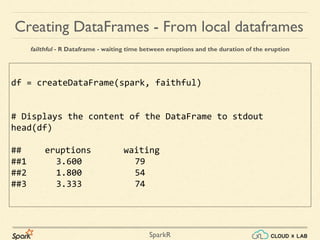
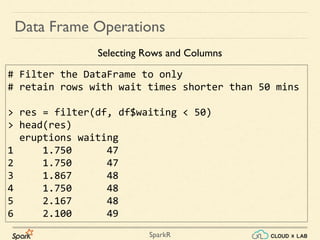
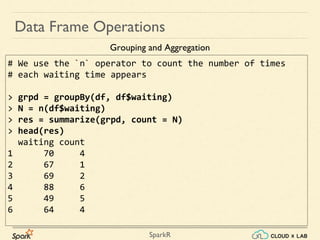
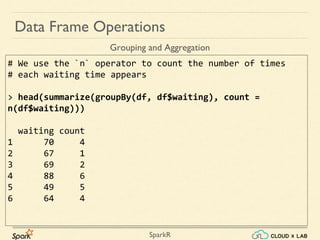
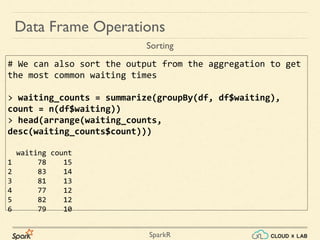
Sparkr is an R package that acts as a lightweight frontend to utilize Apache Spark for distributed data frames, facilitating operations like selection, filtering, and aggregation on large datasets. It allows users to create data frames from various sources, including local R data frames and JSON files, and supports distributed machine learning through MLlib. The document details practical examples of data frame operations such as filtering, grouping, and SQL query execution.