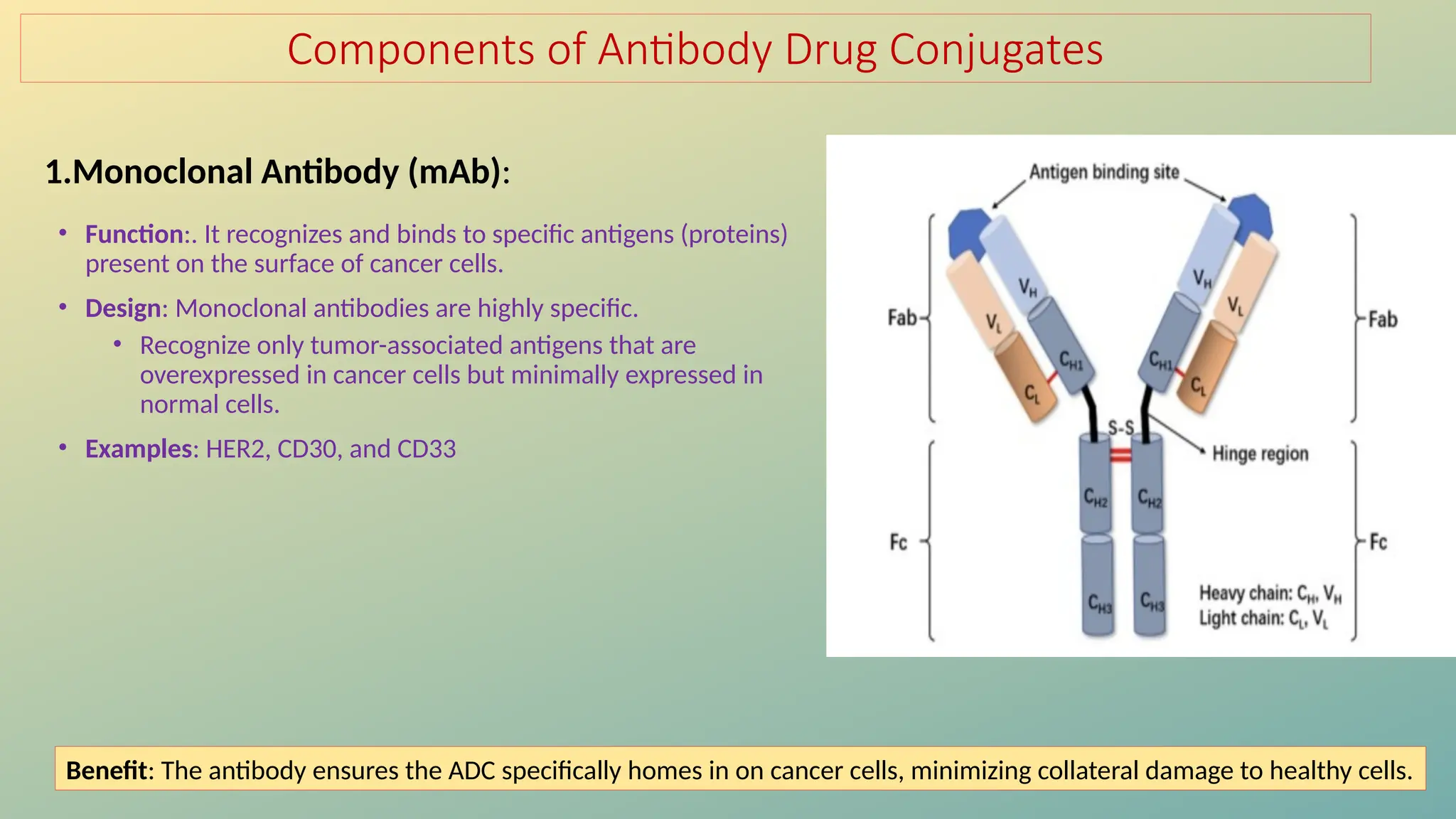
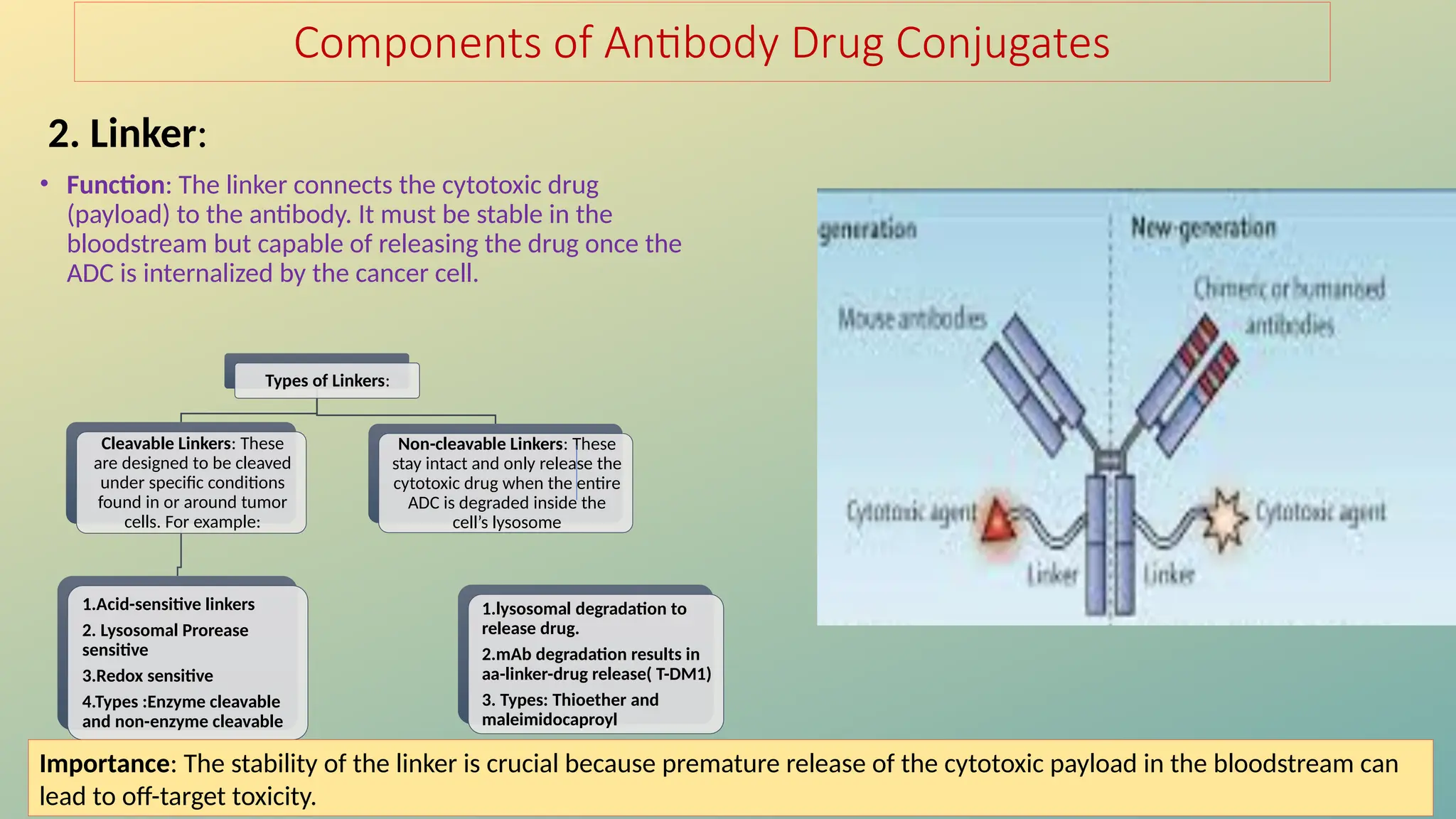
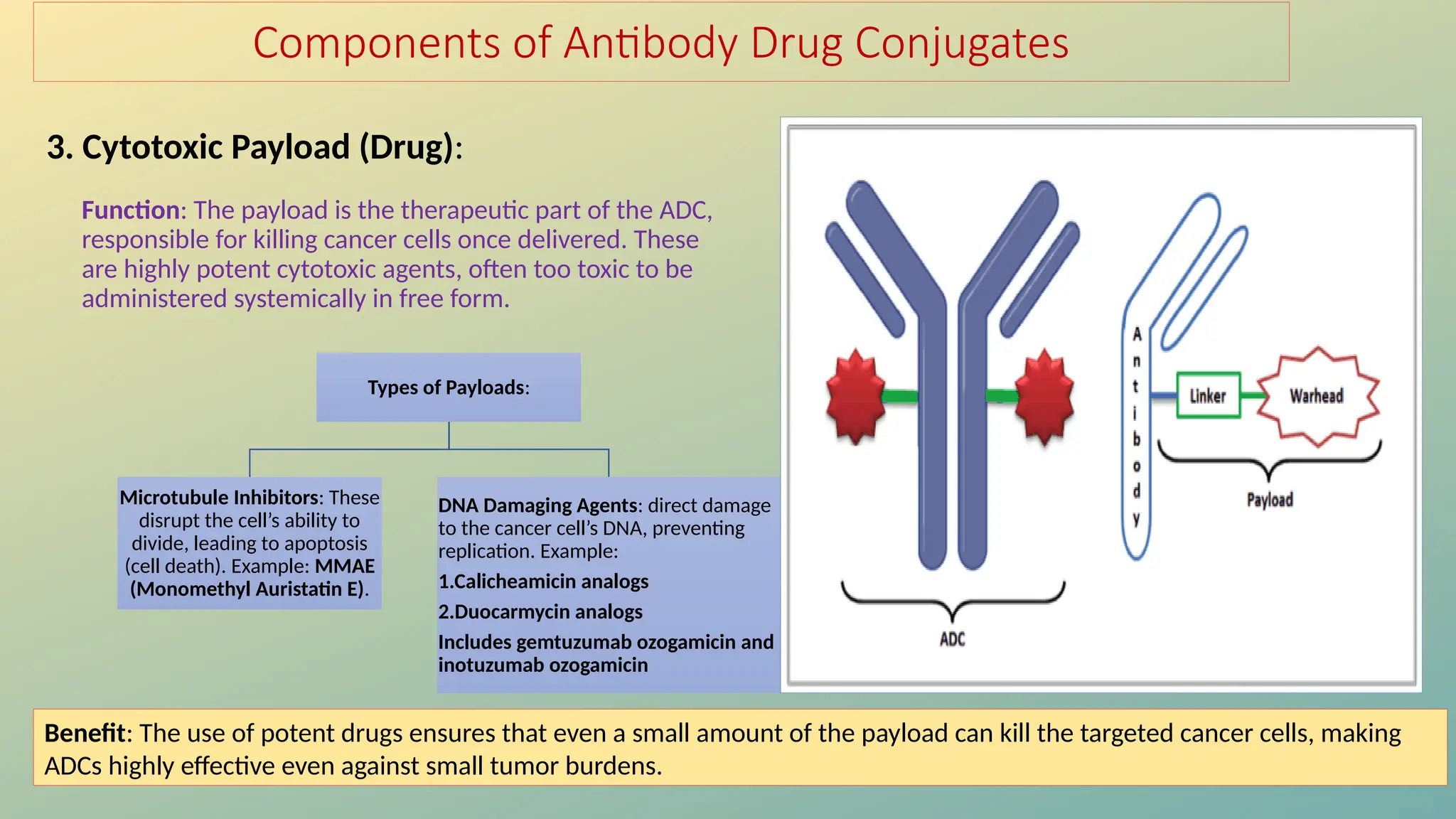
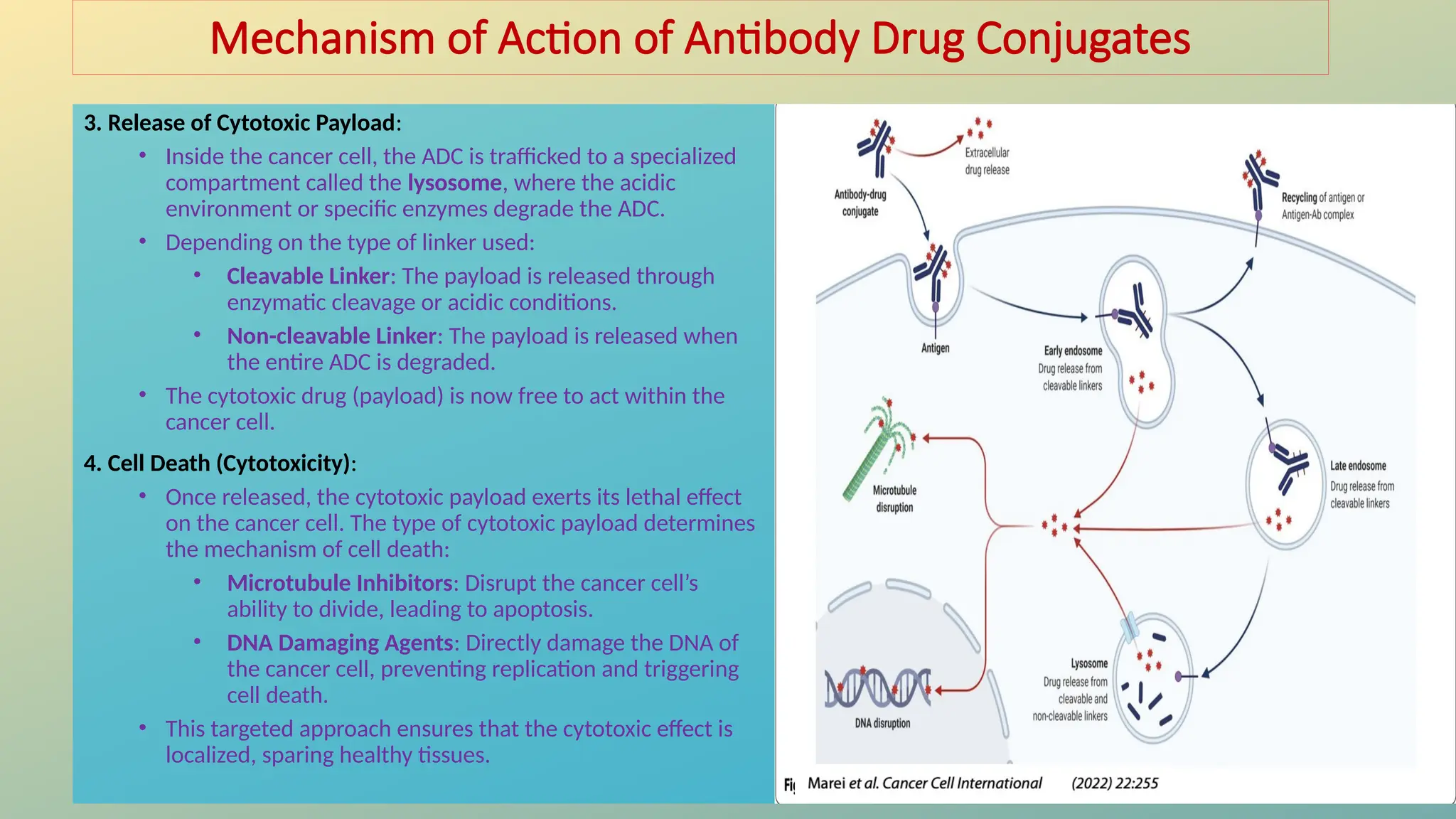
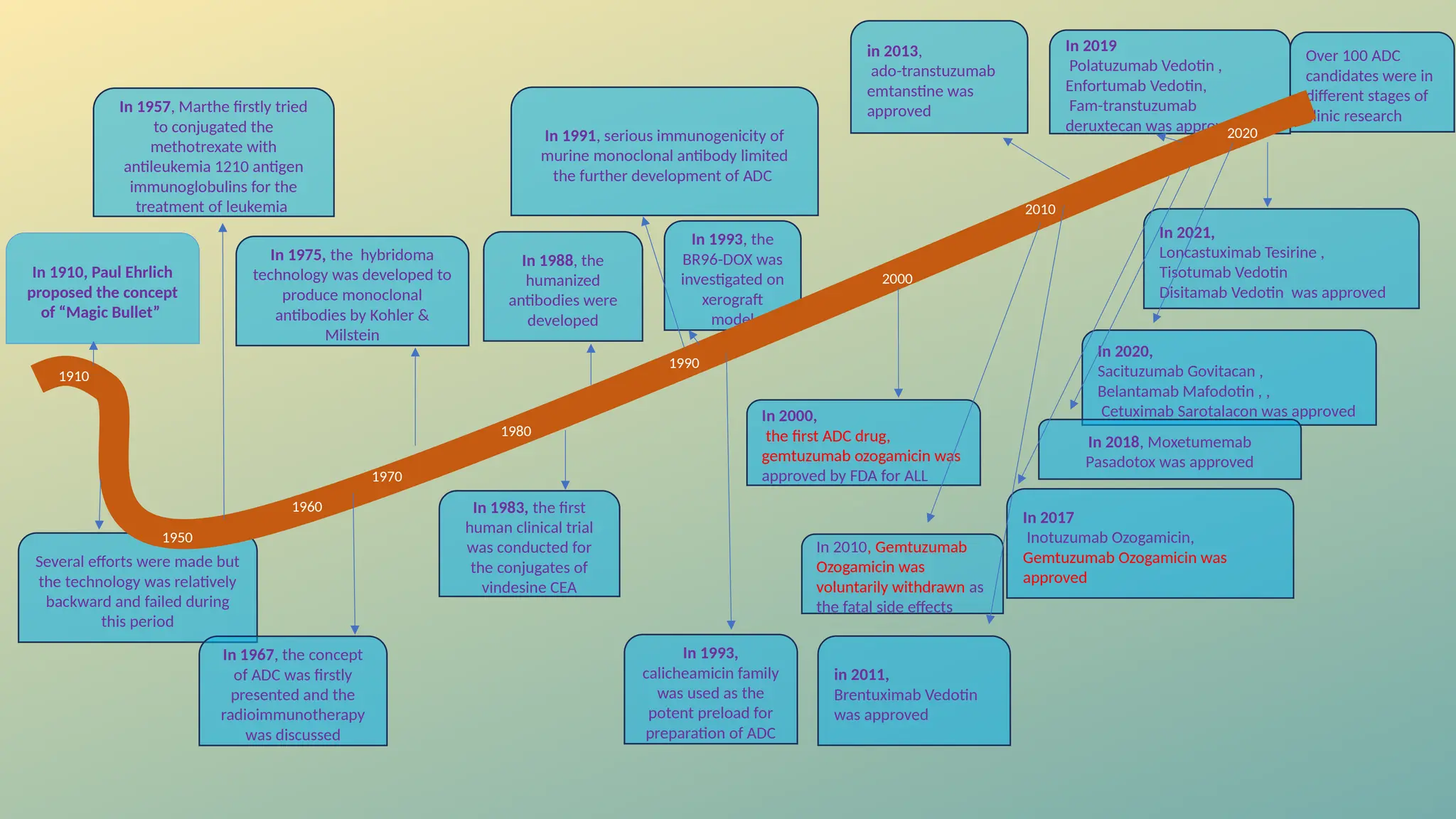
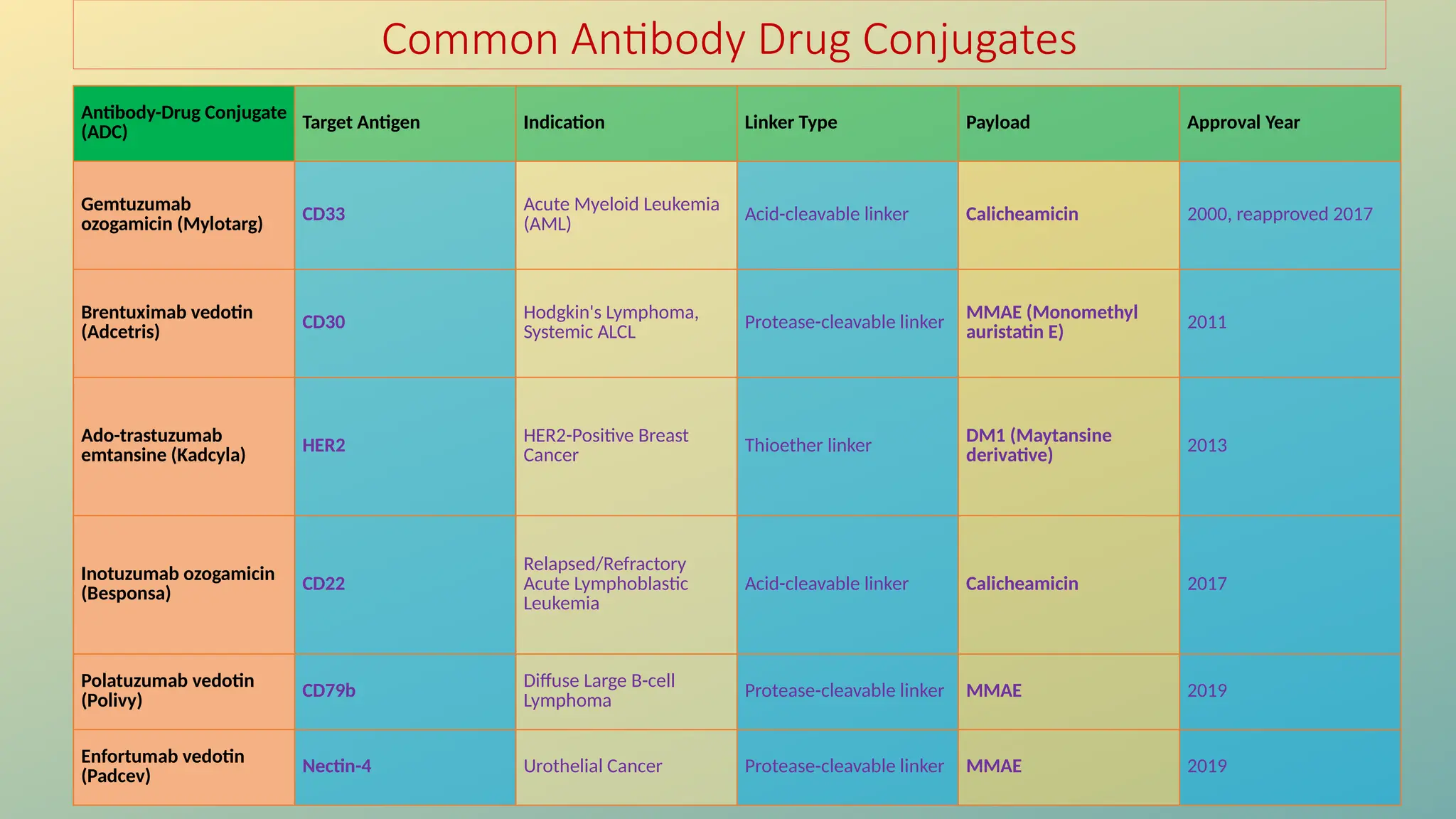
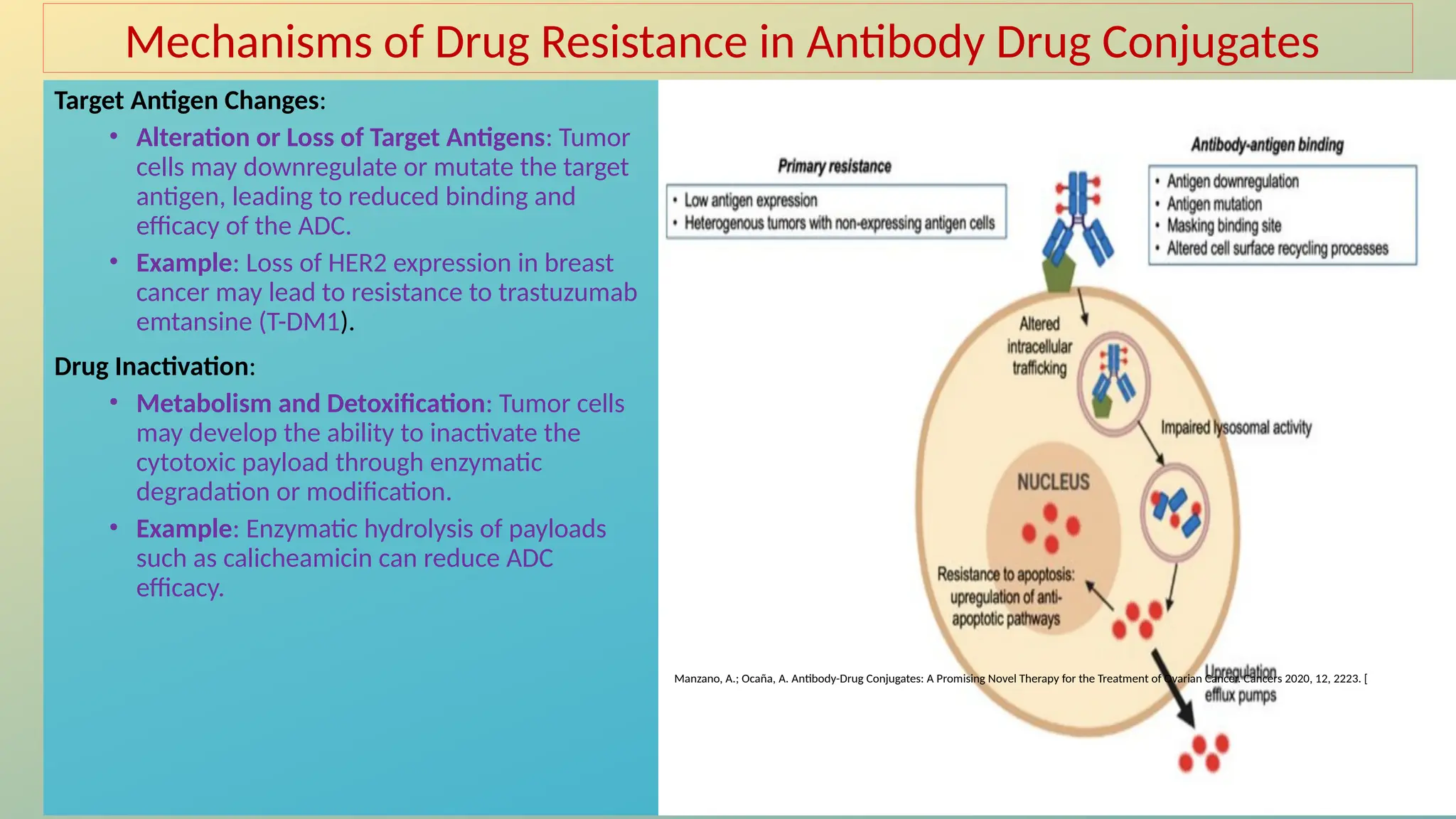
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are biopharmaceuticals designed to deliver cytotoxic drugs specifically to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. They consist of a monoclonal antibody, a cytotoxic payload, and a linker that stabilizes the conjugate in circulation and allows drug release inside the targeted cells. ADCs enhance treatment efficacy, reduce systemic toxicity, and improve survival rates, but face challenges such as target antigen heterogeneity, off-target effects, and high development costs.