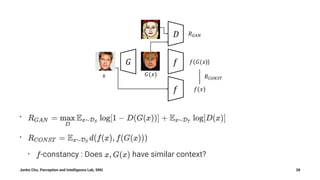
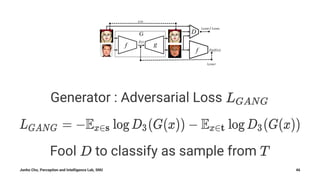
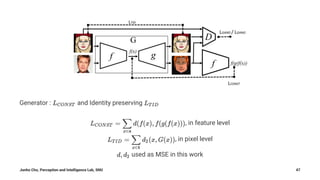
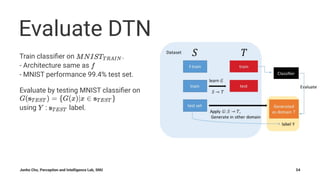
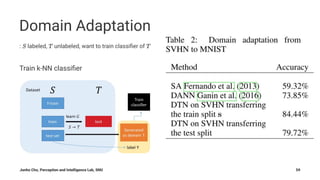
The document summarizes Junho Cho's presentation on image translation using generative adversarial networks (GANs). It discusses several papers on this topic, including pix2pix, which uses conditional GANs to perform supervised image-to-image translation on paired datasets; Domain Transfer Network (DTN), which uses an unsupervised method to perform cross-domain image generation; and CycleGAN and DiscoGAN, which can perform unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. The presentation provides an overview of each method and shows examples of their applications to tasks such as semantic segmentation, style transfer, and domain adaptation.