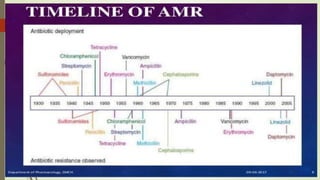
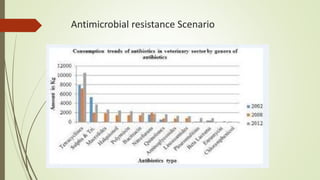
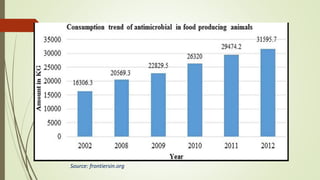
This document summarizes a seminar on antimicrobial resistance in Nepal. It discusses how antimicrobial resistance is a major public health issue as it can render treatments ineffective and allow infections to spread. It provides examples of resistant bacteria like MRSA. It then covers factors contributing to resistance like overuse of antibiotics in humans, animals, and the environment. The challenges of resistance in Nepal are outlined, such as poverty and lack of awareness. Finally, it proposes mitigation strategies including only using antibiotics when prescribed, reducing unnecessary use in animals, and addressing the issue in Nepal's public health system.