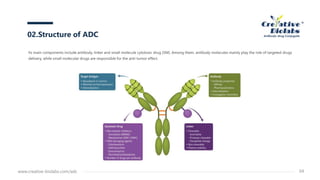
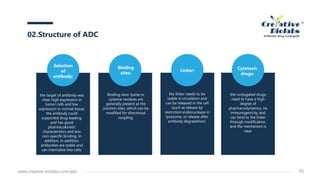
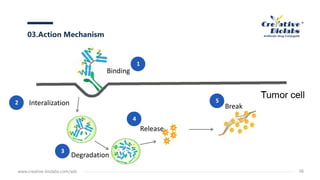
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) enhance anti-tumor efficacy by targeting cytotoxic drugs to tumor cells through monoclonal antibodies, minimizing damage to normal tissues. The document discusses the structure, mechanism of action, and potential toxicity risks of ADCs, emphasizing the importance of components like linkers and the antibody's characteristics. Furthermore, it highlights developmental trends and the need for precise drug-antibody ratios to optimize treatment outcomes.