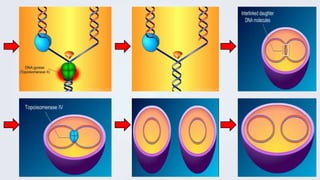
This document discusses quinolones, a class of synthetic antimicrobial compounds. It begins by introducing nalidixic acid, the first quinolone, and how later fluorination led to more potent fluoroquinolone derivatives. Mechanism of action is described as inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase, preventing DNA replication. Adverse effects include tendonitis, CNS effects, and QT prolongation with some agents. Therapeutic uses include urinary tract infections, gonorrhea, respiratory infections, and more. Resistance develops via mutations impairing drug binding or drug efflux.