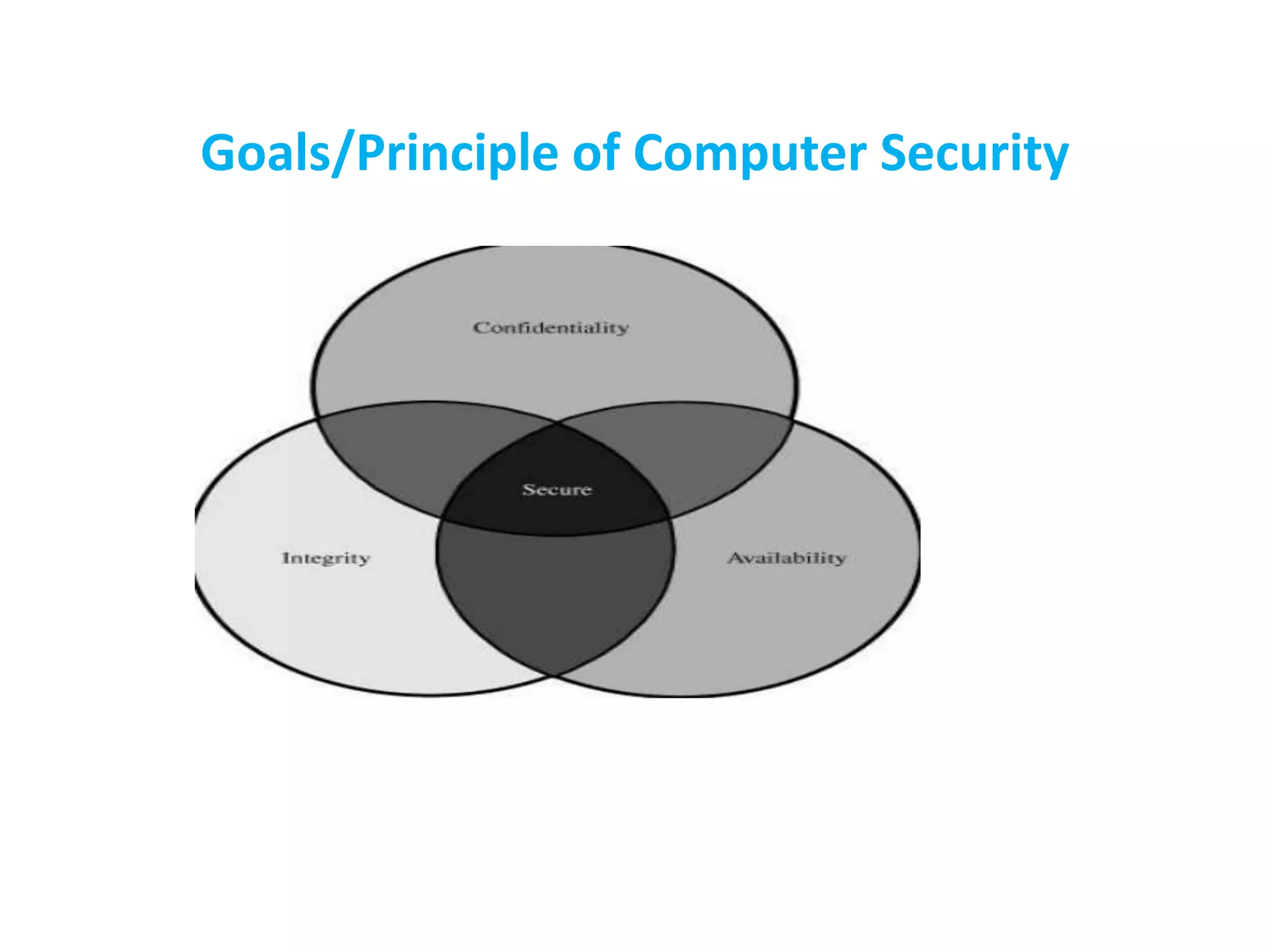
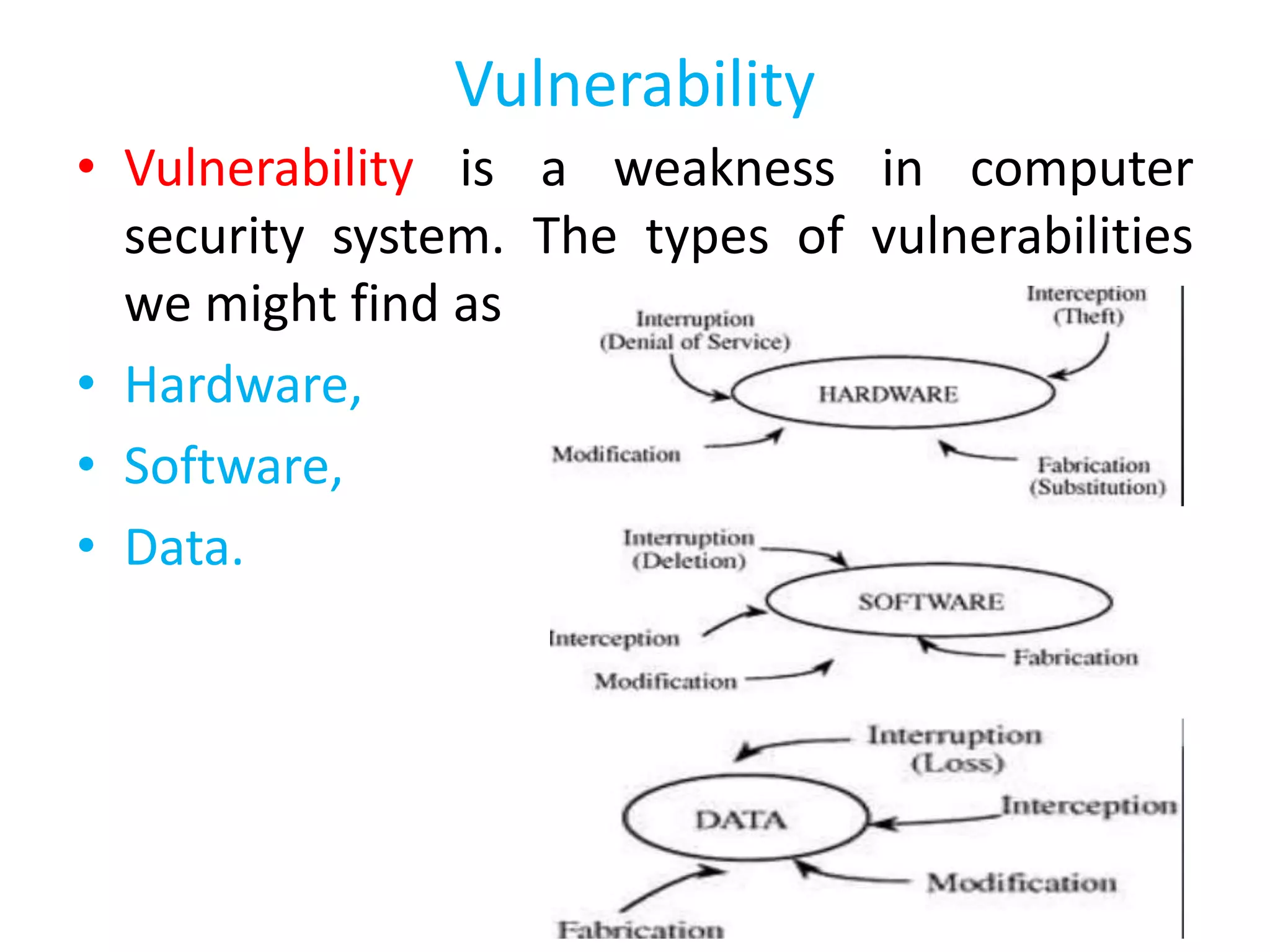
This document discusses computer security. It defines computer security as the protection of computer systems from theft, damage, disruption or misdirection of hardware, software, information and services. The core goals of computer security are confidentiality, integrity and availability of computer assets and data. Vulnerabilities, threats such as computer crimes, and attacks like denial-of-service pose risks to computer security. Defenses include access control, antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection and prevention systems.