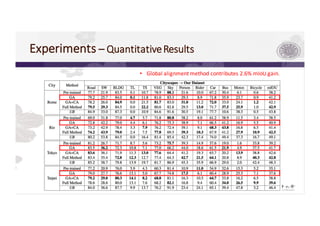
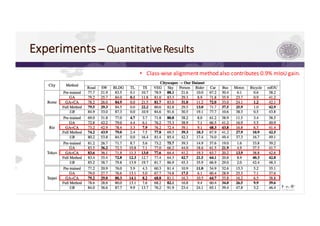
This document discusses adapting an AI object identification (AOI) system to changes in domains. It proposes using attention and domain adaptation techniques. Specifically:
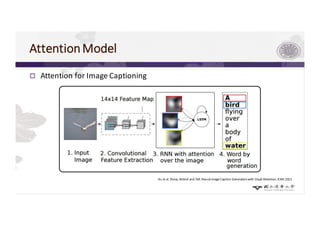
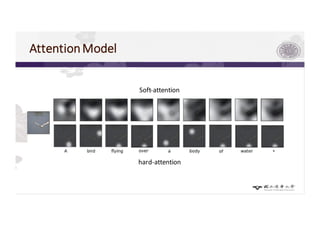
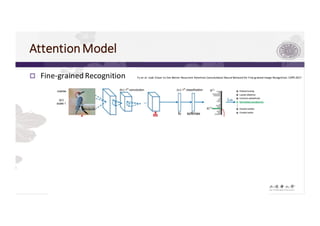
1) AOI is like fine-grained recognition, which can benefit from attention models that focus on discriminative regions.
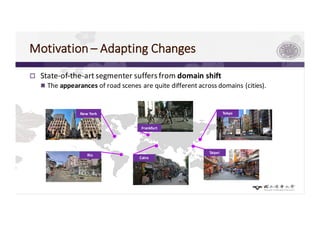
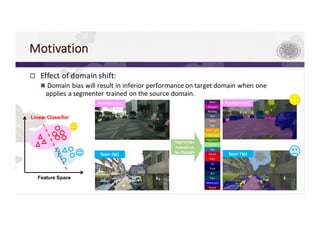
2) Domain shift between different sensors/viewpoints can degrade performance, but domain adaptation methods like attention models and domain adversarial learning can help address this.
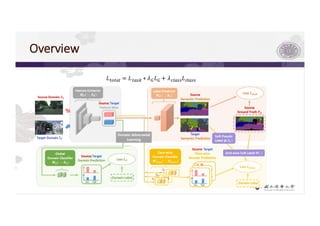
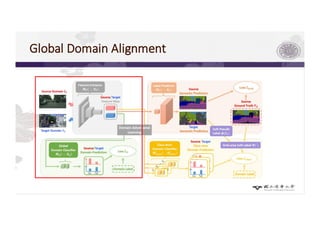
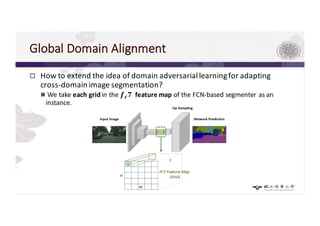
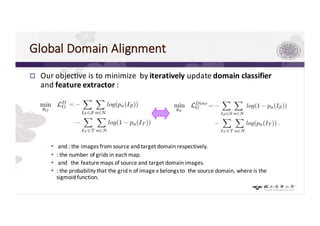
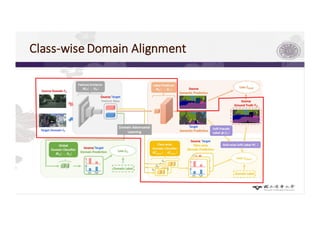
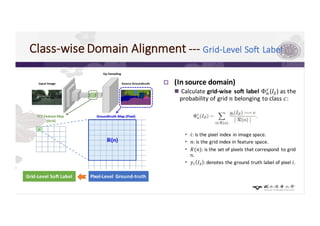
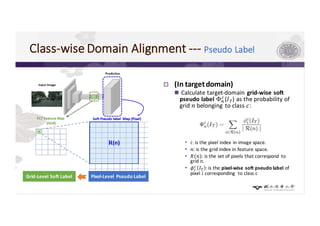
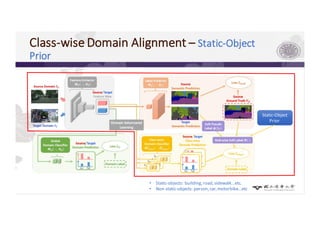
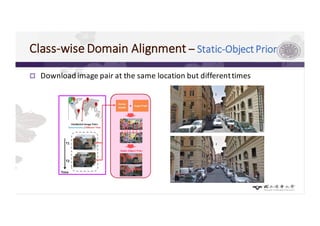
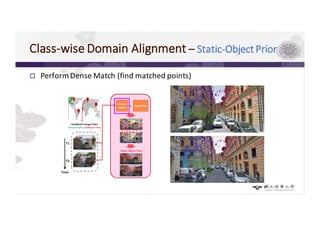
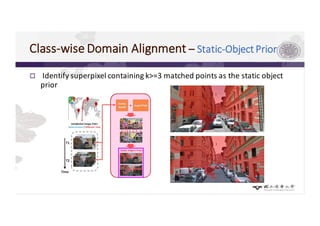
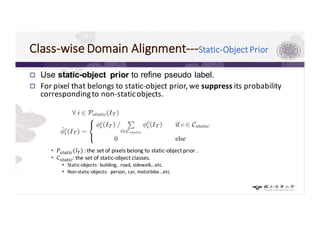
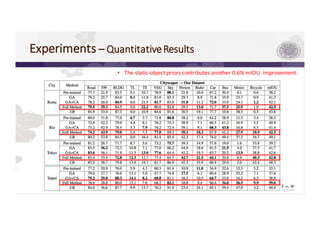
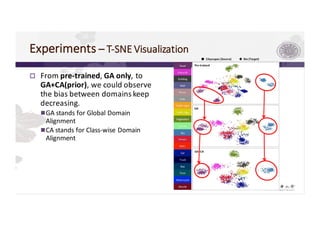
3) The paper proposes a method for unsupervised cross-city adaptation of road scene segmenters using global and class-wise domain alignment with an attention-based static object prior. This achieves state-of-the-art performance adapting models between cities.





![Motivation
p Goal: use domain adaptation to mitigate the effect of domain shift.
p Approaches:
n Supervised Fine-Tuning: CAN access the label on the target domain.
• Straightforward but time-consuming and expensive.
n Unsupervised Adaptation: CAN’T access the label on the target domain.
• More challenging but low cost.
Pixel labeling of one
Cityscapes image takes
90 minutes on average.[4]
[4] M. Cordts, M.Omran, S. Ramos, T. Rehfeld,M. Enzweiler, R. Benenson,U.Franke,S.Roth, and B. Schiele, “The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene
understanding,” in CVPR,IEEE,2016.
a
Practical in real life !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201701-180815025708/85/AOI-11-320.jpg)