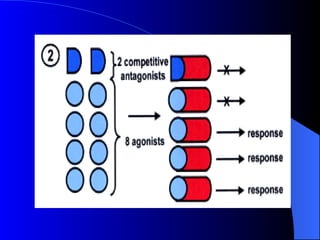
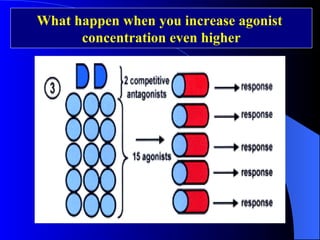
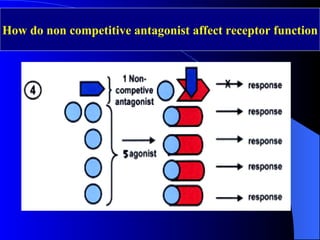
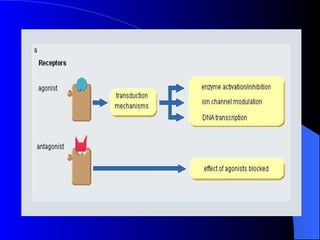
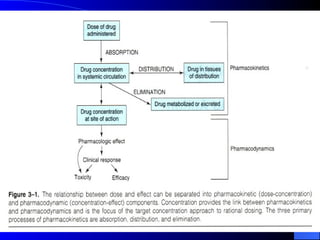
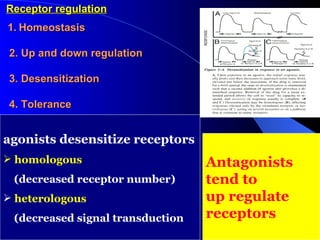
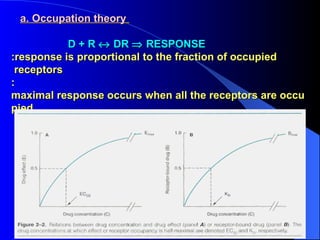
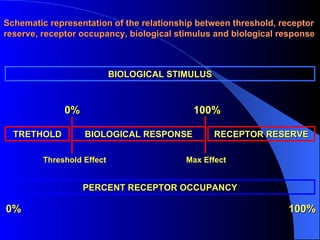
Pharmacodynamics is the study of how drugs act on the body and biological system, including receptor interactions and mechanisms of action. Most drugs act by binding to receptors, and spare receptors allow a maximal response even when not all receptors are occupied, as only a portion need to be bound. Agonists activate receptors to produce a response, with full agonists having maximal efficacy and partial agonists having less efficacy than full agonists. Antagonists block the action of agonists without activating the receptors themselves.


































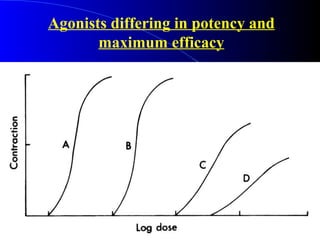
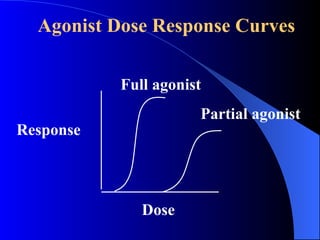
![[D] (concentration units) % Maximal Effect 0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00 1000.00 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 Partial agonist Full Agonist Partial agonist PARTIAL AGONISTS - EFFICACY Even though drugs may occupy the same # of receptors, the magnitude of their effects may differ.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1pharmacodynamics-090825051618-phpapp02/85/Lecture-1-Pharmacodynamics-45-320.jpg)