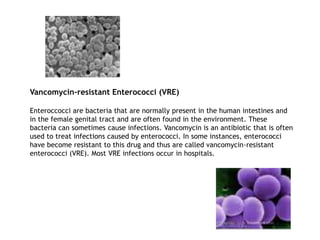
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing health concern as many disease-causing bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites have developed resistance to existing drugs used to treat infections. Microbes develop resistance through natural evolution and selection pressures from overuse and misuse of antimicrobials. Inappropriate and unnecessary use in human medicine, agriculture, and a lack of new drug development are exacerbating the problem. New rapid diagnostics and antimicrobial stewardship are needed to help curb rising drug resistance.