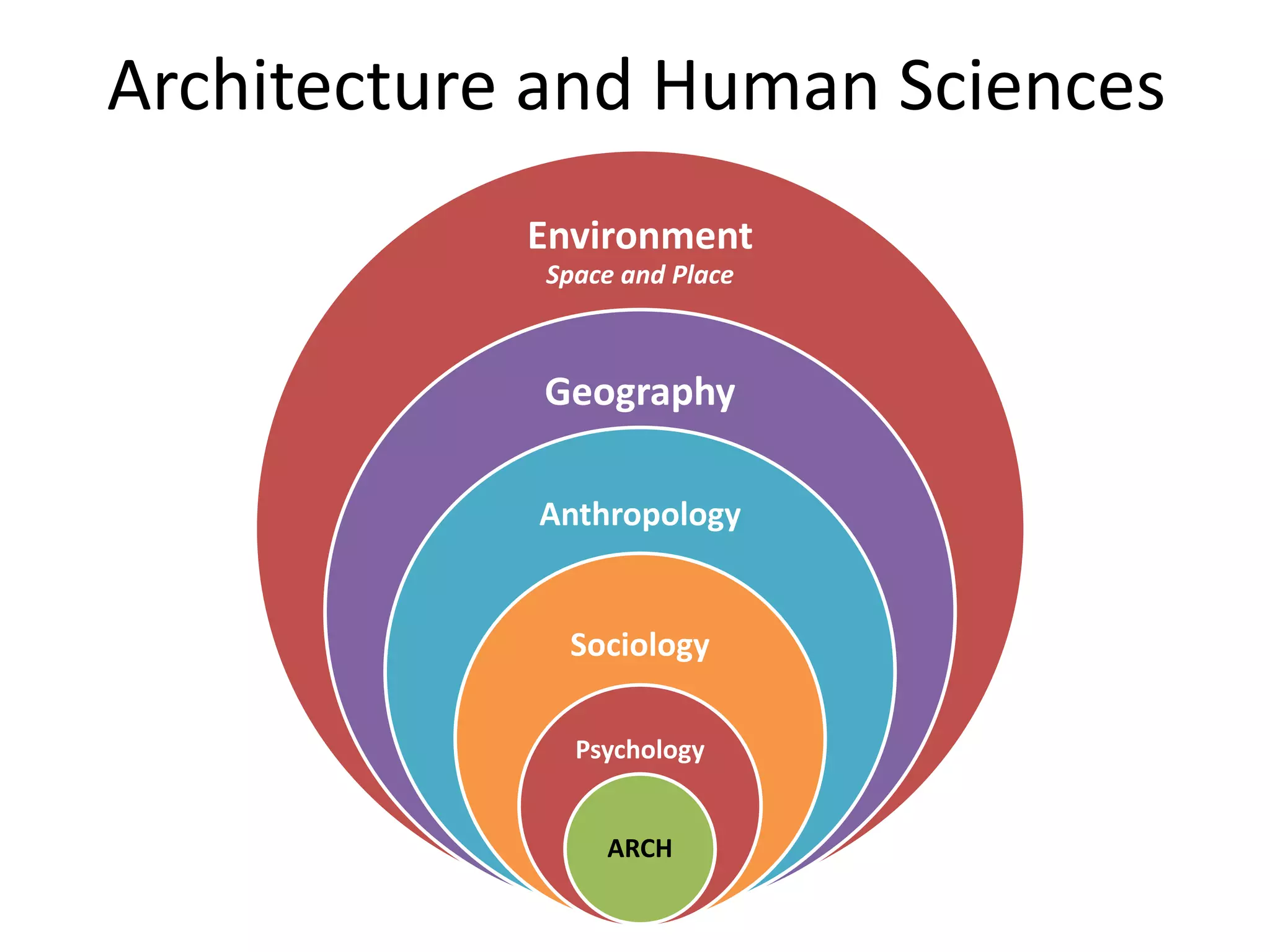
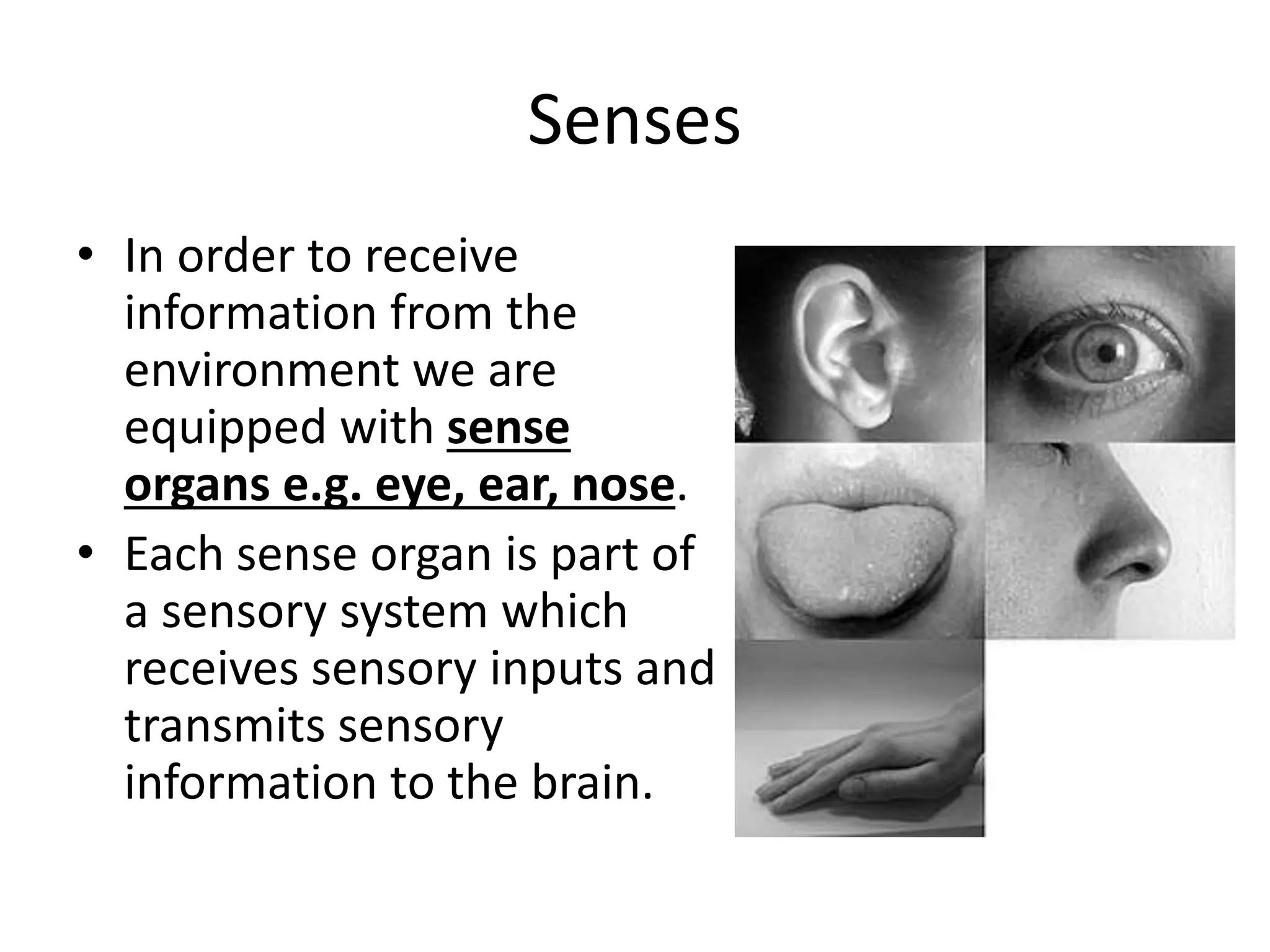
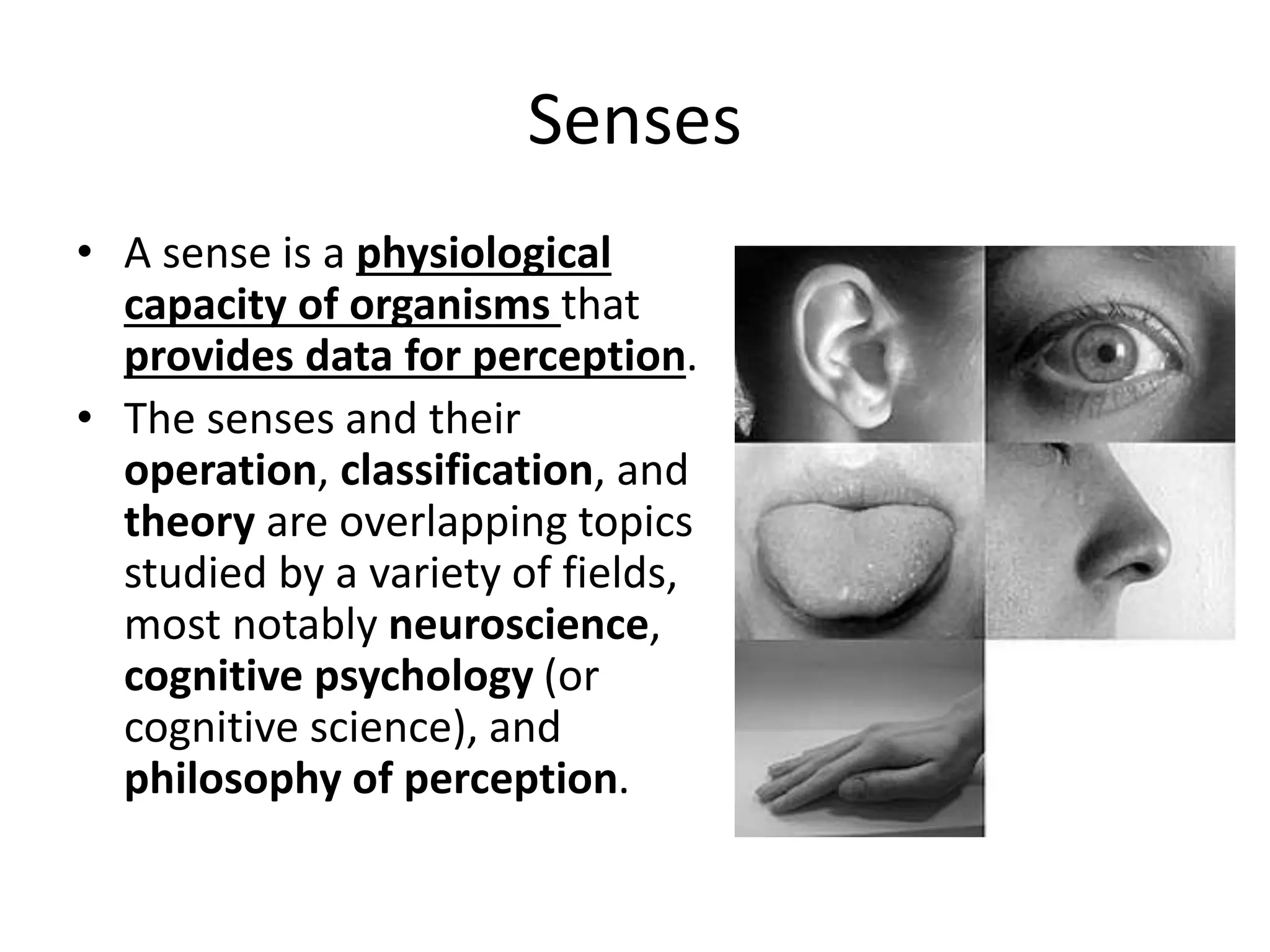
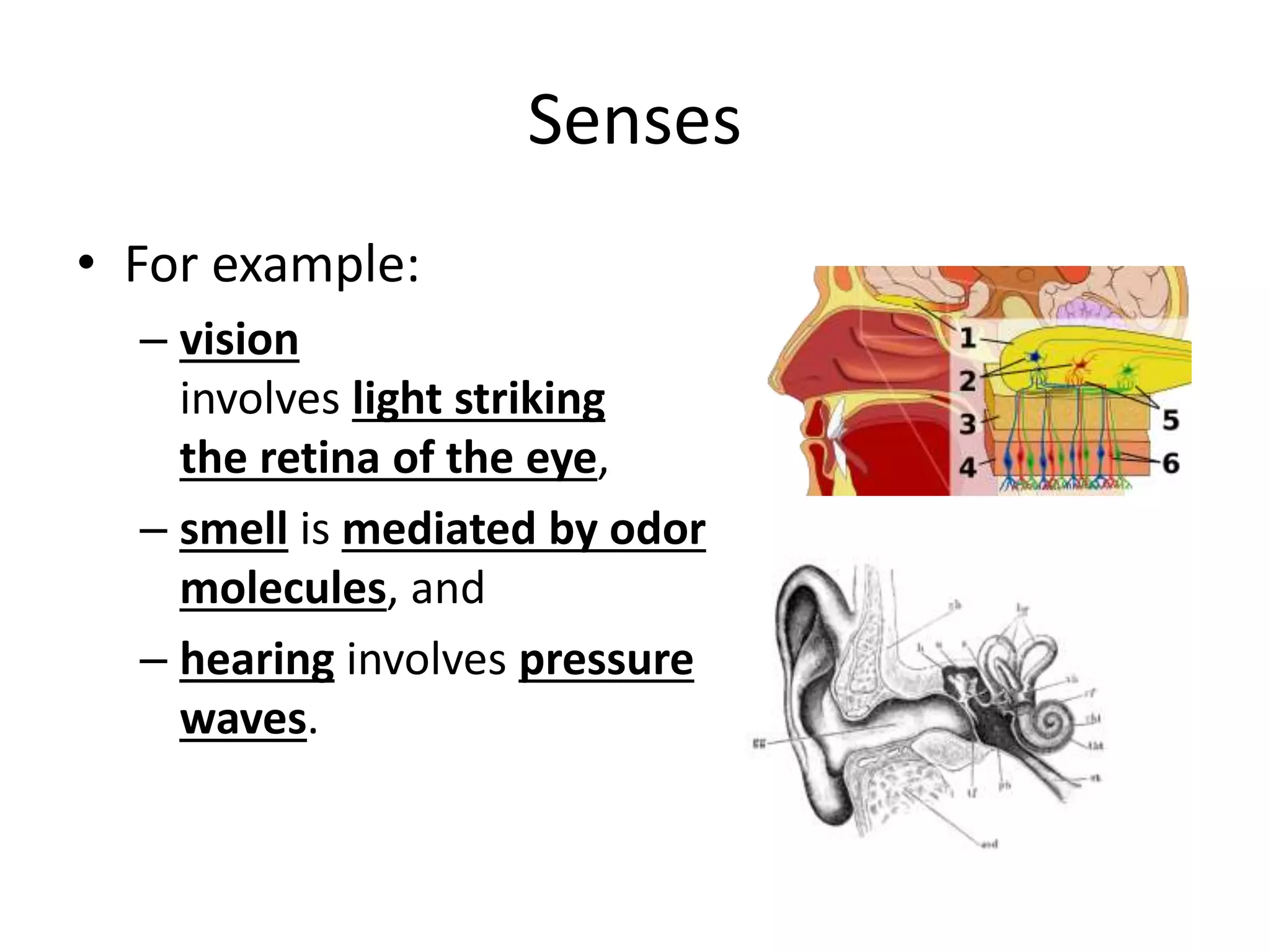
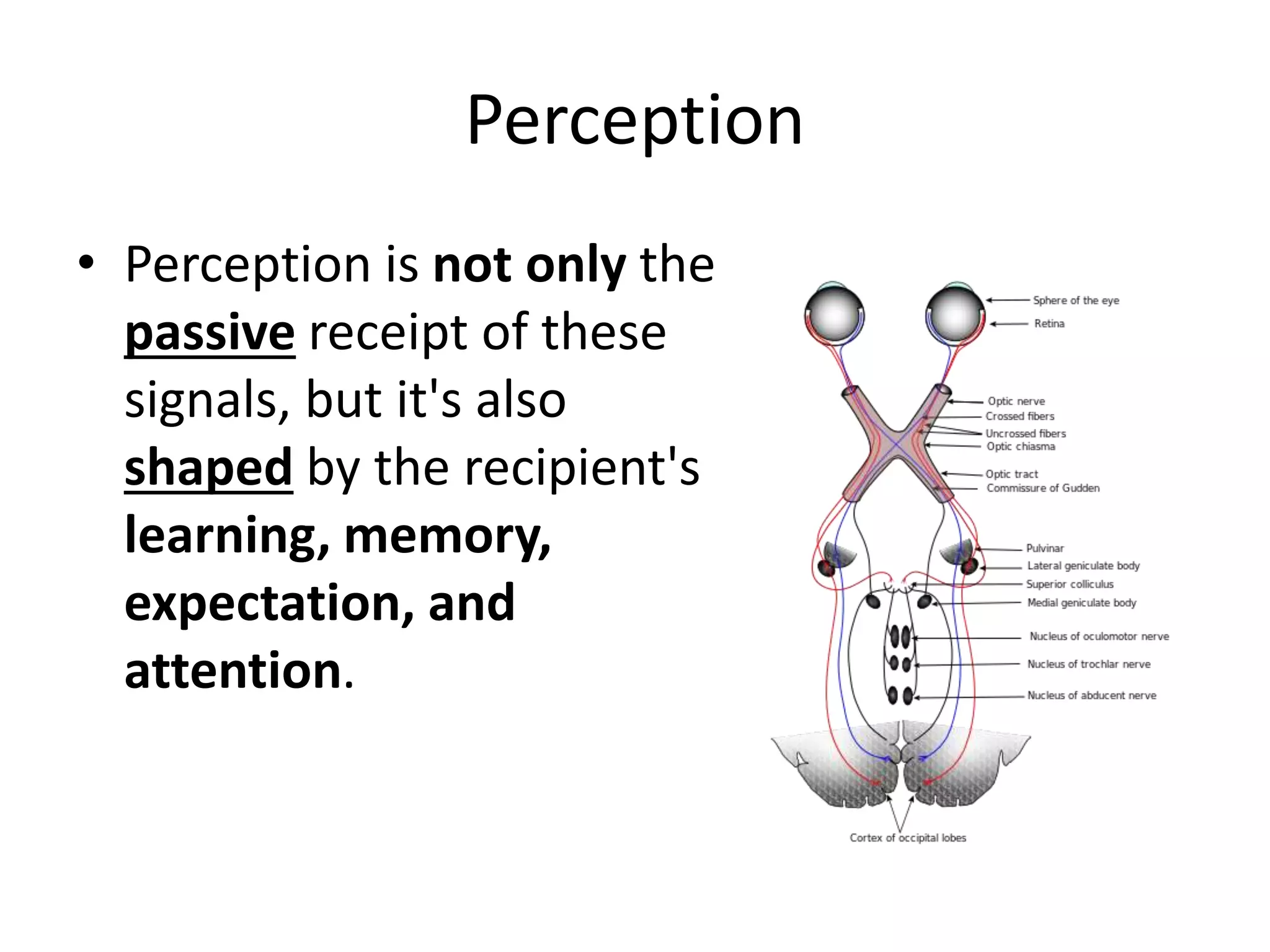
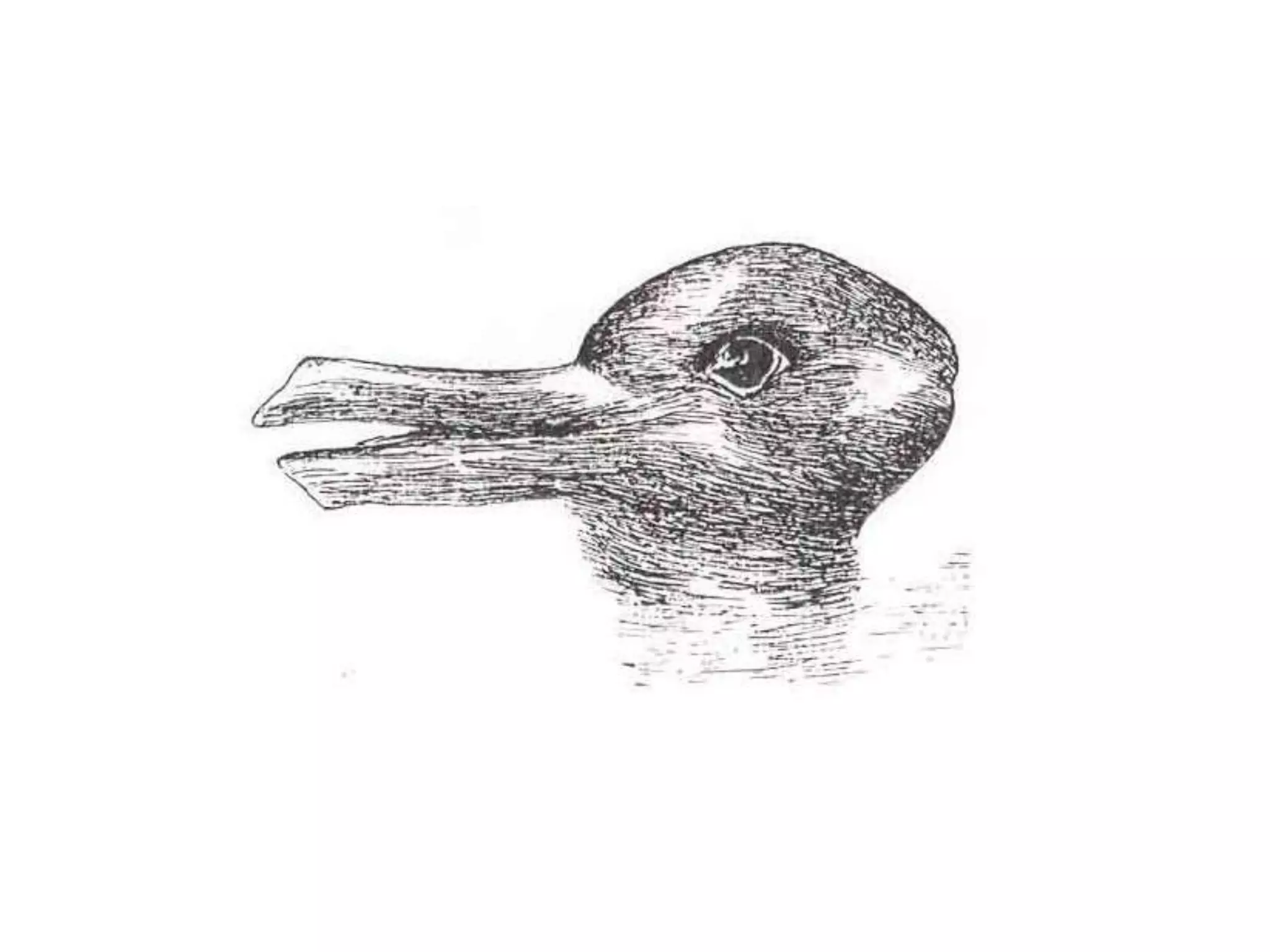
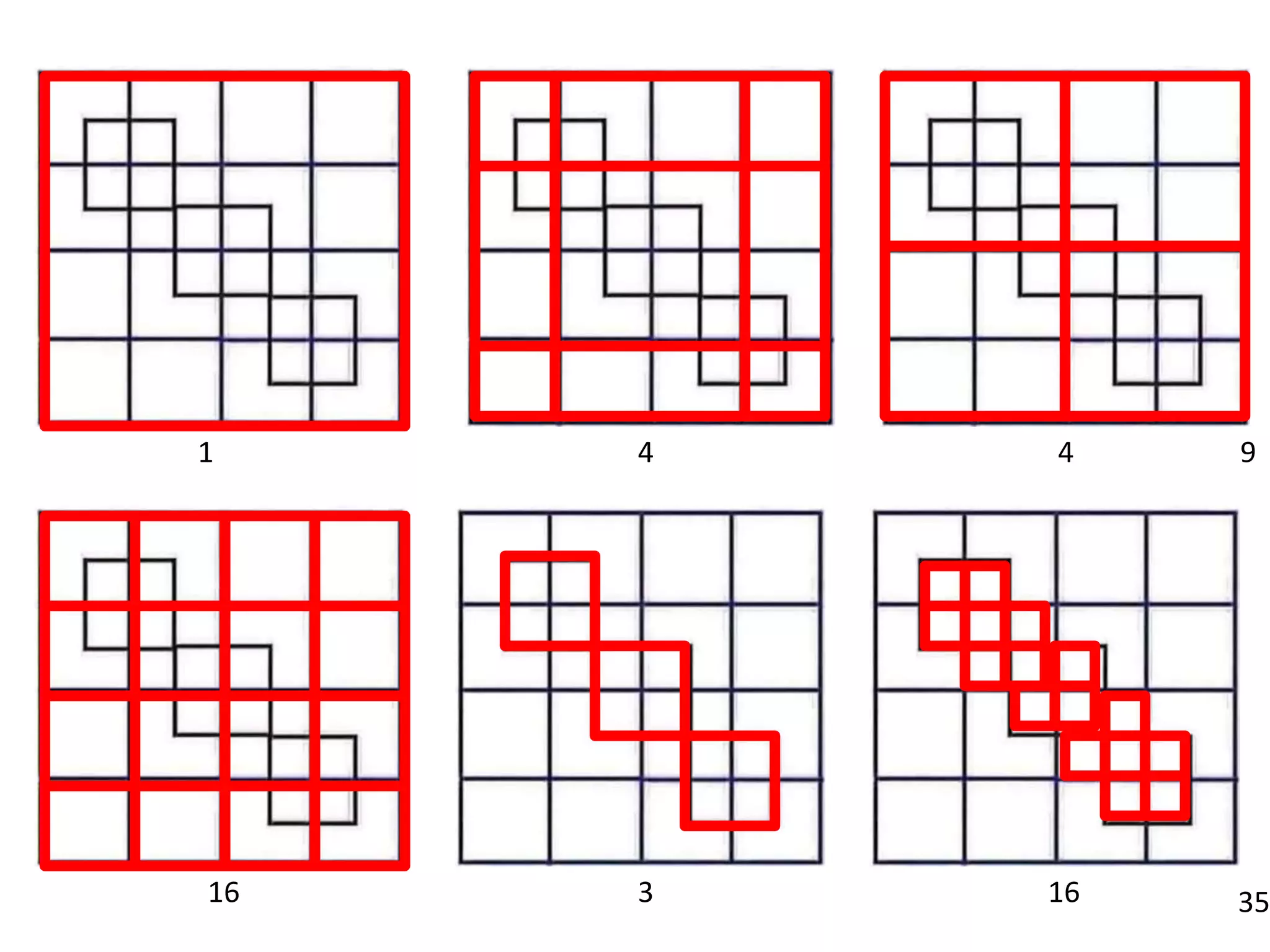
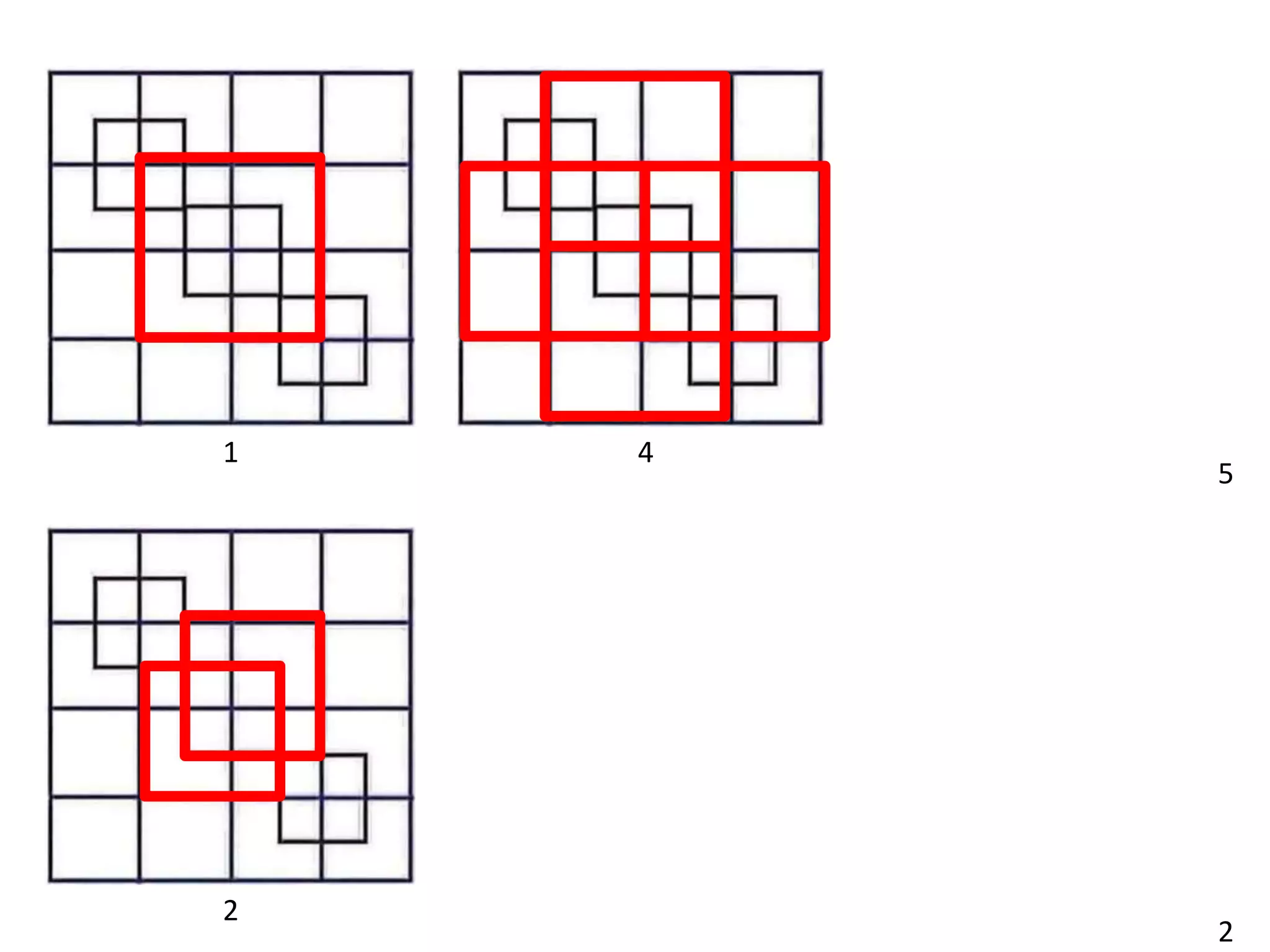
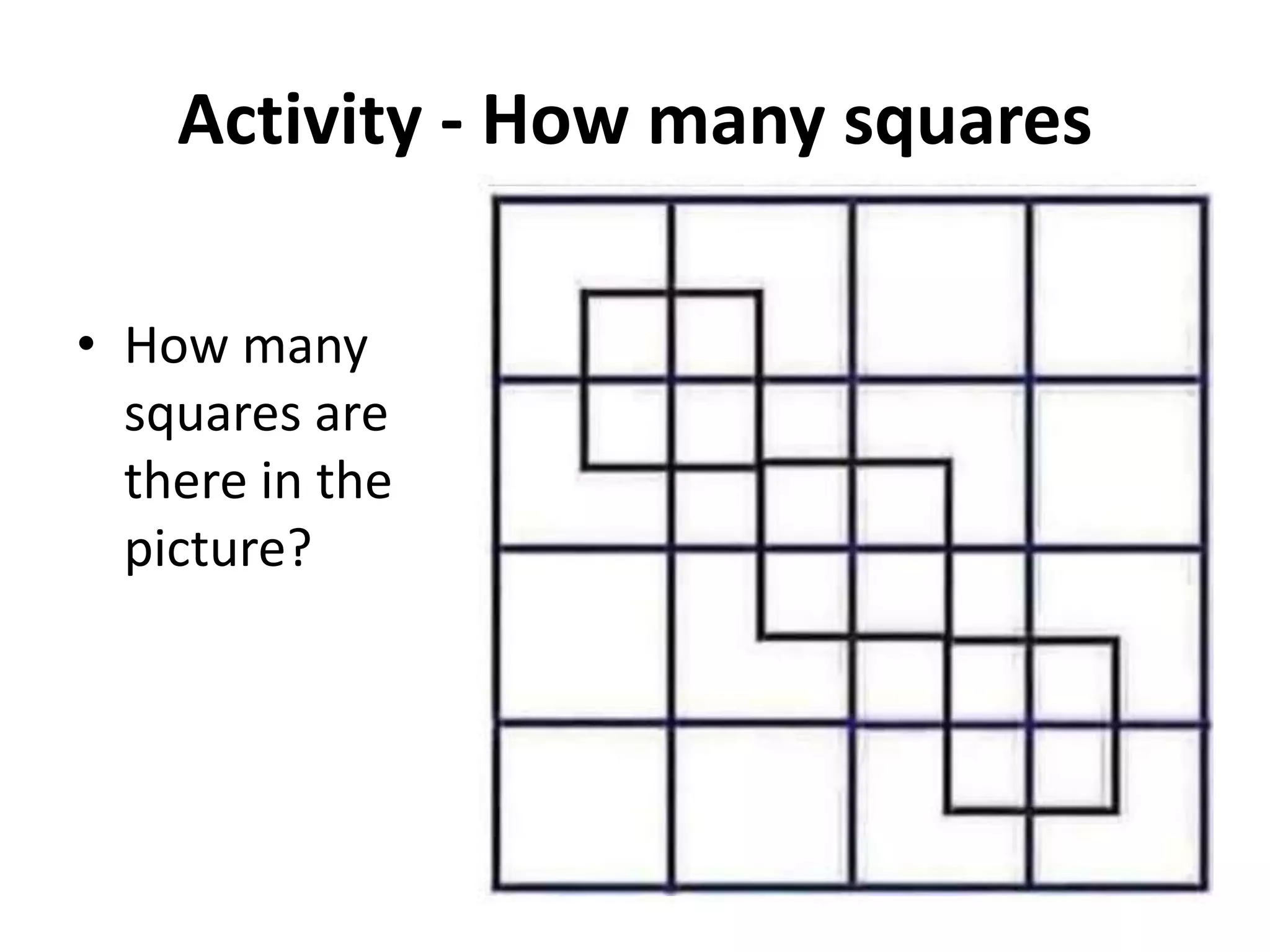This document discusses how human sciences relate to architecture and human perception. It defines human sciences as academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture, including fields like psychology, sociology, anthropology, and history. It contrasts human sciences with natural sciences, noting that human sciences focus more on human behavior and are more abstract. The document then discusses human perception, defining it as how sensory information is organized, identified, and interpreted to understand the environment. It describes the different human senses and sensory systems, and notes that perception involves both the receipt of sensory signals and cognitive processes like learning, memory, and attention.