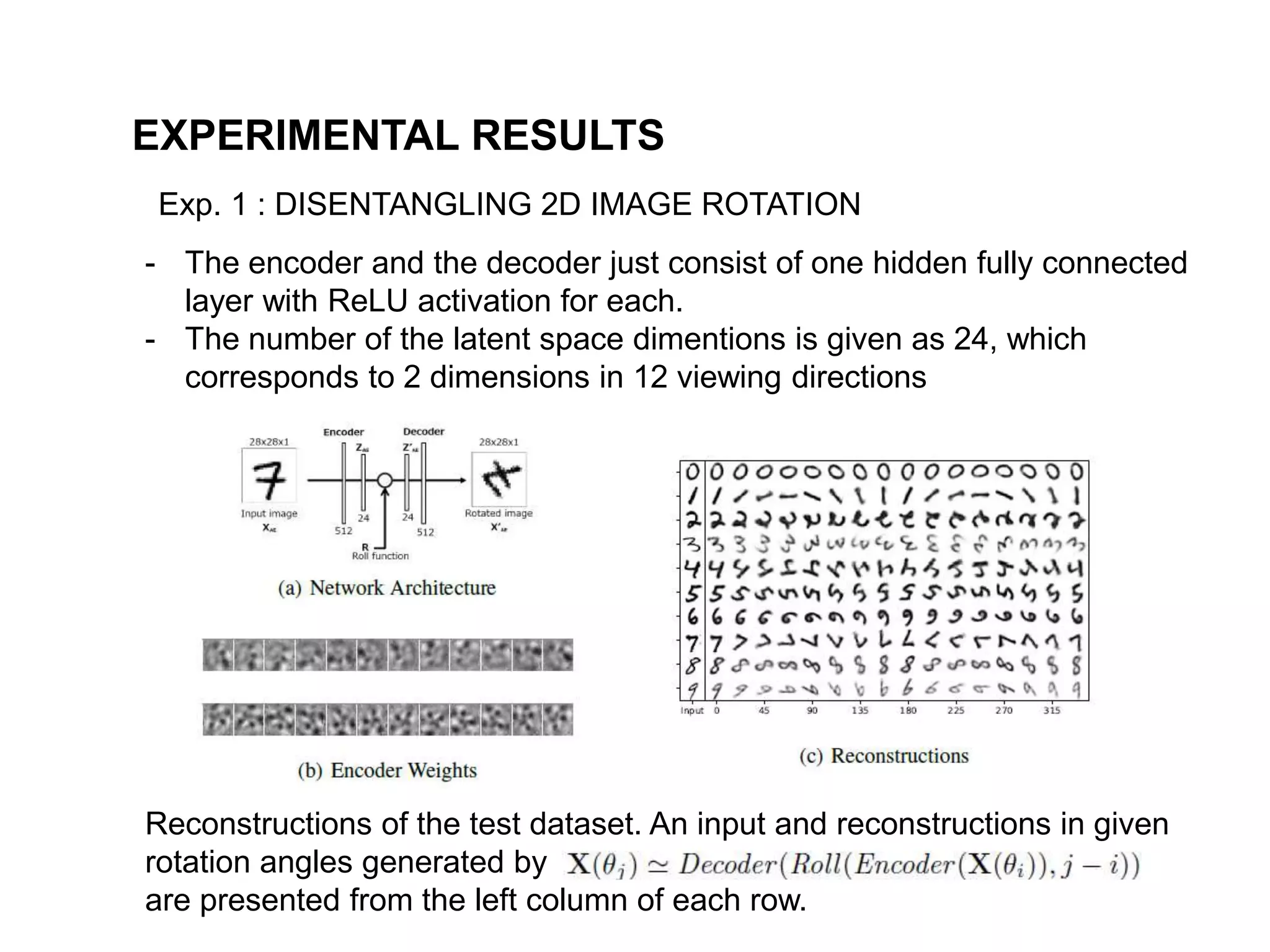
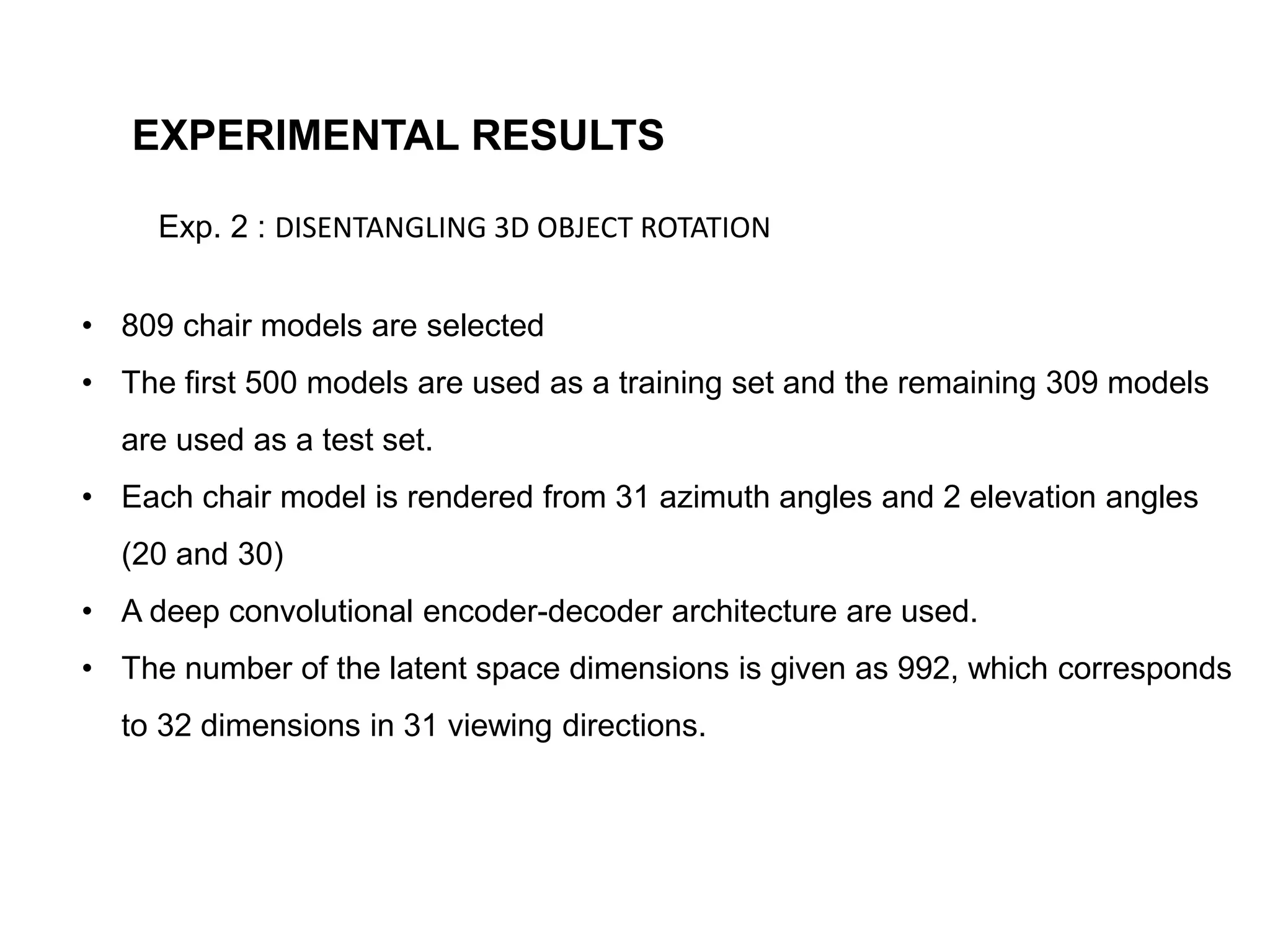
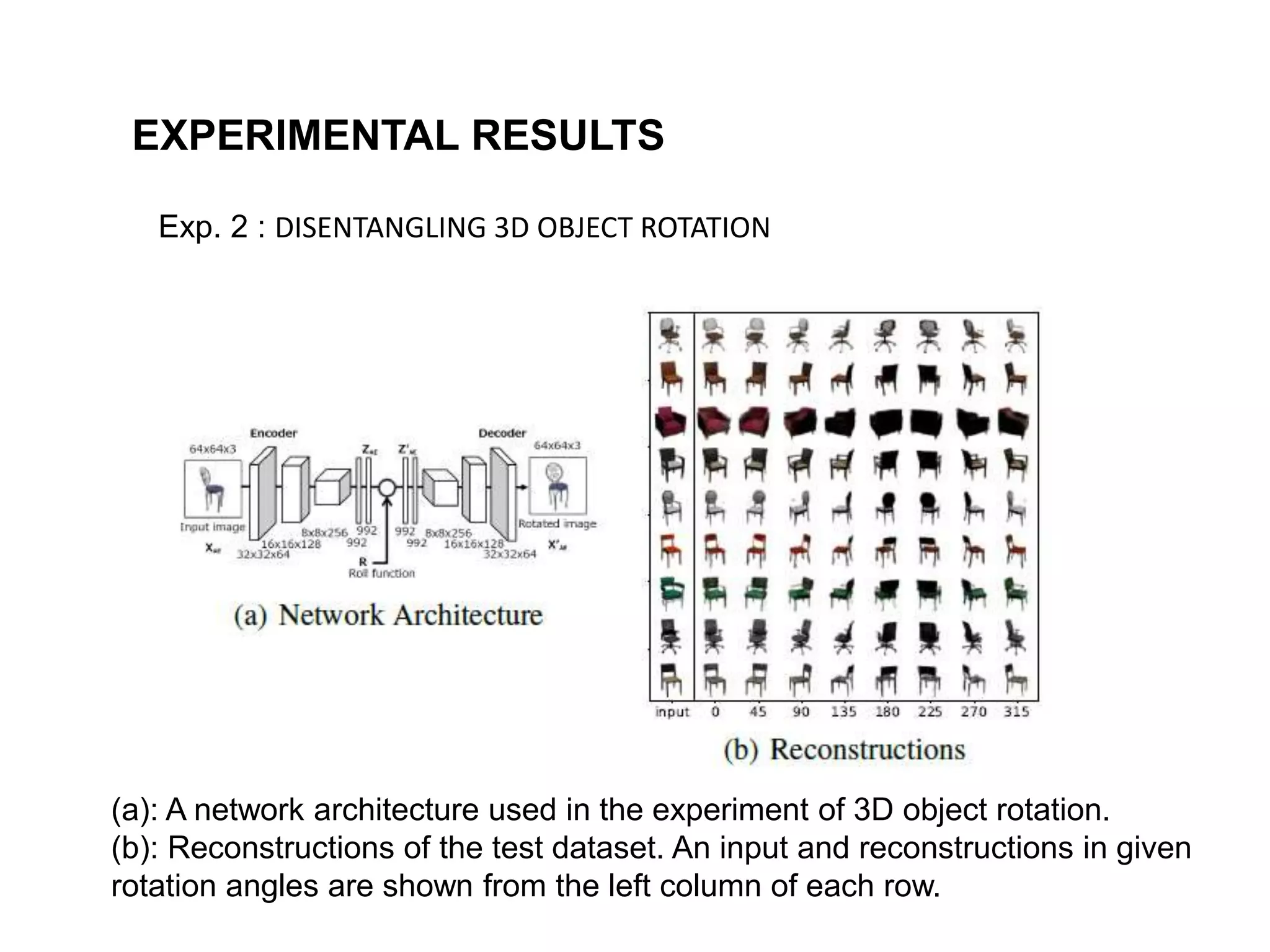
The document discusses a method for disentangling object identity from posture information using a rollable latent space approach, which enables the training of networks without high costs typically associated with acquiring various pose images. It presents a modified auto-encoder that maps angular rotations in the image space to shifts in the latent vector space, allowing for effective feature augmentation and the inference of latent vectors for untrained poses. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this method through 2D and 3D object rotation reconstructions.