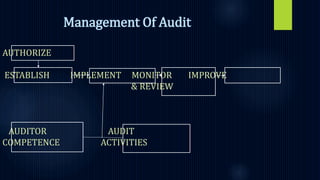
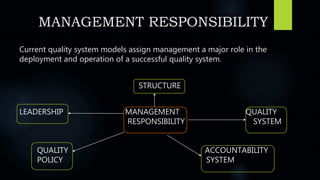
The document discusses the importance of quality systems and audits in pharmaceutical manufacturing, detailing the definitions and types of audits, such as internal and external audits, and management's key responsibilities in maintaining quality. It emphasizes the need for a risk-based quality system approach, adequate resources, and effective communication within the organization to meet quality objectives and regulatory requirements. The FDA supports this approach to ensure compliance and improve product quality.