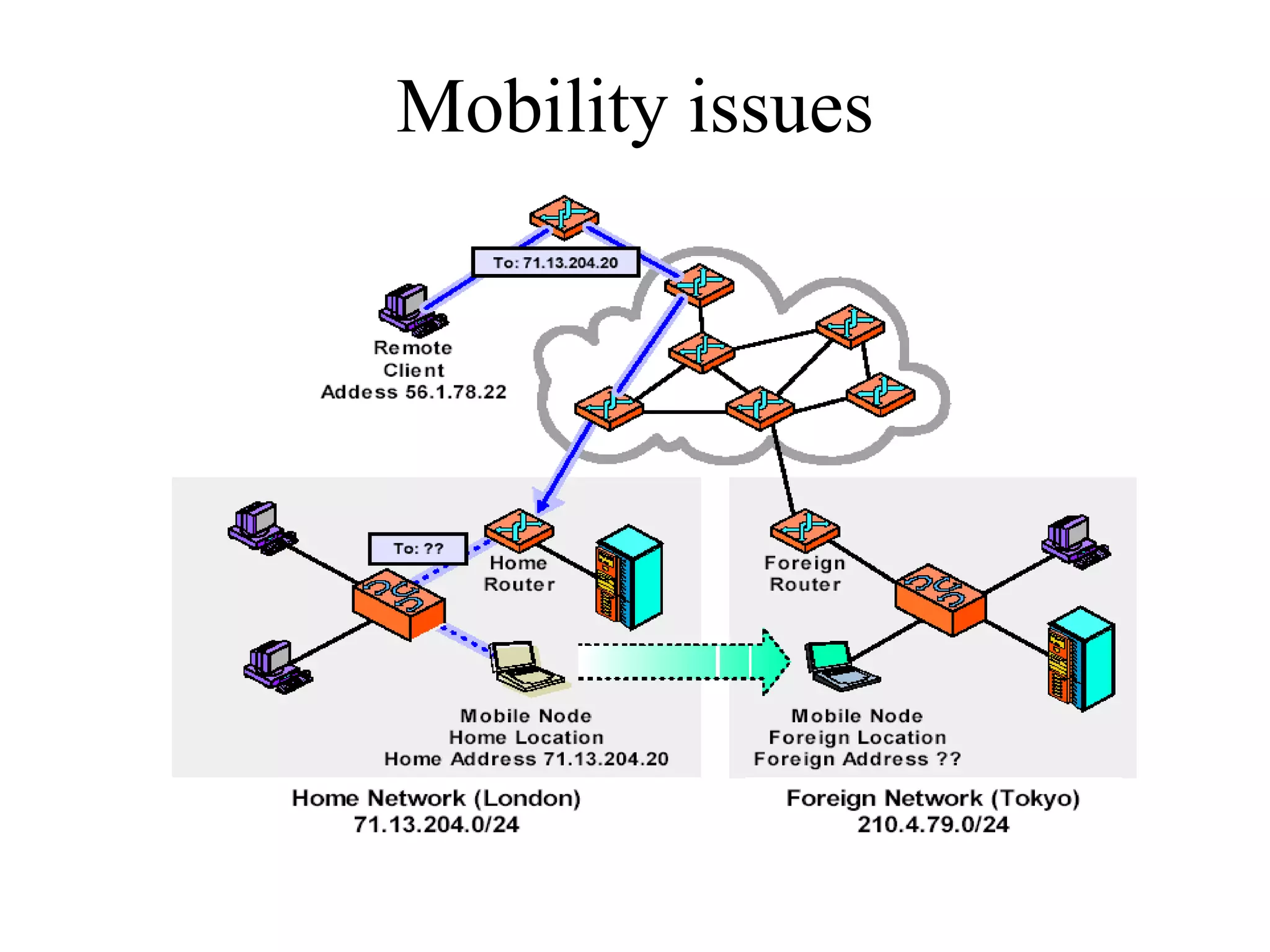
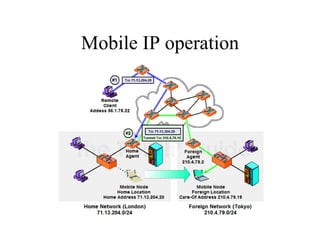
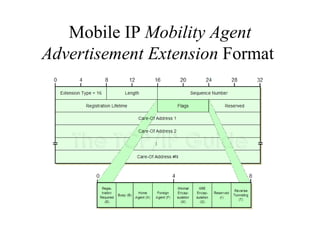
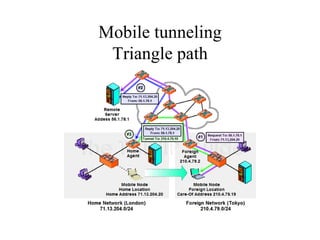
Mobile IP allows devices to move between networks while maintaining the same IP address. It uses a home agent and foreign agent to forward data to the device's current location. When a mobile node moves to a new network, it acquires a care-of address and registers this with its home agent so data can be tunneled to it. The home agent intercepts data for the mobile node and encapsulates it for forwarding to the care-of address via direct delivery or through the foreign agent. This allows seamless mobility as the mobile node does not need a new IP address when changing networks.