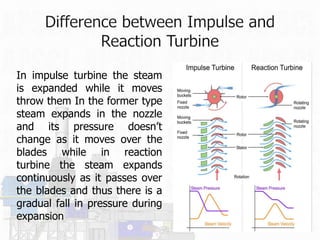
The document discusses Ashuganj Power Station Company Ltd (APSCL), the second largest power company in Bangladesh. It was established in 1966 in Ashuganj, B-Baria. APSCL has 9 generating units with a total installed capacity of 777 MW and present de-rated capacity of 731 MW. The purpose of the internship described in the document was for students to learn about various power generation systems used at APSCL including steam turbine, gas turbine, and combined cycle power plants. The document provides details on these systems and their components.