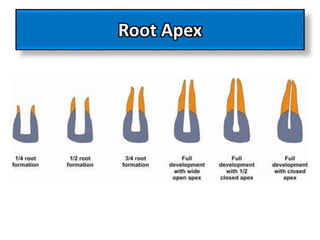
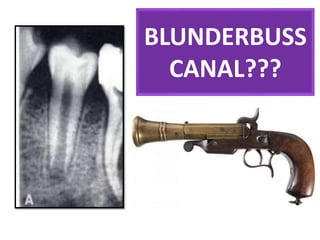
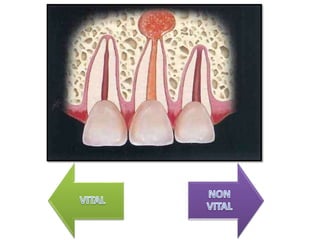
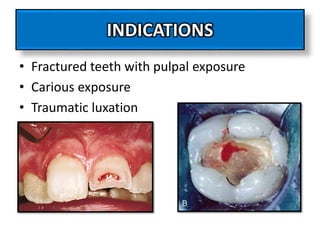
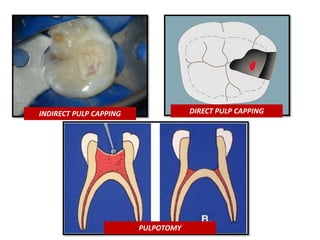
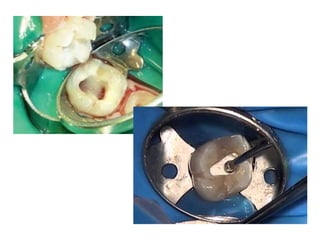
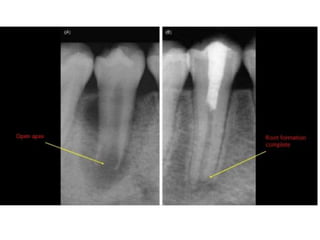
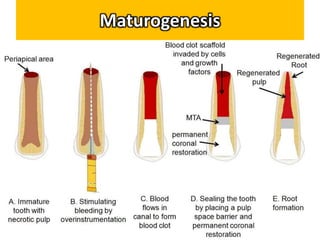
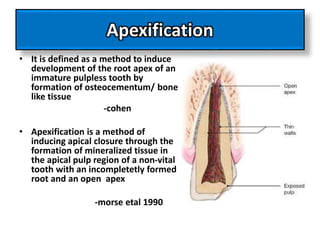
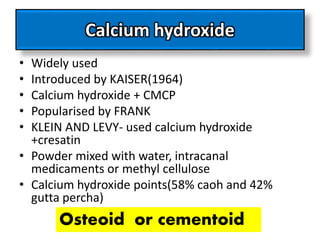
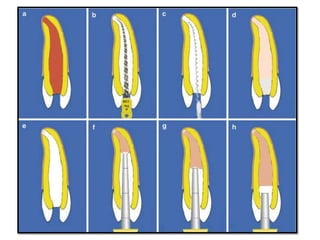
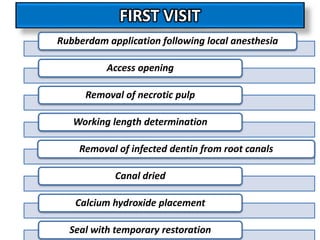
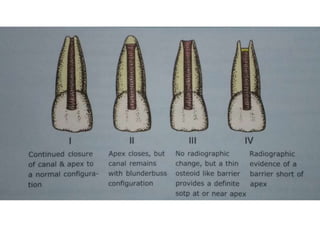
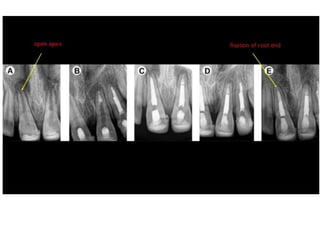
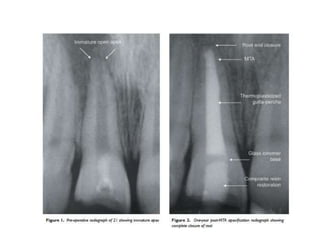
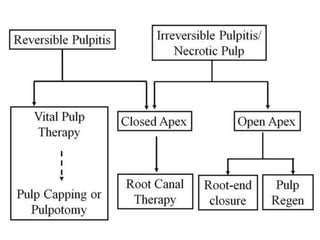
This document discusses apexogenesis, apexification, and maturogenesis procedures for immature teeth. Apexogenesis aims to allow continued root development through vital pulp procedures. Apexification induces apical closure in non-vital teeth with open apices through formation of mineralized tissue. Goals include maintaining pulp vitality or inducing a barrier against which gutta percha can be packed during root canal treatment. Calcium hydroxide and MTA are common materials used. Multiple visits over 6 months to 2 years may be needed for apical closure depending on factors like apical size and infection level.