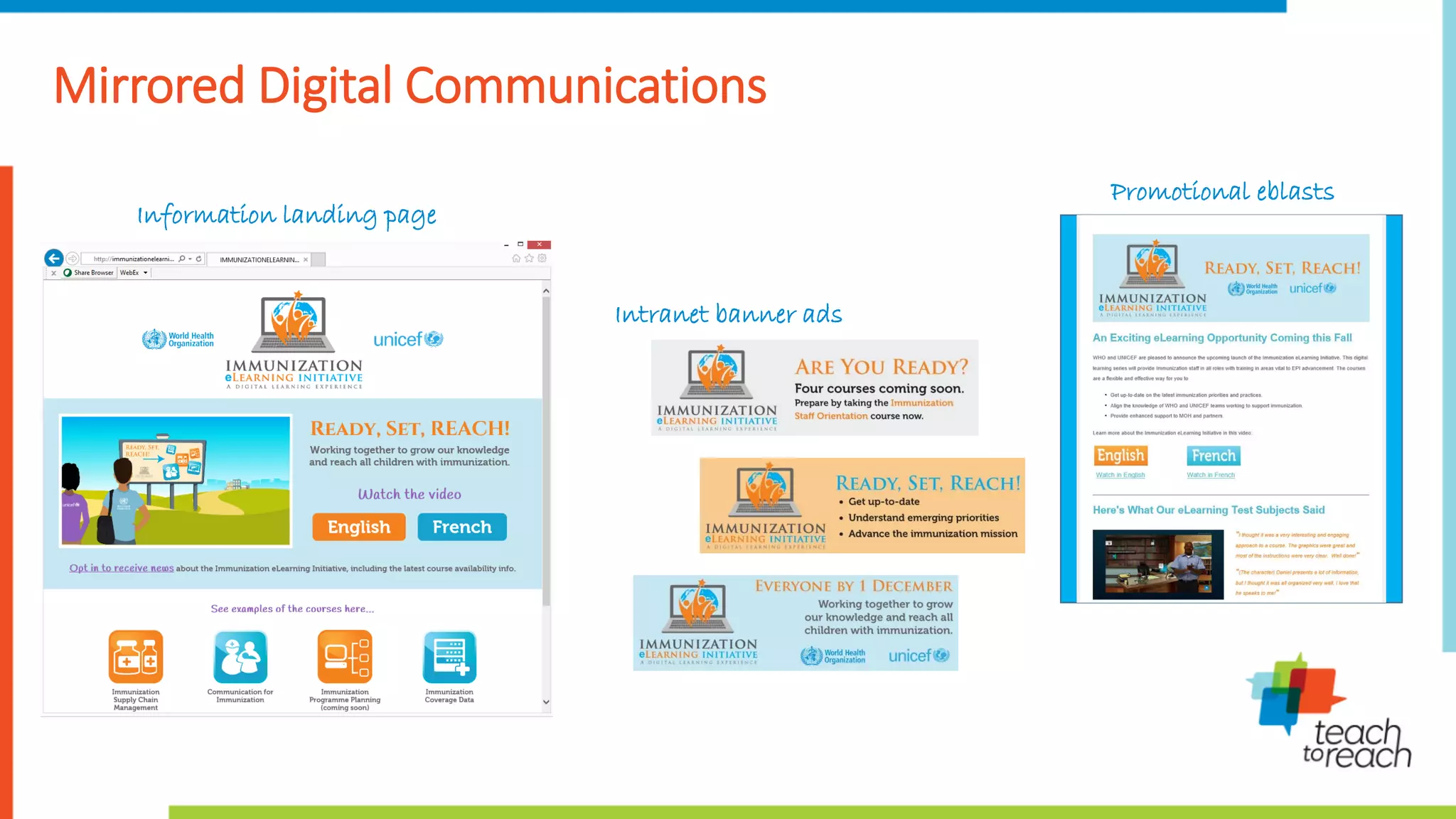
This document summarizes a presentation on change management models and their application to an immunization eLearning initiative. It discusses several common change management models, including Kotter's 8 steps, Lewin's 3 stages of "Unfreeze-Change-Refreeze", and Prosci's 3 phases. It then reviews preparation work done by WHO and UNICEF to understand training needs and barriers to adopting an eLearning program. The presentation outlines change management strategies used, such as identifying influencers, developing communications, and providing incentives, to help achieve goals of high training participation and acceptance of online learning. It shares some promotional materials and engagement activities used and discusses pilot programs at WHO and GAVI's change management efforts.