This document discusses organizational change and different frameworks for understanding it. It covers:
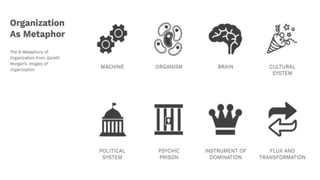
1. Gareth Morgan's metaphors for understanding organizations, including machines, organisms, cultures, political systems, and more.
2. What bureaucracy is, including regulations, hierarchies, formal communication, division of labor, work norms, meritocracy, and professionalization.
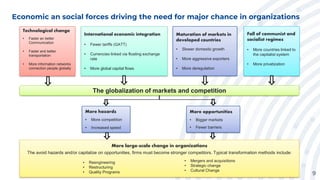
3. The economic and social forces driving the need for major organizational change, such as technological advances, globalization, increased competition, and more opportunities in larger markets.
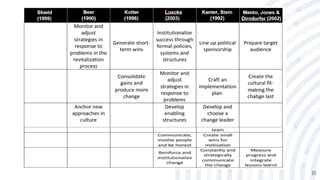
4. Several models for processes of organizational change proposed by theorists like Shield, Beer, Kotter, Luecke, Kanter and Stein, and Mento, Jones, and Dirnd