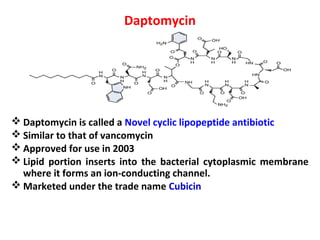
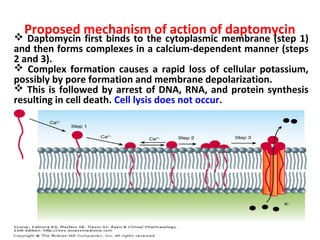
This document summarizes several antibiotics that affect bacterial cell membranes, including polymyxins, daptomycin, isoniazid, and ethambutol. Polymyxins are polypeptide antibiotics that disrupt the structure of gram-negative bacterial cell membranes. Daptomycin forms ion-conducting channels in bacterial membranes that cause potassium loss and arrest of macromolecular synthesis. Isoniazid inhibits mycolic acid synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell walls. Ethambutol inhibits arabinogalactan formation in M. tuberculosis cell walls.