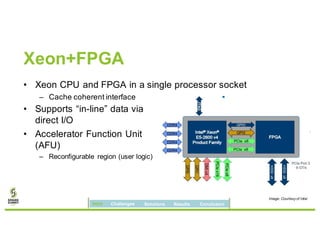
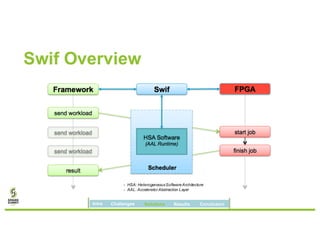
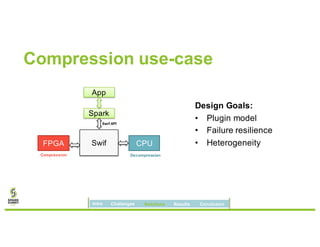
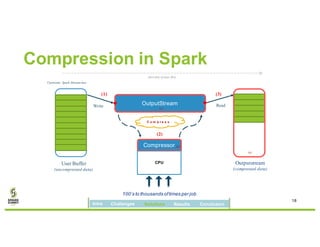
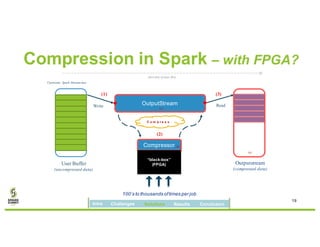
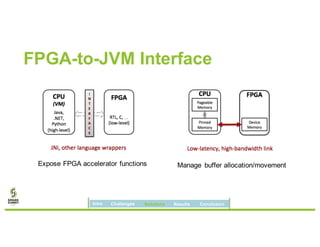
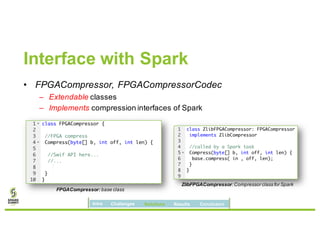
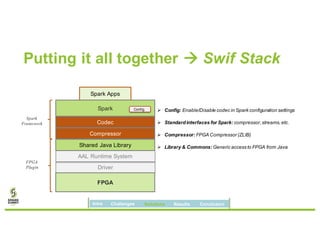
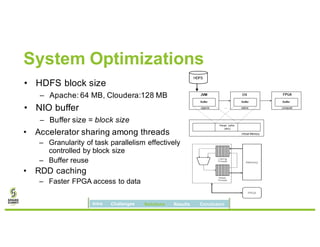
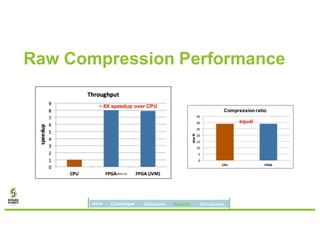
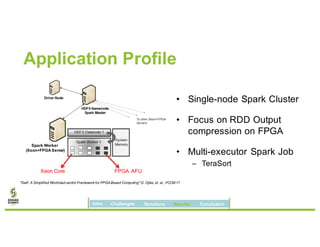
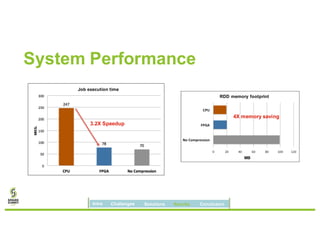
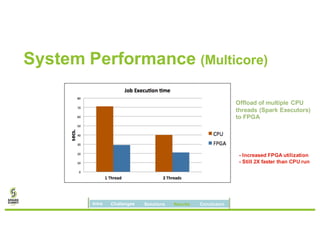
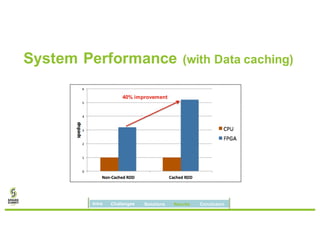
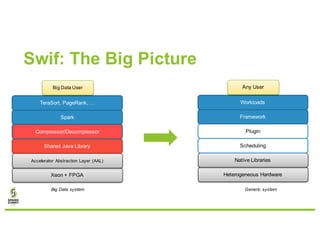
David Ojika's research at the University of Florida focuses on enhancing Apache Spark performance through data compression using FPGA technology in conjunction with Xeon processors. The study introduces a simplified framework called SWIF that allows seamless integration of FPGA accelerators for data compression, achieving significant speed improvements and memory savings without altering existing applications. The results demonstrate a 3.2x job speedup and a 4x reduction in RDD memory footprint, showcasing the potential for FPGA acceleration in big data environments.