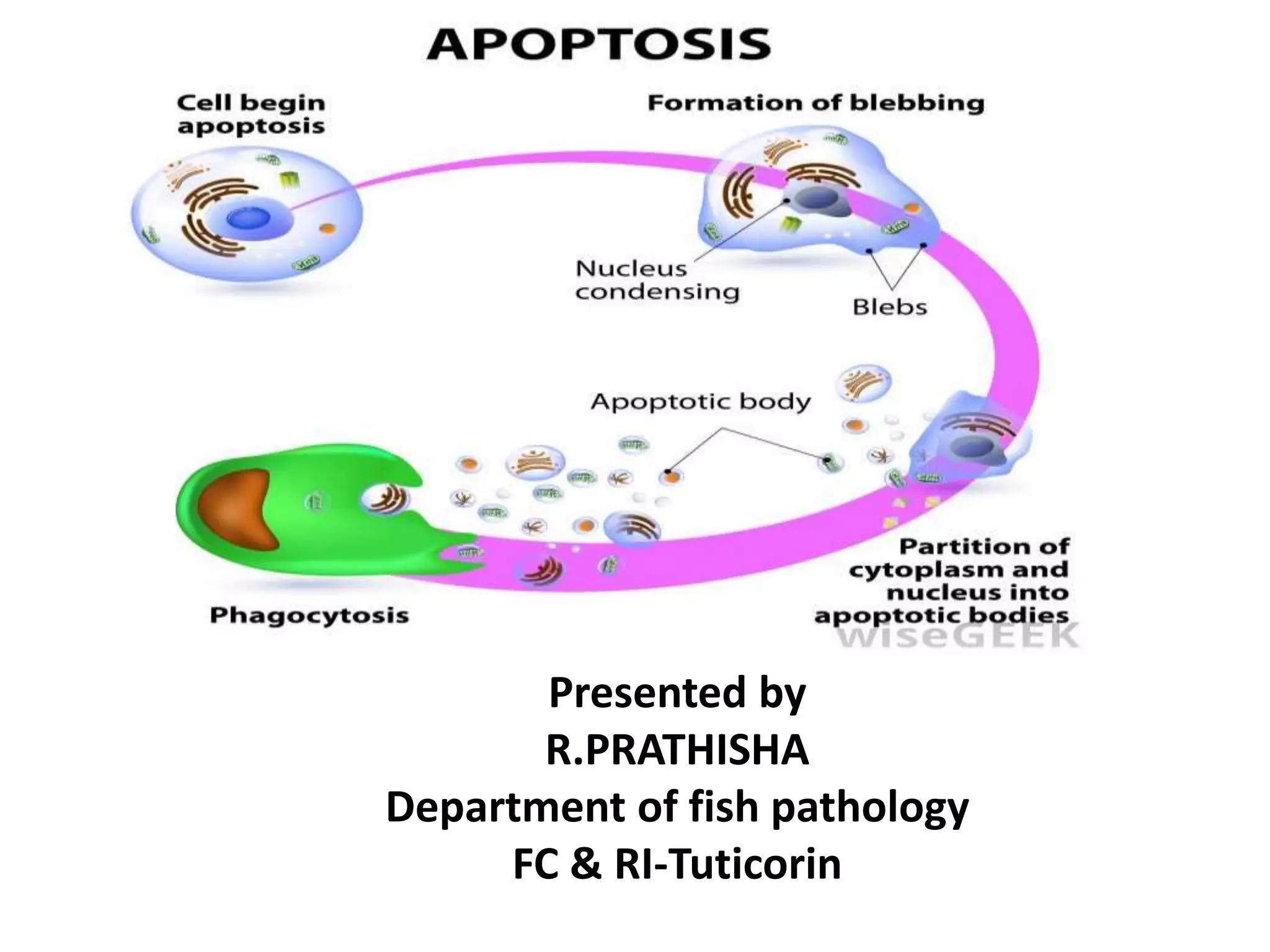
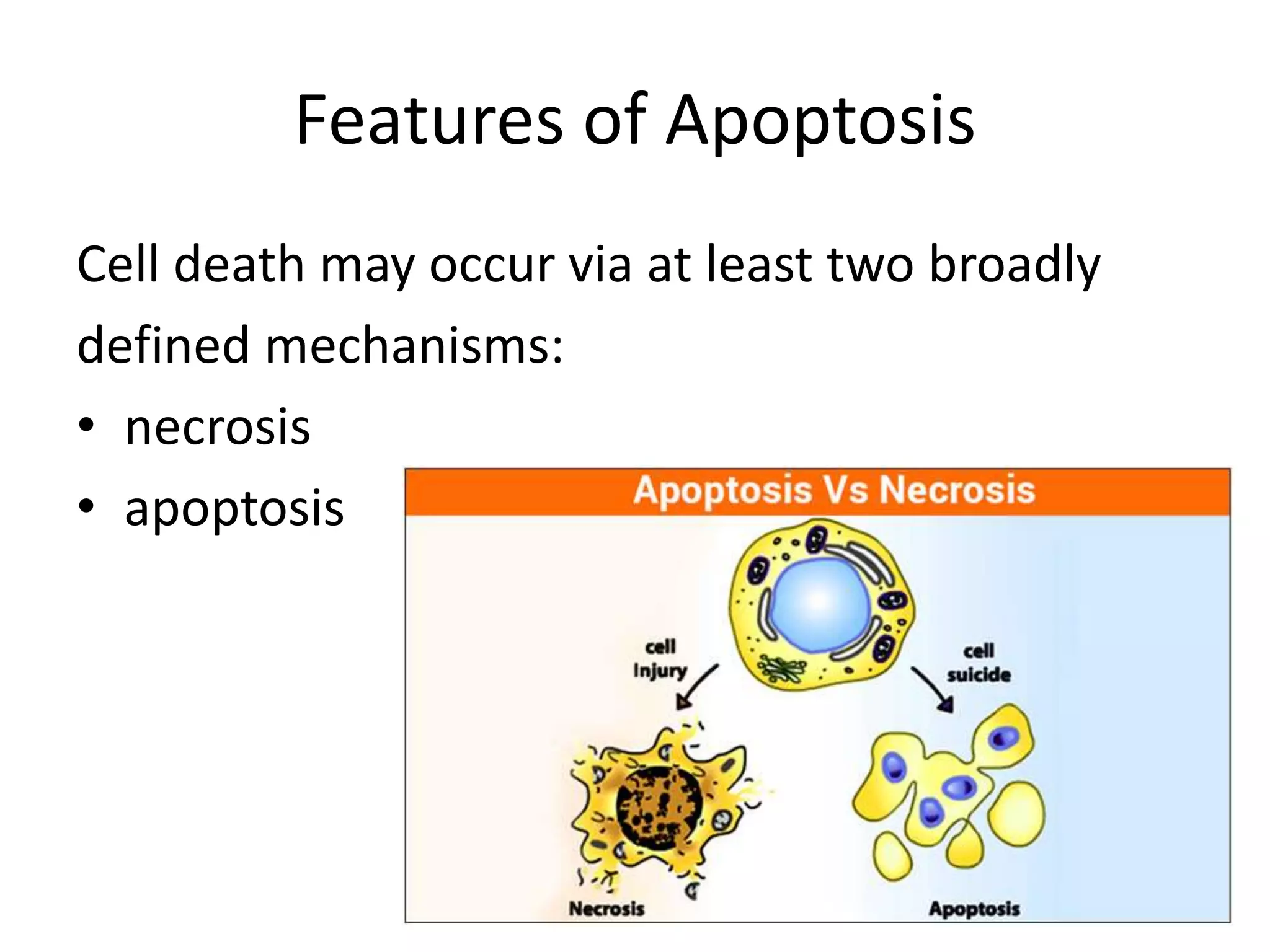
Apoptosis is a tightly regulated form of programmed cell death that plays an important role in tissue homeostasis, development, and the immune system. It is characterized by fragmentation of DNA and the nucleus. There are two main pathways that trigger apoptosis - the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway and the extrinsic death receptor pathway - which both activate caspases and lead to dismantling of the cell. Apoptosis is important for removing damaged, unneeded, or infected cells, and balancing it with cell proliferation is critical for health.