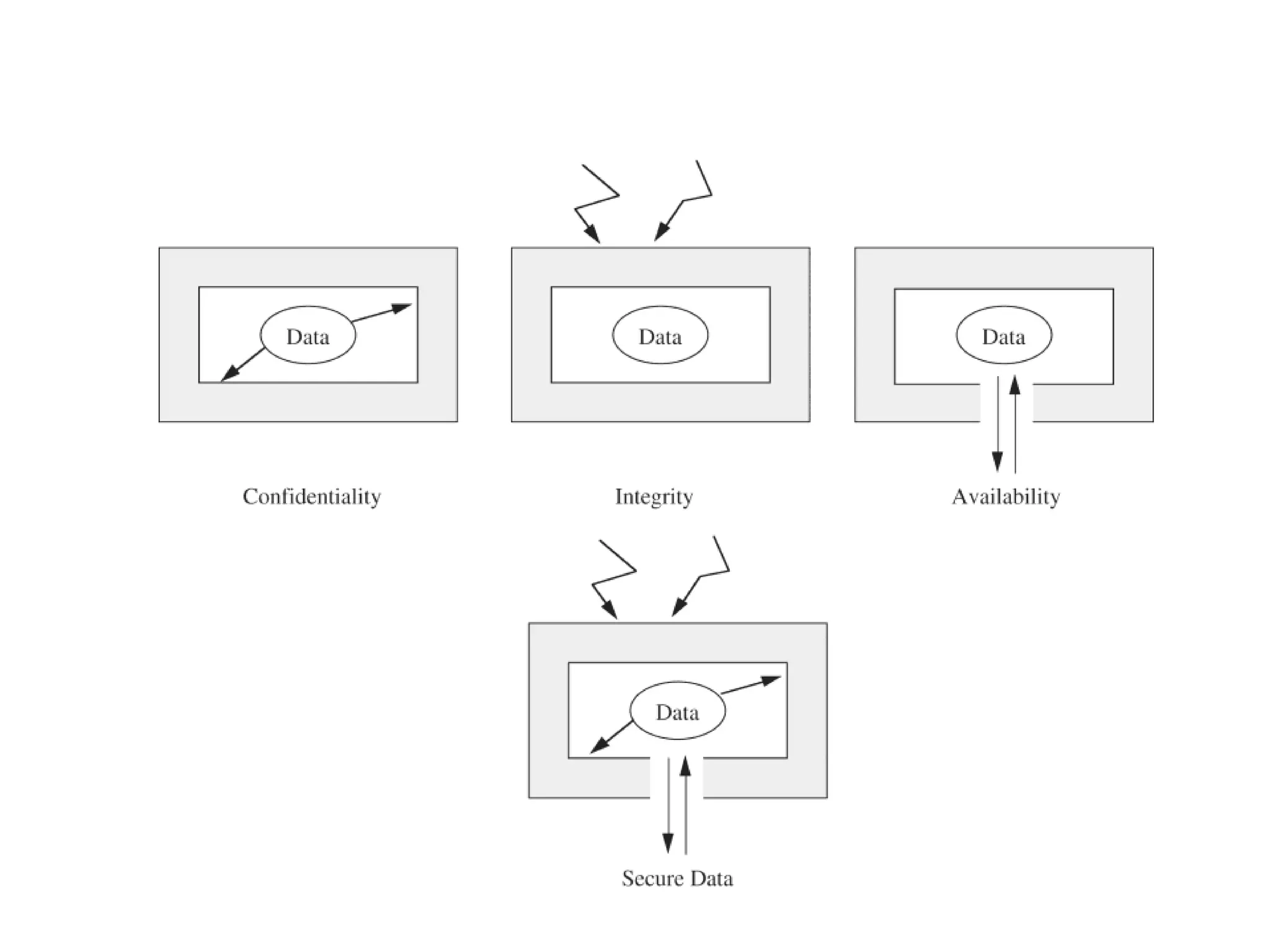
This document provides an introduction to computer security. It defines key security concepts like threats, vulnerabilities, and controls. It discusses common attacks like interception, interruption, and modification. It also outlines security goals of confidentiality, integrity and availability. The document examines security risks for hardware, software, data and networks, and categorizes types of computer criminals. It concludes that security aims to prevent, deter, deflect, detect and recover from harm through various defense methods.