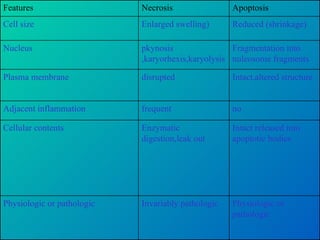
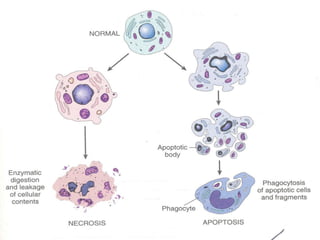
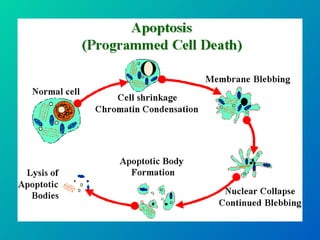
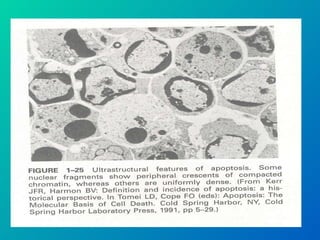
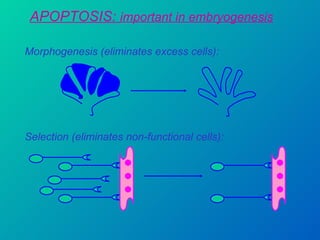
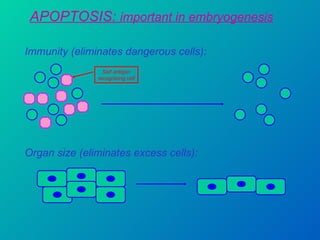
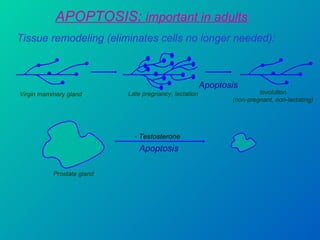
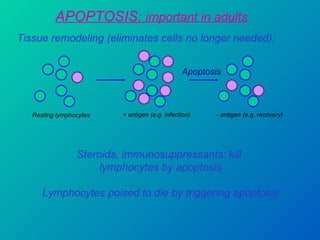
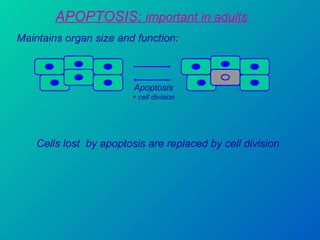
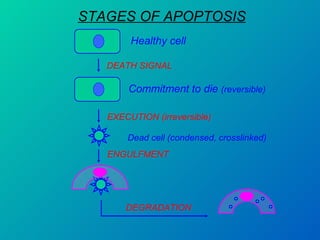
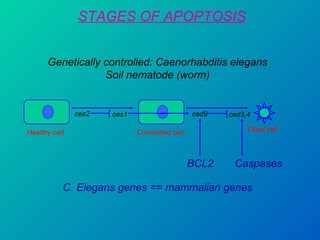
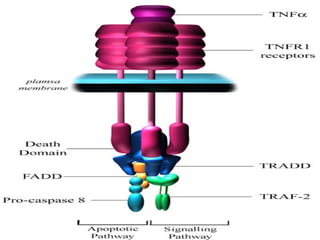
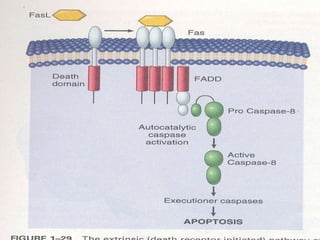
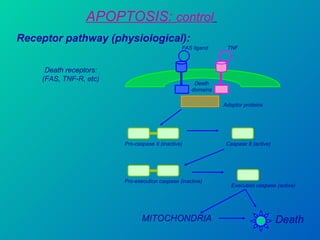
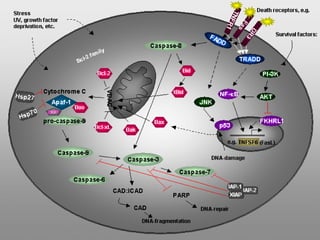
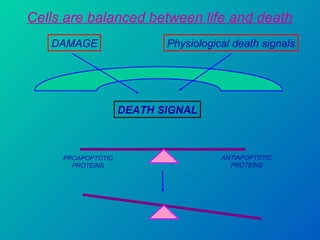
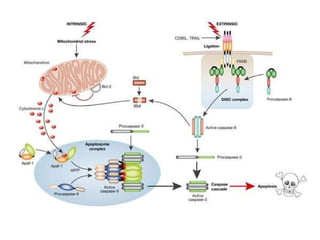
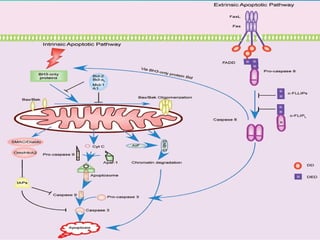
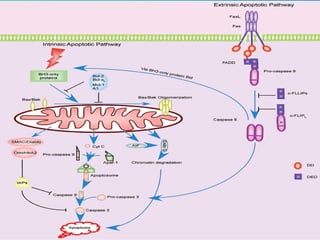
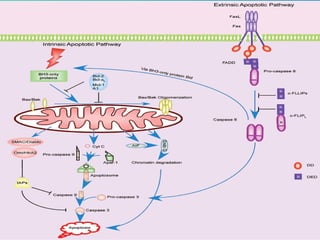
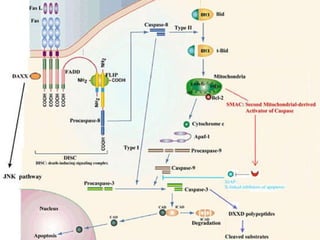
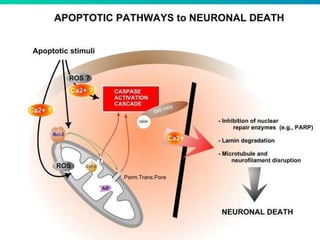
1. Apoptosis is a tightly regulated form of programmed cell death that plays an important role in development, tissue homeostasis, and the immune system. It is characterized by morphological changes including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, and formation of apoptotic bodies.
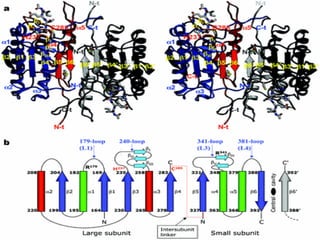
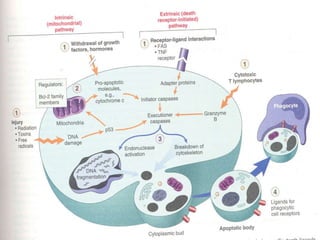
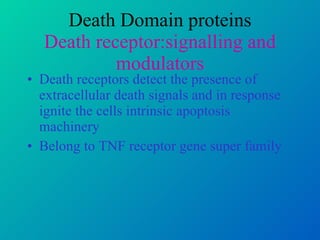
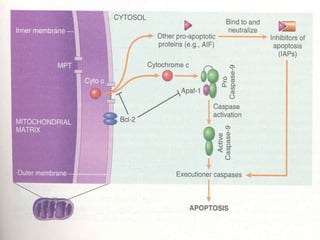
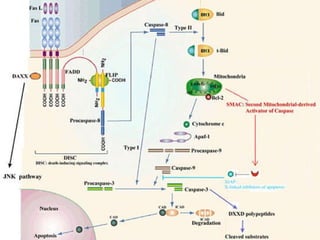
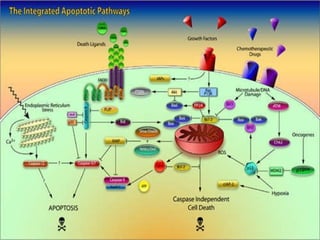
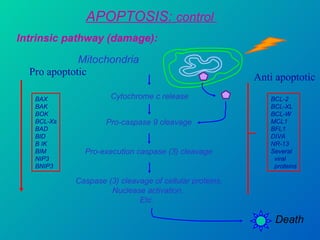
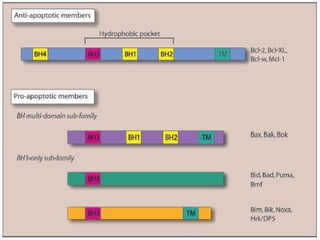
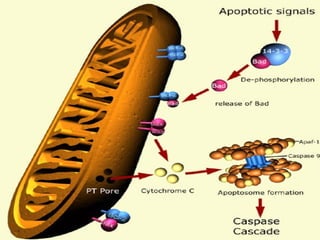
2. The process of apoptosis involves initiator caspases that activate executioner caspases, leading to degradation of nuclear and cytoplasmic components. Mitochondria also play a key role by releasing pro-apoptotic factors. Various proteins regulate apoptosis, including Bcl-2 family members and inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs).
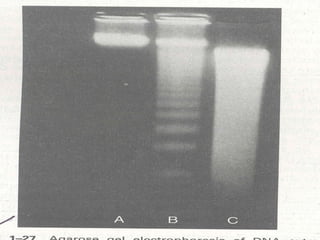
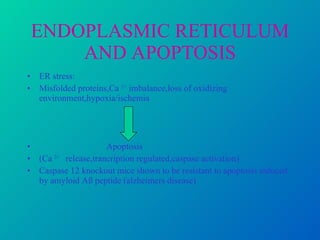
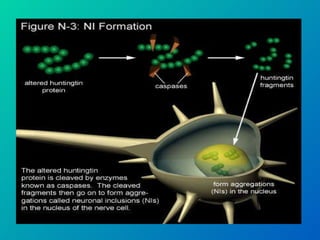
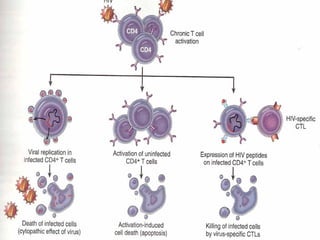
3. Dysregulation of apoptosis contributes to diseases like cancer, neurodegeneration, and HIV/AIDS. Detection of