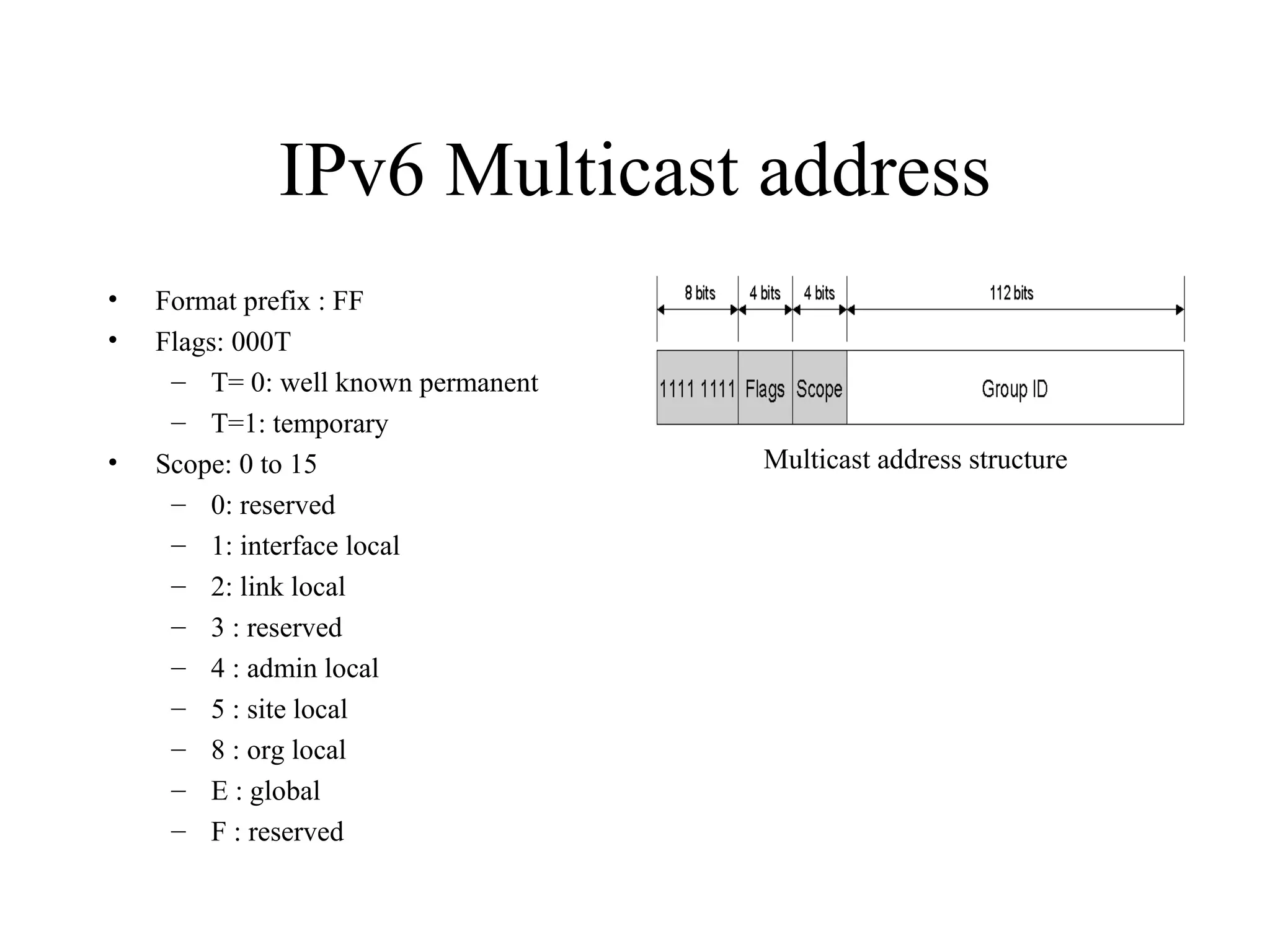
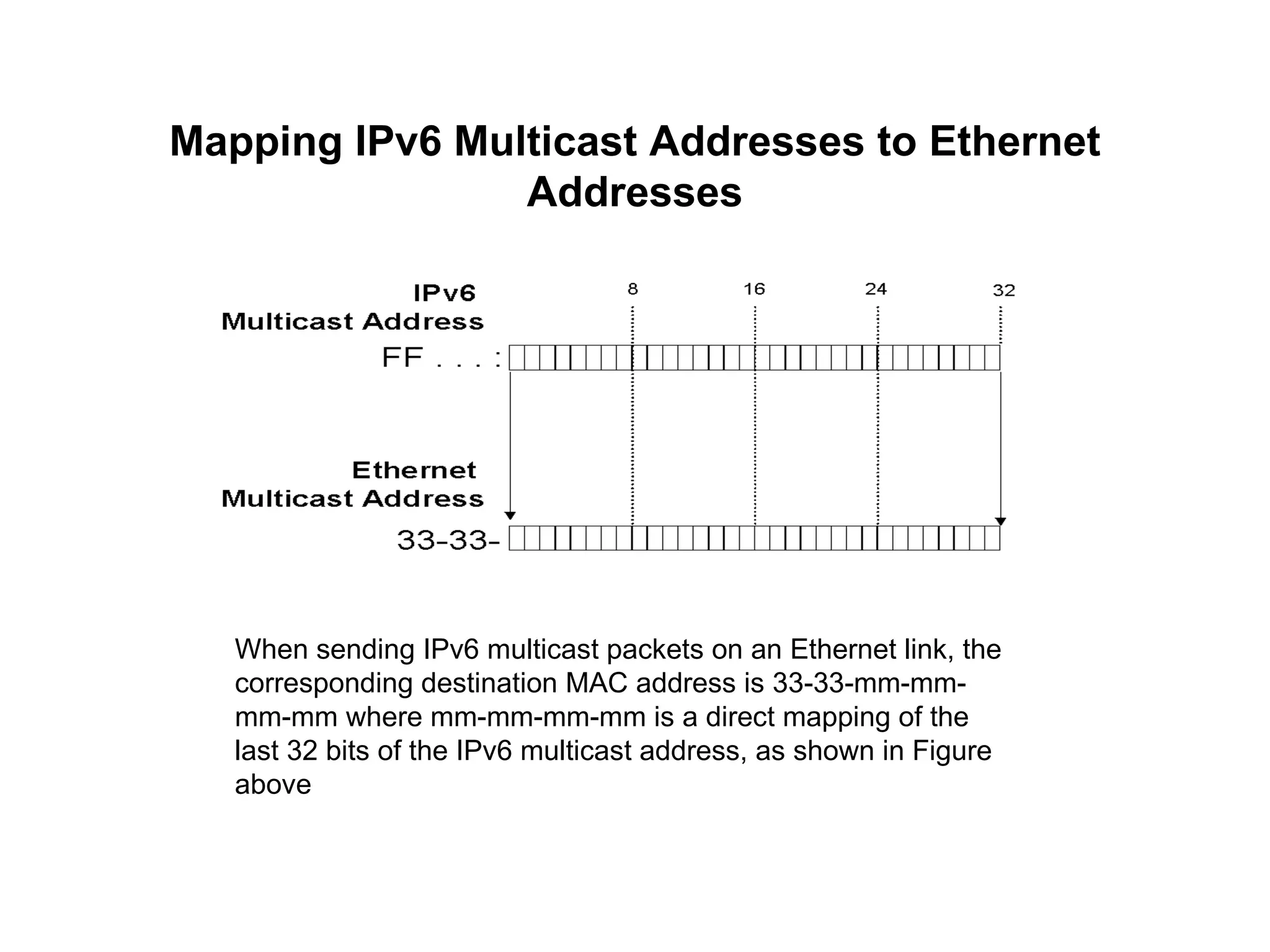
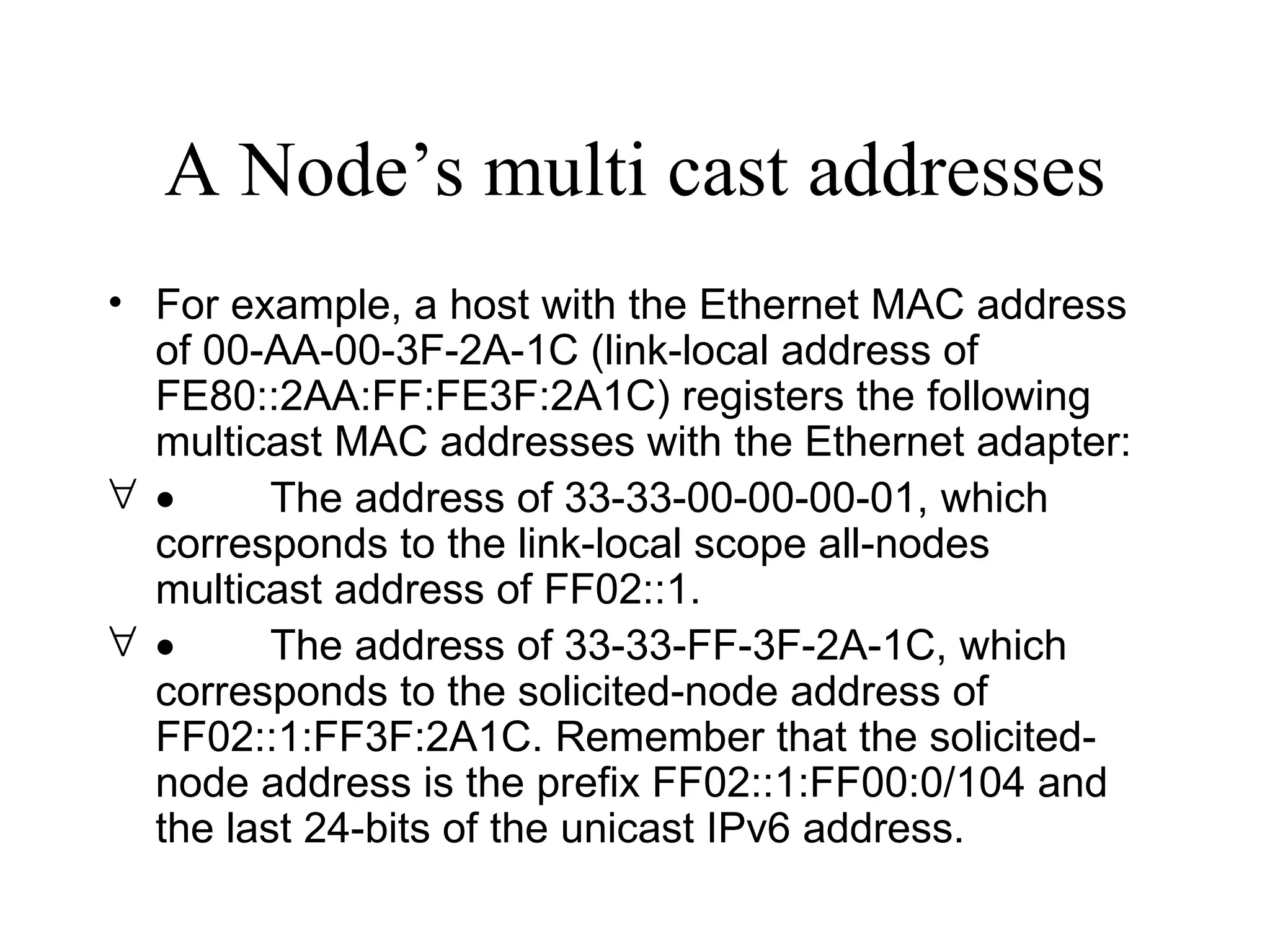
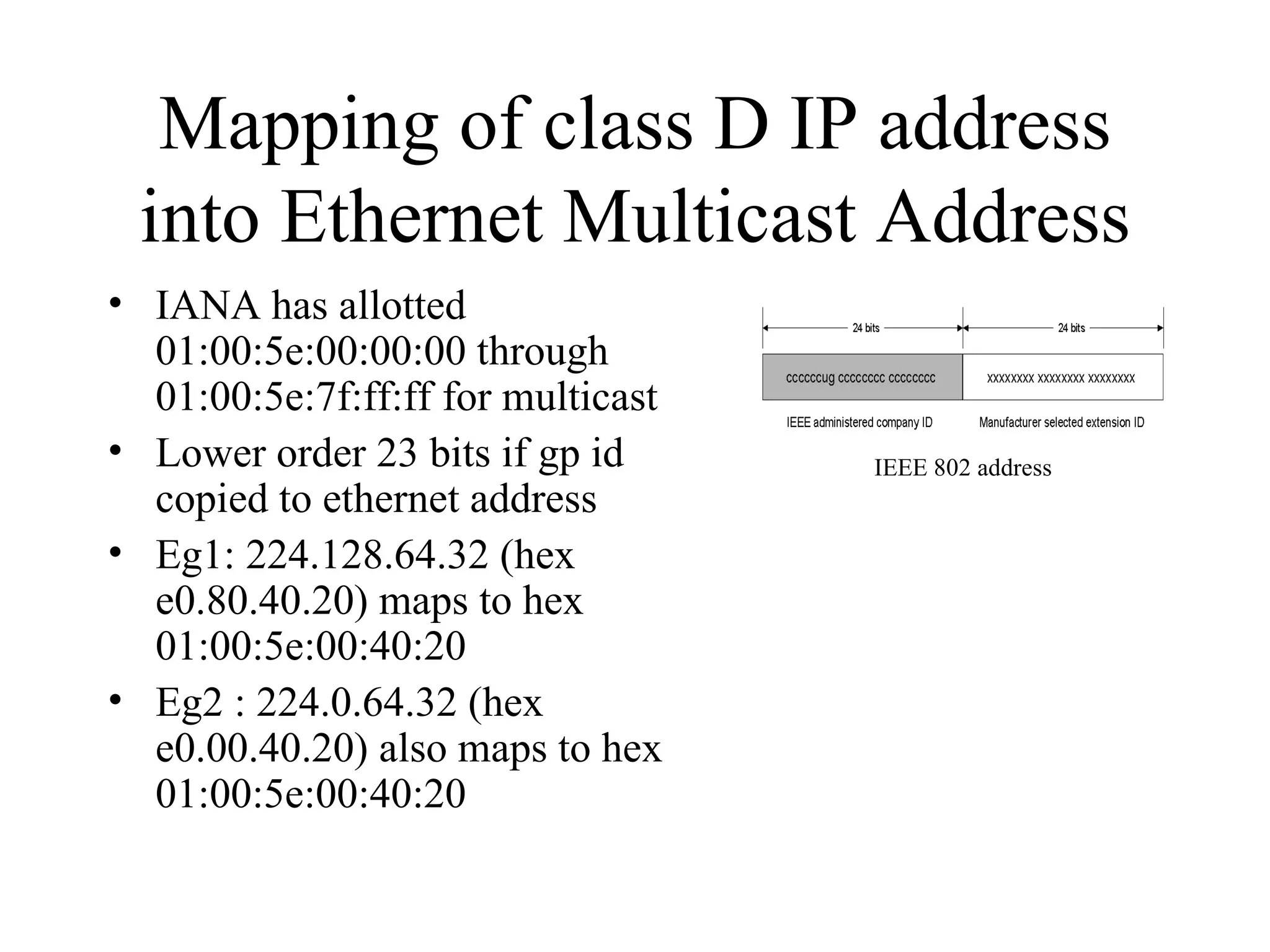
Anycast is a new address type in IPv6 that refers to one among many interfaces with the same address. It is used to identify sets of routers or servers. Anycast addresses are allocated from unicast space and packets sent to an anycast address are routed to the nearest interface. Multicast addresses use a class D range in IPv4 from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 and have a specific format in IPv6 to identify multicast groups and are mapped to Ethernet addresses for multicast transmission.