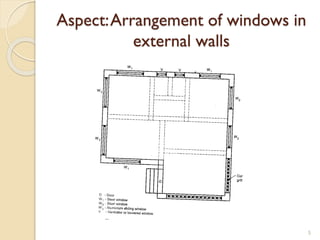
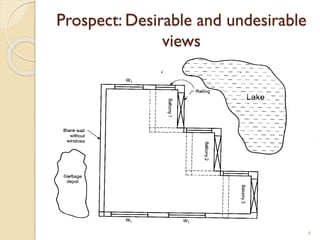
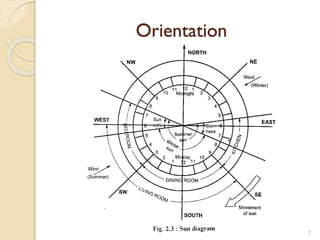
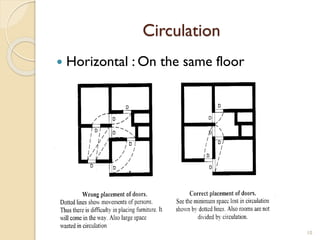
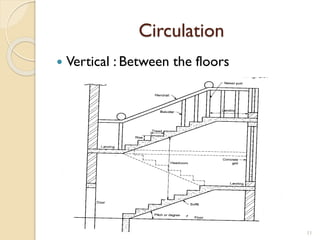
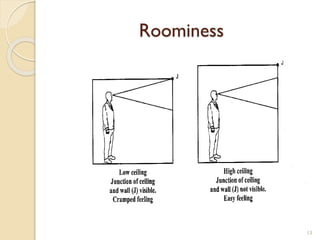
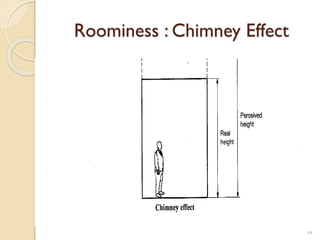
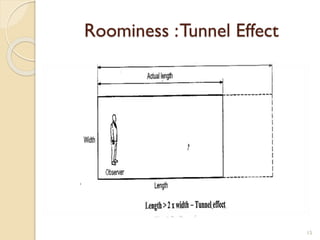
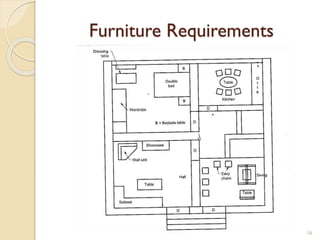
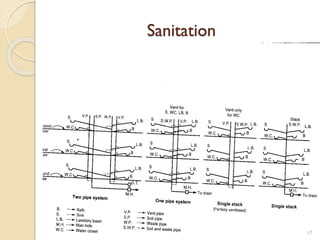
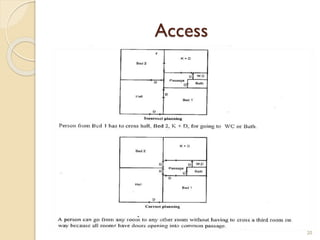
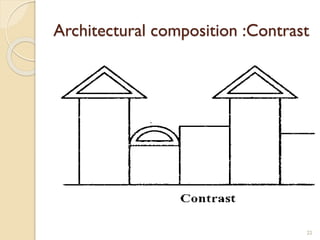
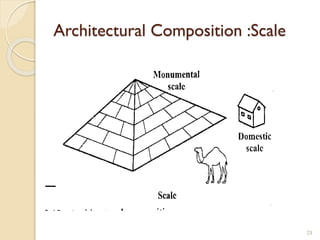
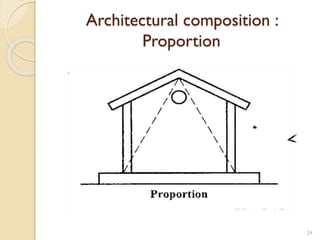
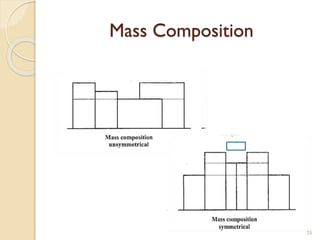
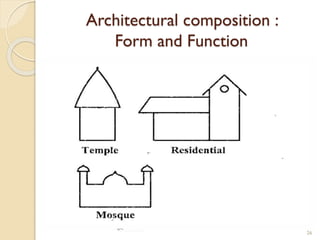
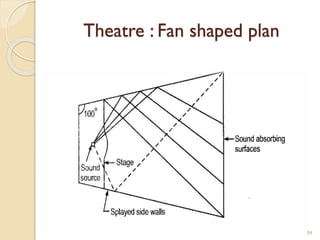
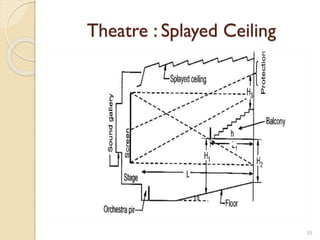
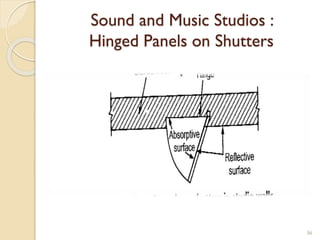
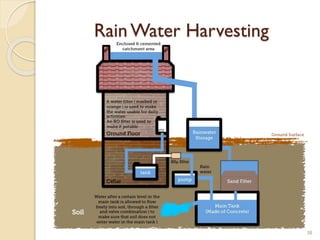
This document summarizes key principles of architectural planning and building design, including 14 principles of planning such as aspect, orientation, privacy, and circulation. It discusses topics like sound insulation, acoustics, building services, staircases, lifts, and escalators. It also covers challenges like designing green buildings, ecosystem preservation, and creating self-sufficient homes. The document is a lecture on these topics presented to civil engineering students.