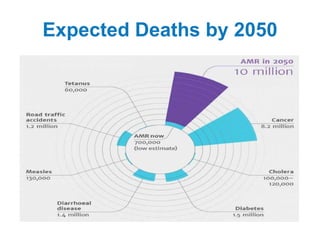
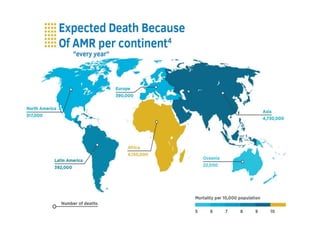
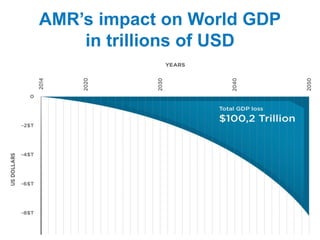
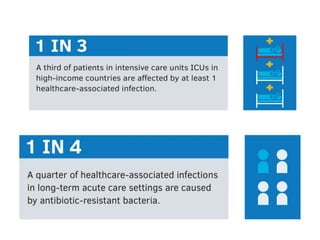
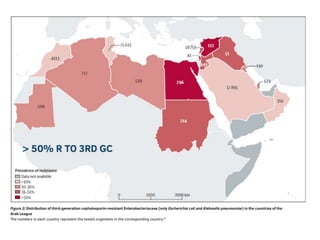
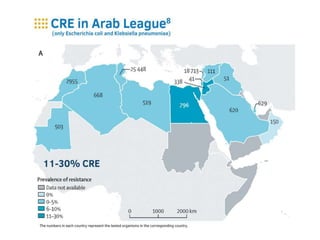
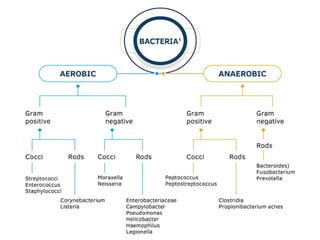
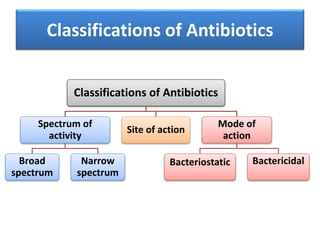
This document discusses antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic use. It defines antibiotics and their classifications including site of action, mode of action, and spectrum of activity. It discusses the misuse of antibiotics and factors that can lead to drug resistance. Antimicrobial resistance has reached crisis levels and is linked to overuse of antibiotics. The document recommends educating healthcare professionals, hospitals, pharmacists, students and patients about appropriate antibiotic usage to curb rising antimicrobial resistance.







![What is Misuse of Antibiotics?:
• When antibiotics are prescribed unnecessarily;
• When antibiotic administration is delayed in critically
ill patients;
• When antibiotic treatment is not given according to
microbiological culture data results.
• When the dose is lower or higher than appropriate for
the specific patient; and
• When the route of administrations [IV vs. oral] not
appropriate
• When the duration of treatment is too short or too
long;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antimicrobialresistanceawareness-220409200822/85/ANTIMICROBIAL-RESISTANCE-AWARENESS-pptx-11-320.jpg)