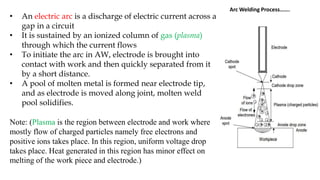
Arc welding is a process that joins metal by heating it with an electric arc between an electrode and the workpiece. The arc produces temperatures over 5500°C, melting the metals to form a weld. Most arc welding processes use a consumable electrode that doubles as the filler material. The arc is shielded by gases like argon or fluxes to prevent contamination of the weld. Arc welding finds applications in manufacturing industries like automotive and construction due to its ability to make strong, permanent joints in metals.